Abstract
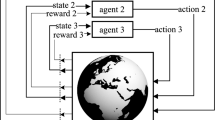
The distributed autonomous robotic system has superiority of robustness and adaptability to dynamical environment, however, the system requires the cooperative behavior mutually for optimality of the system. The acquisition of action by reinforcement learning is known as one of the approaches when the multi-robot works with cooperation mutually for a complex task. This paper deals with the transporting problem of the multi-robot using Q-learning algorithm in the reinforcement learning. When a robot carries luggage, we regard it as that the robot leaves a trace to the own migrational path, which trace has feature of volatility, and then, the other robot can use the trace information to help the robot, which carries luggage. To solve these problems on multi-agent reinforcement learning, the learning control method using stress antibody allotment reward is used. Moreover, we propose the trace information of the robot to urge cooperative behavior of the multi-robot to carry luggage to a destination in this paper. The effectiveness of the proposed method is shown by simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Hong S, Miyazaki M, Lee H (2006) Learning control of carrier robots with cooperative behavior. Electronics, Information and Systems Conference, IEEJ, MC4-1
Arai S (2001) Multiagent reinforcement learning frameworks: steps toward practical use. J JSAI 16(4):476–481
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning: an introduction, The MIT Press
Watkins CJCH, Dayan P (1992) Technical note: Q-learnging. Machine Learning 8:279–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 13th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, January 31–February 2, 2008
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshita, T., Shin, JS., Miyazaki, M. et al. A cooperative behavior learning control of multi-robot using trace information. Artif Life Robotics 13, 144–147 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-008-0574-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-008-0574-9