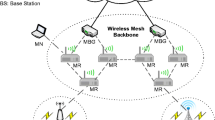
Abstract
The main advantage of a wireless network is user mobility, which calls for efficient routing support at the network layer. An architecture combines hierarchical mobile IPv6 and network mobility for a network mobile and mobile nodes move in tandem and make a hierarchy in the wireless network to management of micro-mobility and seamless handoff. But the capability of the architecture for intra domain route optimization is impaired. So we propose functionality in domain nodes to enable intra domain path optimization for ubiquitous network. It is shown that intra domain cost effect is beneficial in every hierarchical domain that spans mesh network topology. We address the key function for our proposed scheme and analyze the usefulness of our proposed method using mathematically. We show that our proposed scheme performs much better than Network Mobility protocol, especially when the number of mobile nodes or mobile routers or correspondent nodes increases in hierarchically nested in ubiquitous networks.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devarapalli V, Wakikawa R, Petrescu A, Thubert P (2005) Network mobility (NEMO) basic support protocol. IETF RFC 3963, January 2005
Johnson D, Perkins C, Arkko J (2003) Mobility support in IPv6. Draft-ietf-mobileip-ipv6-22.txt, May 2003
Wu D (2005) Qos provisioning in wireless networks. Wireless Communication and Mobile Computing 5:957–969
Lan KC, Perera E, Petander H, Libman L, Dwertmann C, Hassan M (2005) MOBNET: the design and implementation of a network mobility testbed. 14th IEEE workshop on local and metropolitan area network, September 2005
Thubert P, Molteni M (2004) IPv6 reverse routing header and its application to mobile networks. Internet draft: draft-thubert-nemoreverse-routing-header-05.txt, June 2004
Suzuki T, Igarashi K, Miura A, Yabusaki M (2005) Care-of prefix routing for moving networks. IEICE Trans Commun E88-B(7) July 2005
Novaczki S, Bokor L, Jeney G, Imre S (2008) Design and evaluation of a novel HIP-based network mobility protocol. J Netw 3(1), January 2008
Watfa M, Commuri S (2006) The three dimensional coverage problem. J Netw JNW 1(4):10–20
Noor SA, Janjusa KA, Zhang L (2007) Route optimization techniques in network mobility (NEMO). Wireless and Optical Communication Networks, 2007
Alberto EP (2001) Location privacy in IPv6—tracking the binding updates. IMIT. August 2001
Moskowitz R, Nikander P, Jokela P, Henderson T (2007) Host identity protocol, IETF Internet draft (draft-ietf-hip-base-08), June 2007
Henderson T (2007) End-host mobility and multihoming with the host identity protocol. IETF Internet draft (draft-ietf-hip-mm05), March 2007
Nikander P, Laganier J (2007) Host identity protocol (HIP) domain name system (DNS) extensions. IETF Internet draft (draft-ietf-hip-dns-09), April 2007
Conta A, Deering S (1998) Generic packet tunneling in IPv6 specification. IETF RFC 2473, December 1998
Jabbari B (1996) Teletraffic aspects of evolving and next-generation wireless communication networks. IEEE Pers Commun Mag 3(6):4–9
Nanda S (1993) Teletraffic models for urban and suburban microcells: cell sizes and handoff rates. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 42(4):673–682
Fang Y (2005) Modeling and performance analysis for wireless mobile networks: a new analytical approach. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 13(5):989–1002
Waitzman D, Partridge C, Deering S (eds) (1998) Distance vector multicast routing protocol. RFC1075, November 1998
Moy J (1999) Multicast routing extension for OSPF. CACM 37(8):61–66, August 1999
Ballardie A, Francis P, Crowcroft J (1993) Core based trees (CBT): an architecture for scalable inter-domain multicast routing. ACM SIGCOMM 93:85–95
Deering S, Estrin D, Farinacci D, Jacbson V (1994) An architecture for wide-area multicast routing. ACM SIGCOMM 94
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Hongik University new faculty research support fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HY., Chang, H. & Jeong, YS. Intra domain route optimization for ubiquitous network. Pers Ubiquit Comput 13, 449–455 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-009-0219-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-009-0219-6