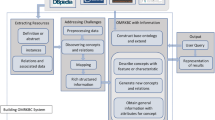
Abstract
One of the key elements of the Semantic Web technologies is domain ontologies and those ontologies are important constructs for multi-agent system. The Semantic Web relies on domain ontologies that structure underlying data enabling comprehensive and transportable machine understanding. It takes so much time and efforts to construct domain ontologies because these ontologies can be manually made by domain experts and knowledge engineers. To solve these problems, there have been many researches to semi-automatically construct ontologies. Most of the researches focused on relation extraction part but manually selected terms for ontologies. These researches have some problems. In this paper, we propose a hybrid method to extract relations from domain documents which combines a named relation approach and an unnamed relation approach. Our named relation approach is based on the Hearst’s pattern and the Snowball system. We merge a generalized pattern scheme into their methods. In our unnamed relation approach, we extract unnamed relations using association rules and clustering method. Moreover, we recommend candidate relation names of unnamed relations. We evaluate our proposed method by using Ziff document set offered by TREC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berners-Lee T, Hendler J, Lassila O (2001) The Semantic Web. Sci Am 284(5):34–43
Maedche A, Pekar V, Staab S (2002) Ontology learning part one—on discovering taxonomic relations from the web. In: Web Intelligence, Springer, Berlin
Byrd RJ, Ravin Y (1999) Identifying and extracting relations from text. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on applications of natural language to information systems
Hearst MA (1992) Automatic acquisition of hyponyms from large text corpora. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on computational Linguistics
Agichtein E, Gravano L (2000) Snowball: extracting relations from large plain-text collections. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on digital libraries (DL’00)
Frakes WB, Baeza-Yates R (eds) (1992) Information retrieval: data structures and algorithms. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Kim H, Choi I, Kim M (2004) Refining term weights of documents using term dependencies. In: Proceedings of the 26th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 552–553
Lawrie DJ, Croft WB (2003) Generating hierarchical summaries for web searches. In: Proceedings of the 26th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 457–458
Sanderson M, Croft B (1999) Deriving concept hierarchies from text. In: Proceedings of the 22th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 206–213
Lawrie D, Croft WB, Rosenberg A (2001) Finding topic words for hierarchical summarization. In: Proceedings of the 24th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (SIGIR 2001), pp 349–357
Maedche A, Staab S (2000) Semi-automatic engineering of ontologies from text. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on Sw engineering and knowledge engineering (SEKE’2000)
Moreira AF, Vieira R, Bordini RH, Hübner JF (2006) Agent-oriented programming with underlying ontological reasoning. In: Proceedings of 3rd international workshop on declarative agent languages and technologies (DALT-05), pp 155–170, vol 3904, Springer
Fuzitaki CN, Moreira ÁF, Vieira R (2010) Ontology reasoning in agent-oriented programming. In: 20th SBIA—Brazilian symposium on artificial intelligence. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 6404, pp 21–30
Lee C, Park S, Lee D, Lee J, Jeong OR, Lee S (2008) A comparison of ontology reasoning systems using query sequences. In: The 2nd international conference on ubiquitous information management and communication, pp 543–546
Cui H, Kan M-Y, Chua T-S (2004) Unsupervised learning of soft patterns for generating definition. In: Proceedings of 13th international world wide web conference
Brill E (1995) Transformation-based error-driven learning and natural language: a case study in part-of-speech tagging. Comput Linguist 21:543–565
Frantzi KT, Ananiadou S, Tsujii J (1998) The C-value/NC-value method of automatic recognition for multi-word terms. Research and advanced technology for digital libraries: second european conference, ECDL’98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, I., Rho, S. & Kim, M. Semi-automatic construction of domain ontology for agent reasoning. Pers Ubiquit Comput 17, 1721–1729 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-012-0606-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-012-0606-2