Abstract
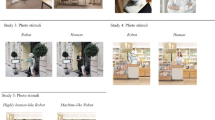
To investigate how robots behave as social entities, we analyze the interaction of humans and “Muu,” an embodied artificial entity. Specifically, our purpose is to find the salient patterns of behavior that distinguish the robot from humans in the course of an interaction. Through exploratory observations, we identify such salient patterns as the manner of repetitions and the address mismatch. We discuss how the social display of such patterns as “marked” features plays a very important role in mutual interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y Yamamoto (1994) ArticleTitleInterpersonal behavior (in Japanese) Cognitive Stud 1 95–99 Occurrence Handle0803.94015
S Takeuchi (1995) ArticleTitleAbout "interpersonal behavior" (in Japanese) Cognitive Stud 2 103–107
B Reeves C Nass (1996) The media equation Cambridge University Press Cambridge
Goan M, Fujii H, Okada M (2005) Child–robot interaction mediated by building blocks: from field observation in a public space. In: Sugisaka M (ed) Proceedings of the International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics (AROB 10), Beppu, Oita, Japan, February 4–6, 2005, pp 194–197
JF Kelley (1984) ArticleTitleAn interactive design methodology for user-friendly natural language office information applications ACM Trans Office Inf Syst 2 26–41 Occurrence Handle10.1145/357417.357420
Nagaoka C, Draguna M, Komori M, et al. (2002) The influence of switching pauses on interpersonal perception in dialogues (in Japanese). Proceedings of the Human Interface Symposium, 2002
H Gerfinkel (1967) Studies in ethnomethodology Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 10th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, February 4–6, 2005
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, H., Okada, M. Can robots get “memberships” by social interaction?. Artif Life Robotics 10, 77–80 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-005-0376-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-005-0376-2