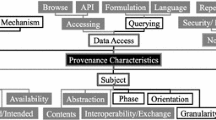
Abstract
Provenance refers to any information describing the production process of an end product, which can be anything from a piece of digital data to a physical object. While this survey focuses on the former type of end product, this definition still leaves room for many different interpretations of and approaches to provenance. These are typically motivated by different application domains for provenance (e.g., accountability, reproducibility, process debugging) and varying technical requirements such as runtime, scalability, or privacy. As a result, we observe a wide variety of provenance types and provenance-generating methods. This survey provides an overview of the research field of provenance, focusing on what provenance is used for (what for?), what types of provenance have been defined and captured for the different applications (what form?), and which resources and system requirements impact the choice of deploying a particular provenance solution (what from?). For each of these three key questions, we provide a classification and review the state of the art for each class. We conclude with a summary and possible future research challenges.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, U., Buneman, P., Cheney, J., Van Den Bussche, J., Kwasnikowska, N., Vansummeren, S.: A graph model of data and workflow provenance. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2010)
Ainy, E., Bourhis, P., Davidson, S.B., Deutch, D., Milo, T.: Approximated summarization of data provenance. In: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 483–492 (2015)
Akoush, S., Sohan, R., Hopper, A.: HadoopProv: towards provenance as a first class citizen in MapReduce. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2013)
Alkhaldi, A., Gupta, I., Raghavan, V., Ghosh, M.: Leveraging metadata in no SQL storage systems. In: IEEE Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), pp. 57–64 (2015)
Alper, P., Belhajjame, K., Goble, C.A., Karagoz, P.: Enhancing and abstracting scientific workflow provenance for data publishing. In: EDBT/ICDT Workshops, pp. 313–318 (2013)
Altintas, I., Barney, O., Jaeger-Frank, E.: Provenance collection support in the Kepler scientific workflow system. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 118–132 (2006)
Alvaro, P., Rosen, J., Hellerstein, J.M.: Lineage-driven fault injection. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 331–346 (2015)
Amann, B., Constantin, C., Caron, C., Giroux, P.: Weblab prov: computing fine-grained provenance links for xml artifacts. In: EDBT/ICDT Workshops, pp. 298–306 (2013)
Amsterdamer, Y., Davidson, S.B., Deutch, D., Milo, T., Stoyanovich, J., Tannen, V.: Putting lipstick on pig : enabling database-style workflow provenance. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 5, 346–357 (2011)
Amsterdamer, Y., Deutch, D., Tannen, V.: On the limitations of provenance for queries with difference. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2011)
Amsterdamer, Y., Deutch, D., Tannen, V.: Provenance for aggregate queries. In: ACM Symposium on principles of database systems (PODS), pp. 153–164 (2011)
Anand, M.K., Bowers, S., Ludäscher, B.: Techniques for efficiently querying scientific workflow provenance graphs. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 287–298 (2010)
Anand, M.K., Bowers, S., Ludäscher, B.: Provenance browser: displaying and querying scientific workflow provenance graphs. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 1201–1204 (2010)
Anand, M.K., Bowers, S., McPhillips, T., Ludäscher, B.: Efficient provenance storage over nested data collections. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 958–969 (2009)
Angelino, E., Yamins, D., Seltzer, M.I.: Starflow: a script-centric data analysis environment. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 236–250 (2010)
Arab, B.S., Gawlick, D., Krishnaswamy, V., Radhakrishnan, V., Glavic, B.: Reenactment for read-committed snapshot isolation. In: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 841–850 (2016)
Balakrishnan, N., Bytheway, T., Carata, L., Sohan, R., Hopper, A.: Towards secure user-space provenance capture. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2016)
Barga, R.S., Digiampietri, L.A.: Automatic capture and efficient storage of e-Science experiment provenance. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 20(5), 419–429 (2008)
Batini, C., Scannapieco, M.: Data Quality: Concepts. Methodologies and Techniques. Springer, New York (2006)
Bavoil, L., Callahan, S.P., Crossno, P.J., Freire, J., Scheidegger, C.E., Silva, C.T., Vo. H.T.: Vistrails: enabling interactive multiple-view visualizations. In: IEEE Visualization (VIS), pp. 135–142 (2005)
Bertino, E., Ghinita, G., Kantarcioglu, M., Nguyen, D., Park, J., Sandhu, R., Sultana, S., Thuraisingham, B., Xu, S.: A roadmap for privacy-enhanced secure data provenance. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 43(3), 481–501 (2014)
Bhagwat, D., Chiticariu, L., Tan, W.C., Vijayvargiya, G.: An annotation management system for relational databases. VLDB J. 14(4), 373–396 (2005)
Bidoit, N., Herschel, M., Tzompanaki, A.: Efficient computation of polynomial explanations of why-not questions. In: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 713–722 (2015)
Bidoit, N., Herschel, M., Tzompanaki, K.: Immutably answering why-not questions for equivalent conjunctive queries. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2014)
Bidoit, N., Herschel, M., Tzompanaki, K.: Query-based why-not provenance with NedExplain. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 145–156 (2014)
Bidoit, N., Herschel, M., Tzompanaki, K.: EFQ: why-not answer polynomials in action. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 8(12), 1980–1983 (2015)
Biton, O., Cohen-Boulakia, S., Davidson, S.B., Hara, C.S.: Querying and managing provenance through user views in scientific workflows. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 1072–1081 (2008)
Borkin, M.A., Yeh, C.S., Boyd, M., Macko, P., Gajos, K.Z., Seltzer, M., Pfister, H.: Evaluation of filesystem provenance visualization tools. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(12), 2476–2485 (2013)
Börzsönyi, S., Kossmann, D., Stocker, K.: The skyline operator. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 421–430 (2001)
Bourhis, P., Deutch, D., Moskovitch, Y.: POLYTICS: provenance-based analytics of data-centric applications. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 1373–1374 (2017)
Bowers, S., McPhillips, T.M., Ludäscher, B.: Provenance in collection-oriented scientific workflows. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 20(5), 519–529 (2008)
Bowers, S., McPhillips, T.M., Riddle, S., Anand, M.K., Ludäscher, B.: Kepler/pPOD: Scientific workflow and provenance support for assembling the tree of life. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 70–77 (2008)
Buneman, P., Khanna, S., Tan, W.C.: Why and where: a characterization of data provenance. In: International Conference on Database Theory (ICDT), pp. 316–330 (2001)
Buneman, P., Khanna, S., Tan, W.C.: On propagation of deletions and annotations through views. In: ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems (PODS), pp. 150–158 (2002)
Cadenhead, T., Khadilkar, V., Kantarcioglu, M., Thuraisingham, B.: A language for provenance access control. In: ACM Conference on Data and Application Security and Privacy (CODASPY), pp. 133–144 (2011)
Cadenhead, T., Khadilkar, V., Kantarcioglu, M., Thuraisingham, B.: Transforming provenance using redaction. In: ACM Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies (SACMAT), pp. 93–102 (2011)
Callahan, S.P., Freire, J., Santos, E., Scheidegger, C.E., Vo, T., Silva, H.T.: VisTrails : visualization meets data management. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 745–747 (2006)
Calvanese, D., Ortiz, M., Simkus, M., Stefanoni, G.: Reasoning about explanations for negative query answers in DL-Lite. J. Artif. Intell. Res.: JAIR 48, 635–669 (2013)
Cao, B., Plale, B., Subramanian, G., Robertson, E., Simmhan, Y.: Provenance information model of Karma version 3. In: Congress on Services—I (SERVICES), pp. 348–351 (2009)
Cao, Y., Jones, C., Mcphillips, T., Jones, M.B., Ludäscher, B., Missier, P., Schwalm, C., Slaughter, P., Vieglais, D., Walker, L., Wei, Y.: DataONE: a data federation with provenance support. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 230–234 (2016)
Caron, C., Amann, B., Constantin, C., Giroux, P.: WePIGE: the Weblab provenance information generator and explorer. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 664–667 (2014)
Chapman, A., Jagadish, H., Ramanan, P.: Efficient provenance storage. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 993–1006 (2008)
Chapman, A., Jagadish, H.V.: Why not? In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 523–534 (2009)
Chebotko, A., Lu, S., Chang, S., Fotouhi, F., Yang, P.: Secure abstraction views for scientific workflow provenance querying. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 3(4), 322–337 (2010)
Cheney, J.: A formal framework for provenance security. In: IEEE Computer Security Foundations Symposium (CSF), pp. 281–293 (2011)
Cheney, J., Chiticariu, L., Tan, W.C.: Provenance in databases: why, how, and where. Found Trends Databases 1(4), 379–474 (2009)
Cheney, J., Perera, R.: An analytical survey of provenance sanitization. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 113–126 (2014)
Chester, S., Assent, I.: Explanations for skyline query results. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 349–360 (2015)
Cheung K., Hunter, J.: Provenance explorer—customized provenance views using semantic inferencing. In: International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), pp. 215–227 (2006)
Chirigati, F., Shasha, D., Freire, J.: ReproZip: using provenance to support computational reproducibility. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP), pp. 1–4 (2013)
Chiticariu, L., Tan, W.C.: Debugging schema mappings with routes. In: Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB), pp. 79–90 (2006)
Chothia, Z., Liagouris, J., McSherry, F., Roscoe, T.: Explaining outputs in modern data analytics. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 9(12), 1137–1148 (2016)
Commission, E.: Horse meat: one year after—actions announced and delivered! (2014). Accessed March 15, 2016
Cranmer, K., Heinrich, L., Jones, R., South, D.M.: Analysis preservation in ATLAS. J. Physi. 664(3) (2015). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/664/3/032013
Crawl, D., Altintas, I.: A provenance-based fault tolerance mechanism for scientific workflows. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 152–159 (2008)
Crawl, D., Wang, J., Altintas, I.: Provenance for mapreduce-based data-intensive workflows. In: Workshop on Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS), pp. 21–30 (2011)
Cui, Y., Widom, J.: Lineage tracing for general data warehouse transformations. In: Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB), pp. 471–480 (2001)
Cui, Y., Widom, J., Wiener, J.L.: Tracing the lineage of view data in a warehousing environment. ACM Trans. Database Syst: TODS 25(2), 179–227 (2000)
Curbera, F., Doganata, Y.N., Martens, A., Mukhi, N., Slominski, A.: Business provenance—a technology to increase traceability of end-to-end operations. In: On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems OTM, pp. 100–119 (2008)
Dai, C., Lin, D., Bertino, E., Kantarcioglu, M.: An approach to evaluate data trustworthiness based on data provenance. In: Workshop on Secure Data Management (SDM), pp. 82–98 (2008)
Davidson, S.B., Cohen-Boulakia, S., Eyal, A., Ludäscher, B., McPhillips, T.M., Bowers, S., Anand, M.K., Freire, J.: Provenance in scientific workflow systems. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 30(4), 44–50 (2007)
Davidson, S.B., Freire, J.: Provenance and scientific workflows: challenges and opportunities. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 1345–1350 (2008)
De Nies, T., Taxidou, I., Dimou, A., Verborgh, R., Fischer, P.M., Mannens, E., de Walle, R.: Towards multi-level provenance reconstruction of information diffusion on social media. In: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 1823–1826 (2015)
Deelman, E., Berriman, G.B., Chervenak, A.L., Corcho, Ó., Groth, P.T., Moreau, L.: Metadata and provenance management. In: Shoshani, A., Rotem, D. (eds.) Scientific Data Management: Challenges, Technology, and Deployment. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton (2009)
Deelman, E., Singh, G., Su, M., Blythe, J., Gil, Y., Kesselman, C., Mehta, G., Vahi, K., Berriman, G.B., Good, J., Laity, A.C., Jacob, J.C., Katz, D.S.: Pegasus: a framework for mapping complex scientific workflows onto distributed systems. Sci. Program. 13(3), 219–237 (2005)
Dellis, E., Seeger, B.: Efficient computation of reverse skyline queries. In: Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB), pp. 291–302 (2007)
Deutch, D., Gilad, A., Moskovitch, Y.: selP: selective tracking and presentation of data provenance. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 1484–1487 (2015)
Deutch, D., Moskovitch, Y., Tannen, V.: A provenance framework for data-dependent process analysis. Proc. VLDB Endow. 7(6), 457–468 (2014)
Dey, S., Belhajjame, K., Koop, D., Raul, M., Ludäscher, B.: Linking prospective and retrospective provenance in scripts. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2015)
Dey, S.C., Zinn, D., Ludäscher, B.: Propub: towards a declarative approach for publishing customized, policy-aware provenance. In: Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management (SSDBM), pp. 225–243 (2011)
Ellkvist, T., Koop, D., Anderson, E.W., Freire, J., Silva, C.T.: Using provenance to support real-time collaborative design of workflows. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 266–279 (2008)
Fehrenbach, S., Cheney, J.: Language-integrated provenance. In: Symposium on Principles and Practice of Declarative Programming (PPDP), pp. 214–227 (2016)
Foster, J.N., Green, T.J., Tannen, V.: Annotated XML: queries and provenance. In: ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems (PODS), pp. 271–280 (2008)
Freire, J., Koop, D., Santos, E., Silva, C.T.: Provenance for computational tasks: a survey. Comput. Sci. Eng. 10(3), 11–21 (2008)
Freire, J., Silva, C.T., Callahan, S.P., Santos, E., Scheidegger, C.E., Vo, H.T.: Managing rapidly-evolving scientific workflows. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 10–18 (2006)
Gadelha, L.M.R., Clifford, B., Mattoso, M., Wilde, M., Foster, I.: Provenance management in Swift. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 27(6), 775–780 (2011)
Gao, Y., Liu, Q., Chen, G., Zheng, B., Zhou, L.: Answering why-not questions on reverse top-k queries. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 8(7), 738–749 (2015)
Garijo, D., Corcho, Ó., Gil, Y.: Detecting common scientific workflow fragments using templates and execution provenance. In: International Conference on Knowledge Capture (K-CAP), pp. 33–40 (2013)
Gehani, A., Tariq, D.: SPADE: support for provenance auditing in distributed environments. In: Proceedings of the International Middleware Conference, pp. 101–120 (2012)
Glavic, B., Alonso, G.: The perm provenance management system in action. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 1055–1058 (2009)
Glavic, B., Alonso, G., Miller, R.J., Haas, L.M.: TRAMP: understanding the behavior of schema mappings through provenance. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 3(1), 1314–1325 (2010)
Glavic, B., Esmaili, K.S., Fischer, P.M., Tatbul, N.: Ariadne: managing fine-grained provenance on data streams. In: Conference on Distributed Event-Based Systems (DEBS), pp. 39–50 (2013)
Goble, C.: Position statement: musings on provenance, workflow and (semantic web) annotations for bioinformatics. In: Workshop on Data Derivation and Provenance, pp. 152–159 (2002)
Goecks, J., Nekrutenko, A., Taylor, J.: Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 11(8), R86 (2010)
Green, T.J., Karvounarakis, G., Tannen, V.: Provenance semirings. In: ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems (PODS), pp. 31–40 (2007)
Green, T.J., Karvounarakis, G., Taylor, N.E., Biton, O., Ives, Z.G., Tannen, V.: ORCHESTRA: facilitating collaborative data sharing. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 1131–1133 (2007)
Groth, P., Gil, Y., Cheney, J., Miles, S.: Requirements for provenance on the web. Int. J. Digit. Curation 7(1), 39–56 (2012)
Groth, P., Miles, S., Fang, W., Wong, S.C., Zauner, K.-P., Moreau, L.: Recording and using provenance in a protein compressibility experiment. In: IEEE Symposium on High Performance Distributed Computing (HPDC), pp. 201–208 (2005)
Groth, P., Moreau, L.: PROV-Overview: An Overview of the PROV Family of Documents (2013). Accessed 15 March 2016
Grust, T., Rittinger, J.: Observing SQL queries in their natural habitat. ACM Trans. Database Syst.: TODS 38(1), 3-1–3-33 (2012)
Hartig, O., Zhao, J.: Using web data provenance for quality assessment. In: Workshop on the Role of Semantic Web in Provenance Management (SWPM) (2009)
He, Z., Lo, E.: Answering why-not questions on top-k queries. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 750–761 (2012)
He, Z., Lo, E.: Answering why-not questions on top-k queries. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng.: TKDE 26(6), 1300–1315 (2014)
Herschel, M.: A hybrid approach to answering why-not questions on relational query results. ACM J. Data Inf. Qual.: JDIQ 5(3), 10:1–10:29 (2015)
Herschel, M., Eichelberger, H.: The Nautilus Analyzer: understanding and debugging data transformations. In: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 2731–2733 (2012)
Herschel, M., Grust, T.: Transformation lifecycle management with Nautilus. In: Workshop on the Quality of Data (QDB) (2011)
Herschel, M., Hernández, M.A.: Explaining missing answers to SPJUA queries. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 3(1), 185–196 (2010)
Herschel, M., Hlawatsch, M.: Provenance: on and behind the screens. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 2213–2217 (2016)
Hlawatsch, M., Burch, M., Beck, F., Freire, J., Silva, C., Weiskopf, D.: Visualizing the evolution of module workflows. In: International Conference on Information Visualisation (IV), pp. 40–49 (2015)
Hoekstra, R., Groth, P.: Prov-o-viz-understanding the role of activities in provenance. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 215–220 (2014)
Huang, J., Chen, T., Doan, A., Naughton, J.F.: On the provenance of non-answers to queries over extracted data. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 1(1), 736–747 (2008)
Huq, M.R., Apers, P.M.G., Wombacher, A.: Provenancecurious: a tool to infer data provenance from scripts. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 765–768 (2013)
Hussein, J., Moreau, L., Sassone, V.: Obscuring provenance confidential information via graph transformation. In: Conference on Trust Management (IFIP), pp. 109–125 (2015)
Ikeda, R., Park, H., Widom, J.: Provenance for generalized map and reduce workflows. In: Conference on Innovative Data Systems Research (CIDR), pp. 273–283 (2011)
Imieliński, T., Lipski Jr., W.: Incomplete information in relational databases. J. ACM 31(4), 761–791 (1984)
Interlandi, M., Shah, K., Tetali, S.D., Gulzar, M.A., Yoo, S., Kim, M., Millstein, T., Condie, T.: Titian: data provenance support in Spark. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 9(3), 216–227 (2015)
Islam, M.S., Liu, C., Zhou, R.: Flexiq: a flexible interactive querying framework by exploiting the skyline operator. J. Syst. Softw. 97, 97–117 (2014)
Islam, M.S., Zhou, R., Liu, C.: On answering why-not questions in reverse skyline queries. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 973–984 (2013)
Karsai, L., Fekete, A., Kay, J., Missier, P.: Clustering provenance facilitating provenance exploration through data abstraction. In: Workshop on Human-In-the-Loop Data Analytics (HILDA), pp. 6:1–6:5 (2016)
Karvounarakis, G., Green, T.J.: Semiring-annotated data: queries and provenance? SIGMOD Rec. 41(3), 5–14 (2012)
Karvounarakis, G., Green, T.J., Ives, Z.G., Tannen, V.: Collaborative data sharing via update exchange and provenance. ACM Trans. Database Syst.: TODS 38(3), 19:1–19:42 (2013)
Karvounarakis, G., Ives, Z.G., Tannen, V.: Querying data provenance. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 951–962 (2010)
Ko, R.K.L., Will, M.A.: Progger: an efficient, tamper-evident kernel-space logger for cloud data provenance tracking. In: IEEE Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), pp. 881–889 (2014)
Köhler, S., Ludäscher, B., Zinn, D.: First-order provenance games. In: In Search of Elegance in the Theory and Practice of Computation, pp. 382–399 (2013)
Köhler, S., Riddle, S., Zinn, D., McPhillips, T.M., Ludäscher, B.: Improving workflow fault tolerance through provenance-based recovery. In: Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management (SSDBM), pp. 207–224 (2011)
Korolev, V., Joshi, A.: PROB: a tool for tracking provenance and reproducibility of big data experiments. In: Reproduce, HPCA, pp. 264–286 (2014)
Krishnan, S., Wang, J., Franklin, M.J., Goldberg, K., Kraska, T.: Privateclean: data cleaning and differential privacy. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 937–951 (2016)
Kulkarni, D.: A provenance model for key-value systems. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP), pp. 12:1–12:4 (2013)
Kwasnikowska, N., Van den Bussche, J.: Mapping the NRC dataflow model to the open provenance model. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP), pp. 3–16 (2008)
Lerner, B., Boose, E.R.: RDataTracker: collecting provenance in an interactive scripting environment. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP), pp. 1–4 (2014)
Lipford, H.R., Stukes, F., Dou, W., Hawkins, M.E., Chang, R.: Helping users recall their reasoning process. In: IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), pp. 187–194 (2010)
Logothetis, D., De, S., Yocum, K.: Scalable lineage capture for debugging DISC analytics. In: Symposium on Cloud Computing (SOCC), pp. 1–15 (2013)
Macko, P., Chiarini, M.: Collecting provenance via the xen hypervisor. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2011)
Macko, P., Seltzer, M.: Provenance map orbiter: interactive exploration of large provenance graphs. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2011)
Martens, A., Slominski, A., Lakshmanan, G.T., Mukhi, N.: Advanced case management enabled by business provenance. In: International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), pp. 639–641 (2012)
McPhillips, T., Bowers, S., Zinn, D., Ludäscher, B.: Scientific workflow design for mere mortals. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 25(5), 541–551 (2009)
McPhillips, T.M., Song, T., Kolisnik, T., Aulenbach, S., Belhajjame, K., Bocinsky, K., Cao, Y., Chirigati, F., Dey, S.C., Freire, J., Huntzinger, D.N., Jones, C., Koop, D., Missier, P., Schildhauer, M., Schwalm, C.R., Wei, Y., Cheney, J., Bieda, M., Ludäscher, B.: YesWorkflow: a user-oriented, language-independent tool for recovering workflow information from scripts. Int. J. Digit. Curation 10(1), 298–313 (2015)
Meliou, A., Gatterbauer, W., Moore, K.F., Suciu, D.: The complexity of causality and responsibility for query answers and non-answers. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 4(1), 34–45 (2010)
Michlmayr, A., Rosenberg, F., Leitner, P., Dustdar, S.: Service provenance in QoS-aware web service runtimes. In: International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), pp. 115–122 (2009)
Missier, P., Belhajjame, K., Cheney, J.: The W3C PROV family of specifications for modelling provenance metadata. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 773–776 (2013)
Missier, P., Belhajjame, K., Zhao, J., Roos, M., Goble, C.A.: Data lineage model for Taverna workflows with lightweight annotation requirements. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 17–30 (2008)
Missier, P., Bryans, J., Gamble, C., Curcin, V., Danger, R.: ProvAbs: model, policy, and tooling for abstracting PROV graphs. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 3–15 (2014)
Missier, P., Dey, S., Belhajjame, K., Cuevas-Vicenttín, V., Ludäscher, B.: D-prov: extending the prov provenance model with workflow structure. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP), pp. 9:1–9:7 (2013)
Missier, P., Goble, C.: Workflows to open provenance graphs, round-trip. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 27(6), 812–819 (2011)
Missier, P., Paton, N.W., Belhajjame, K.: Fine-grained and efficient lineage querying of collection-based workflow provenance. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 299–310 (2010)
Moreau, L.: The foundations for provenance on the web. Found. Trends Web Sci. 2(2–3), 99–241 (2010)
Moreau, L.: Provenance-based reproducibility in the semantic web. J. Web Semant. 9(2), 202–221 (2011)
Moreau, L., Freire, J., Futrelle, J., McGrath, R., Myers, J., Paulson, P.: The open provenance model. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 27(6), 743–756 (2011)
Müller, T., Grust, T.: Provenance for SQL through abstract interpretation: value-less, but worthwhile. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 8(12), 1872–1875 (2015)
Muniswamy-Reddy, K., Macko, P., Seltzer, M.I.: Provenance for the cloud. In: USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST), pp. 197–210 (2010)
Muniswamy-Reddy, K.-K., Braun, U., Holland, D.A., Macko, P., Maclean, D., Margo, D., Seltzer, M., Smogor, R.: Layering in provenance systems. In: USENIX Annual Technical Conference (2009)
Muniswamy-Reddy, K.-K., Holland, D.A., Braun, U., Seltzer, M.: Provenance-aware storage systems. In: USENIX Annual Technical Conference, pp. 43–56 (2006)
Murta, L., Braganholo, V., Chirigati, F., Koop, D., Freire, J.: noWorkflow: capturing and analyzing provenance of scripts. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 71–83 (2014)
Myers, A.C.: JFlow: practical mostly-static information flow control. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages (POPL), number January, pp. 228–241 (1999)
Nagappan, M., Vouk, M.A.: A Model for sharing of confidential provenance information in a query based system. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 62–69 (2008)
New, S.: The transparent supply chain. Harvard Bus. Rev. 88, 1–5 (2010)
Ni, Q., Xu, S., Bertino, E., Sandhu, R., Han, W.: An access control language for a general provenance model. In: Workshop on Secure Data Management (SDM), pp. 68–88 (2009)
Nies, T.D., Coppens, S., Verborgh, R., Sande, M.V., Mannens, E., Walle, R.V.D., Nies, D., Sande, V., Walle, V.D., Access, L.E., Towards, S.: Easy access to provenance: an essential step towards trust on the web. In: Computer Software and Applications Conference Workshops (COMPSACW) (2013)
Niu, X., Kapoor, R., Glavic, B., Gawlick, D., Liu, Z.H., Krishnaswamy, V., Radhakrishnan, V.: Interoperability for provenance-aware databases using PROV and JSON. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2015)
Oinn, T.M., Addis, M., Ferris, J., Marvin, D., Senger, M., Greenwood, R.M., Carver, T., Glover, K., Pocock, M.R., Wipat, A., Li, P.: Taverna: a tool for the composition and enactment of bioinformatics workflows. Bioinformatics 20(17), 3045–3054 (2004)
Oinn, T.M., Greenwood, R.M., Addis, M., Alpdemir, M.N., Ferris, J., Glover, K., Goble, C.A., Goderis, A., Hull, D., Marvin, D., Li, P., Lord, P.W., Pocock, M.R., Senger, M., Stevens, R., Wipat, A., Wroe, C.: Taverna: lessons in creating a workflow environment for the life sciences. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 18(10), 1067–1100 (2006)
Oliveira, W., Missier, P., Ocaña, K., de Oliveira, D., Braganholo, V.: Analyzing provenance across heterogeneous provenance graphs. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 57–70 (2016)
Olston, C., Reed, B.: Inspector gadget: a framework for custom monitoring and debugging of distributed dataflows. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 4(12), 1237–1248 (2011)
Olston, C., Reed, B., Srivastava, U., Kumar, R., Tomkins, A.: Pig latin: a not-so-foreign language for data processing. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 1099–1110 (2008)
Papadias, D., Tao, Y., Fu, G., Seeger, B.: An optimal and progressive algorithm for skyline queries. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 467–478 (2003)
Park, J., Nguyen, D., Sandhu, R.: A provenance-based access control model. In: Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), pp. 137–144 (2012)
Pham, Q., Malik, T., Foster, I.: Using provenance for repeatability. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2013)
Pimentel, J.A.F., Freire, J., Murta, L., Braganholo, V.: Fine-grained provenance collection over scripts through program slicing. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 199–203 (2016)
Pimentel, J.F., Dey, S., McPhillips, T., Belhajjame, K., Koop, D., Murta, L., Braganholo, V., Ludäscher, B.: Yin & Yang: demonstrating complementary provenance from noWorkflow & YesWorkflow. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 161–165 (2016)
Pimentel, J.F., Freire, J., Braganholo, V., Murta, L.: Tracking and analyzing the evolution of provenance from scripts. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 16–28 (2016)
Prabhune, A., Zweig, A., Stotzka, R., Gertz, M., Hesser, J.: Prov2ONE: an algorithm for automatically constructing ProvONE provenance graphs. In: International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), pp. 204–208 (2016)
Ragan, E.D., Endert, A., Sanyal, J., Chen, J.: Characterizing provenance in visualization and data analysis: an organizational framework of provenance types and purposes. In: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, pp. 31–40 (2015)
Riddle, S., Köhler, S., Ludäscher, B.: Towards constraint provenance games. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2014)
Roy, S., Chiticariu, L., Feldman, V., Reiss, F., Zhu, H.: Provenance-based dictionary refinement in information extraction. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 457–468 (2013)
Sabelfeld, A., Myers, A.C.: Language-based information-flow security. IIEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 21(1), 5–19 (2006)
Simmhan, Y., Plale, B., Gannon, D.: A survey of data provenance in e-science. SIGMOD Rec. 34(3), 31–36 (2005)
Simmhan, Y.L., Plale, B., Gannon, D.: Karma2: provenance management for data driven workflows. Int. J. Web Serv. Res. 5(10), 1–23 (2008)
Souilah, I., Francalanza, A., Sassone, V.: A formal model of provenance in distributed systems. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2009)
Stitz, H., Luger, S., Streit, M., Gehlenborg, N.: AVOCADO: visualization of workflow-derived data provenance for reproducible biomedical research. In: European Conference on Visualization (EuroVis), pp. 481–490 (2016)
Suen, C.H., Ko, R.K.L., Tan, Y.S., Jagadpramana, P., Lee, B.: S2logger: end-to-end data tracking mechanism for cloud data provenance. In: IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), pp. 594–602 (2013)
Szablocs, R., Aleksander, S., Yurdaer, D.: Large-Scale Distributed Storage Systems for Business Provenance. IBM Research Report, RC25154 (2011)
Tan, W., Missier, P., Foster, I., Madduri, R., De Roure, D., Goble, C.: A comparison of using Taverna and BPEL in building scientific workflows: the case of caGrid. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 22(9), 1098–1117 (2010)
Tan, W.C.: Provenance in databases: past, current, and future. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 30(4), 3–12 (2007)
Tan, Y.S., Ko, R.K.L., Holmes, G.: Security and data accountability in distributed systems: a provenance survey. In: IEEE Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications (HPCC) (2013)
Tariq, D., Ali, M., Gehani, A.: Towards automated collection of application-level data provenance. In: Workshop on Theory and Practice of Provenance (TAPP) (2012)
ten Cate, B., Civili, C., Sherkhonov, E., Tan, W.-C.: High-level why-not explanations using ontologies. In: ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems (PODS), pp. 31–43 (2015)
Theoharis Y, Fundulaki I, Karvounarakis G, Christophides V: On provenance of queries on semantic web data. IEEE Internet Comput. 15(1), 31–39 (2011)
Thusoo, A., Sarma, J.S., Jain, N., Shao, Z., Chakka, P., Anthony, S., Liu, H., Wyckoff, P., Murthy, R.: Hive: a warehousing solution over a map-reduce framework. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 2(2), 1626–1629 (2009)
Tran, Q.T., Chan, C.-Y.: How to ConQueR why-not questions. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 15–26 (2010)
Tran, Q.T., Chan, C.-Y., Parthasarathy, S.: Query reverse engineering. VLDB J. 23(5), 721–746 (2014)
Tylissanakis, G., Cotroni, Y.: Data provenance and reproducibility in grid based scientific workflows. In: IEEE Workshop on Grid and Pervasive Computing Conference, pp. 42–49 (2009)
Wang, R.Y., Strong, D.M.: Beyond accuracy: what data quality means to data consumers. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 12(4), 5–33 (1996)
Wang, Y.R., Madnick, S.E. et al.: A polygen model for heterogeneous database systems: the source tagging perspective. In: Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB), pp. 519–538 (1990)
White, T.: Hadoop: The Definitive Guide, 4th edn. O’Reilly Media, Sebastopol (2015)
Woodruff, A., Stonebraker, M.: Supporting fine-grained data lineage in a database visualization environment. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 91–102 (1997)
Wylot, M., Cudré-Mauroux, P., Groth, P.T.: Tripleprov: efficient processing of lineage queries in a native RDF store. In: World Wide Web Conference (WWW), pp. 455–466 (2014)
Zaharia, M., Chowdhury, M., Franklin, M.J., Shenker, S., Stoica, I.: Spark: cluster computing with working sets. In: USENIX Conference on Hot Topics in Cloud Computing (HotCloud) (2010)
Zhang, J., Jagadish, H.V.: Lost source provenance. In: Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), pp. 311–322 (2010)
Zhang, J., Jagadish, H.V.: Revision provenance in text documents of asynchronous collaboration. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 889–900 (2013)
Zhou, W., Fei, Q., Narayan, A., Haeberlen, A., Loo, B.T., Sherr, M.: Secure network provenance. In: ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOPS), pp. 295–310 (2011)
Zhou, W., Mapara, S., Ren, Y., Li, Y., Haeberlen, A., Ives, Z., Loo, B.T., Sherr, M.: Distributed time-aware provenance. Proc. VLDB Endow.: PVLDB 6(2), 49–60 (2012)
Zhou, W., Sherr, M., Tao, T., Li, X., Loo, B.T., Mao, Y.: Efficient querying and maintenance of network provenance at internet-scale. In: ACM Conference on the Management of Data (SIGMOD), pp. 615–626 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for financial support within project D03 of SFB/Transregio 161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herschel, M., Diestelkämper, R. & Ben Lahmar, H. A survey on provenance: What for? What form? What from?. The VLDB Journal 26, 881–906 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-017-0486-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-017-0486-1