Abstract
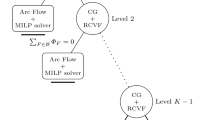
We consider a flow network where the flow of parts can be controlled at the vertices of the network. Based on a modified coarse grid discretization presented in Fügenschuh et al. (SIAM J Scientific Comput 30(3):1490–1507, 2008) we derive a mixed-integer program (MIP). Under suitable assumptions on the cost functional we prove that there exists an equivalent linear program (LP). We present numerical results concerning validity of our result and show the improvement of the computing times using the equivalent LP over the MIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ahuja RK, Magnanti TL, Orlin JB (1993) Network flows: theory, algorithms, and applications. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Armbruster D, de Beer C, Freitag M, Jagalski T, Ringhofer C (2006) Autonomous control of production networks using a pheromone approach. Phys A 363(1): 104–114
Armbruster D, Degond P, Ringhofer C (2006) A model for the dynamics of large queuing networks and supply chains. SIAM J Appl Math 66(3): 896–920
Armbruster D, Degond P, Ringhofer C (2007) Kinetic and fluid models for supply chains supporting policy attributes. Bull Inst Math Acad Sin 2(2): 433–460
Armbruster D, Marthaler D, Ringhofer C (2004) Kinetic and fluid model hierarchies for supply chains. SIAM J Multiscale Model Simul 2(1): 43–61
Courant R, Friedrichs K, Lewy H (1928). Über die partiellen Differenzengleichungen der mathematischen Physik. Math Ann 100: 32–74
Dittel A, Fügenschuh A, Göttlich S, Herty M (2009) MIP presolve techniques for a PDE-based supply chain model. In: Optimization Methods & Software (to appear)
Fügenschuh A, Göttlich S, Herty M (2007) A new modeling approach for an integrated simulation and optimization of production networks. In: Günther H-O, Mattfeld D, Suhl L (eds) Management logistischer Netzwerke. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 45–60
Fügenschuh A, Göttlich S, Herty M, Klar A, Martin A (2008) A discrete optimization approach to large scale supply networks based on partial differential equations. SIAM J Sci Comput 30(3): 1490–1507
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York
Göttlich S, Herty M, Klar A (2005) Network models for supply chains. Comm Math Sci 3(4): 545–559
Göttlich S, Herty M, Klar A (2006) Modelling and optimization of supply chains on complex networks. Comm Math Sci 4(2): 315–330
Göttlich S, Herty M, Kirchner C, Klar A (2006) Optimal control for continuous supply network models. Netw Heterog Media 1(4): 675–688
Herty M, Klar A, Piccoli B (2007) Existence of solutions for supply chain networks based on partial differential equations. SIAM J Math Anal 39(1): 160–173
ILOG CPLEX Division, Alder Avenue, Suite 200, Incline Village, NV 89451, USA. Information available at URL http://www.cplex.com
Koch T (2004) Rapid mathematical programming. Ph.D. Thesis, Berlin
Nemhauser G, Wolsey L (1988) Integer and combinatorial optimization. Wiley/Interscience/Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fügenschuh, A., Göttlich, S., Herty, M. et al. Efficient reformulation and solution of a nonlinear PDE-controlled flow network model. Computing 85, 245–265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-009-0038-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-009-0038-7