Abstract
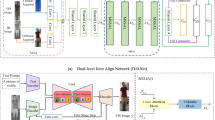
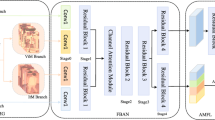
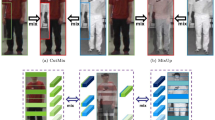
Cross-modality person re-identification between RGB and IR images presents significant challenges due to substantial modality discrepancies. While existing approaches often focus on learning either modality-specific or modality-shared features, overemphasis on the former may hinder cross-modality matching, whereas the latter are more beneficial for this task. To address this challenge, we propose CM-DASN (Cross-Modality Dynamic Attention Selection Network), a novel approach based on dynamic attention optimization. The core of our method is the Dynamic Attention Selection Module (DASM), which adaptively selects the most effective combination of attention heads in the later stages of training, thereby balancing the learning of modality-shared and modality-specific features. We employ a softmax score-based feature selection mechanism to extract and enhance the most discriminative cross-modality feature representations. By alternating supervised learning of high-scoring modality-shared and modality-specific features in the later training stages, the model focuses on learning highly discriminative modality-shared features while retaining beneficial modality-specific information. Furthermore, we design a multi-stage, multi-scale cross-modality feature alignment strategy to more effectively learn cross-modality representations by aligning features of different scales in a phased, progressive manner. This approach considers both global structure and local details, thereby improving cross-modality person re-identification performance. Our method achieves higher cross-modality matching accuracy with minimal increases in model parameters and computational time. Extensive experiments on the SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed framework, demonstrating that it outperforms most existing state-of-the-art approaches in terms of performance. The source code is available at https://github.com/hulu88/CM_DASN.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in this study are public datasets, which can be accessed through their official websites or academic institutions.
References
Leng, Q., Ye, M., Tian, Q.: A survey of open-world person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 30(4), 1092–1108 (2020)
He, S., Luo, H., Wang, P., Wang, F., Li, H., Jiang, W.: Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 14993–15002 (2021)
Tan, L., Dai, P., Ji, R., Wu, Y.: Dynamic prototype mask for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. MM ’22, pp. 531–540. Association for Computing Machinery, ??? (2022)
Zhu, K., Guo, H., Yan, T., Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Tang, M.: Pass: Part-aware self-supervised pre-training for person re-identification. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 198–214 (2022). Springer
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.: Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 2872–2893 (2021)
Lu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, T., Li, B., Chu, Q., Yu, N.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13379–13389 (2020)
Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S., Yu, H.-X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5380–5389 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Kang, Y., Zhao, S., Shen, J.: Dual-semantic consistency learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 18, 1554–1565 (2022)
Wu, Q., Dai, P., Chen, J., Lin, C.-W., Wu, Y., Huang, F., Zhong, B., Ji, R.: Discover cross-modality nuances for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4330–4339 (2021)
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: IJCAI, vol. 1, p. 6 (2018)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y.-Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 618–626 (2019)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., Uszkoreit, J., Houlsby, N.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,arXiv: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Raghu, M., Unterthiner, T., Kornblith, S., Zhang, C., Dosovitskiy, A.: Do vision transformers see like convolutional neural networks? Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 12116–12128 (2021)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Li, W., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2285–2294 (2018)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 480–496 (2018)
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., Zhou, X.: Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 274–282 (2018)
Wang, Y., Jiang, K., Lu, H., Xu, Z., Li, G., Chen, C., Geng, X.: Encoder-decoder assisted image generation for person re-identification. Multimedia Tools Appl. 81(7), 10373–10390 (2022)
Ye, M., Wang, Z., Lan, X., Yuen, P.C.: Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: IJCAI, vol. 1, p. 2 (2018)
Li, D., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 34, 4610–4617 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, H.: Adaptive middle modality alignment learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision (2024)
Feng, J., Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S.: Shape-erased feature learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 22752–22761 (2023)
Li, H., Li, M., Peng, Q., Wang, S., Yu, H., Wang, Z.: Correlation-guided semantic consistency network for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 34(6), 4503–4515 (2024)
Hua, X., Cheng, K., Lu, H., Tu, J., Wang, Y., Wang, S.: Mscmnet: Multi-scale semantic correlation mining for visible-infrared person re-identification. Pattern Recogn. 159, 111090 (2025)
Cheng, K., Geng, Q., Huang, S., Tu, J., Lu, H.: Learning shared features from specific and ambiguous descriptions for text-based person search. Multimedia Syst. 30, 94 (2024)
Wang, X., Wu, Z., Luo, J., Wang, G.: Aligngan: Learning to align cross-modal images via conditional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3658–3667 (2019)
Ye, M., Shen, J., J. Crandall, D., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVII 16, pp. 229–247 (2020). Springer
Liu, H., Tan, X., Zhou, X.: Parameter sharing exploration and heterogeneous attention network for cross-modal re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 23, 3648–3659 (2020)
Fu, C., Hu, Y., Wu, X., Shi, H., Mei, T., He, R.: Cm-nas: Cross-modality neural architecture search for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 11823–11832 (2021)
Lu, H., Zou, X., Zhang, P.: Learning progressive modality-shared transformers for effective visible-infrared person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 37, 1835–1843 (2023)
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: A discriminatively learned cnn embedding for person re-identification. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 1–20 (2018)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.: Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Wang, G., Zhang, T., Cheng, J., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Hou, Z.: Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3623–3632 (2019)
Park, H., Lee, S., Lee, J., Ham, B.: Learning by aligning: Visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12046–12055 (2021)
Huang, Z., Liu, J., Li, L., Zheng, K., Zha, Z.-J.: Modality-adaptive mixup and invariant decomposition for rgb-infrared person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 36, 1034–1042 (2022)
Ye, M., Chen, C., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Dynamic tri-level relation mining with attentive graph for visible infrared re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 17, 386–398 (2021)
Liu, J., Wang, J., Huang, N., Zhang, Q., Han, J.: Revisiting modality-specific feature compensation for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(10), 7226–7240 (2022)
Chen, C., Ye, M., Qi, M., Wu, J., Jiang, J., Lin, C.-W.: Structure-aware positional transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 2352–2364 (2022)
Zhang, Q., Lai, C., Liu, J., Huang, N., Han, J.: Fmcnet: Feature-level modality compensation for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7349–7358 (2022)
Jiang, K., Zhang, T., Liu, X., Qian, B., Zhang, Y., Wu, F.: Cross-modality transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 480–496 (2022). Springer
Zhao, J., Wang, H., Zhou, Y., Yao, R., Chen, S., Saddik, A.E.: Spatial-channel enhanced transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 25, 3668–3680 (2023)
Chai, Z., Ling, Y., Luo, Z., Lin, D., Jiang, M., Li, S.: Dual-stream transformer with distribution alignment for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(11), 6764–6776 (2023)
Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., Tan, Z.: Protohpe: Prototype-guided high-frequency patch enhancement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. MM ’23, pp. 944–954. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA (2023)
Wei, Z., Yang, X., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Dual-adversarial representation disentanglement for visible infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 2186–2200 (2024)
Yang, X., Dong, W., Li, M., Wei, Z., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Cooperative separation of modality shared-specific features for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 26, 8172–8183 (2024)
Zhang, H., Cheng, S., Du, A.: Multi-stage auxiliary learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 1–1 (2024)
Pan, H., Pei, W., Li, X., He, Z.: Unified conditional image generation for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 9026–9038 (2024)
Nguyen, T.D., Hong, H.G., Kim, K.-W., Park, K.R.: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 17 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuxin Li and Hu Lu wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Haojie Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lu, H., Qin, T. et al. CM-DASN: visible-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via dynamic attention selection network. Multimedia Systems 31, 138 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-025-01724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-025-01724-6