Abstract
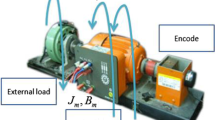
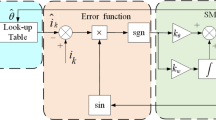
In this article, a sliding mode control (SMC) design based on a Gaussian radial basis function neural network (GRBFNN) is proposed for a synchronous reluctance motor (SynRM) system robust stabilization and disturbance rejection. This method utilizes the Lyapunov function and the steep descent rule to guarantee the convergence of the SynRM drive system asymptotically. Finally, we employ experiments to validate the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Miller TJE, Hutton A, Cossar C, Staton DA (1991) Design of a synchronous reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans Indust Appl 27:741–749
Betz RE, Lagerquist R, Jovanovic M (1993) Control of synchronous reluctance machines. IEEE Trans Indust Appl 29:1110–1121
Utkin VI, Guldner J, Shi J (1999) Sliding mode control in electromechanical systems. Taylor & Francis, Philadelphia
Shyu KK, Lai CK, Tsai YW (2000) Optimal position control of synchronous reluctance motor via totally invariant variable structure control. IEE Proc Control Theor Appl 147:28–36
Chiang HK, Tseng CH (2004) Design and implementation of a grey sliding mode controller for synchronous reluctance motor drive. Control Eng Practice 12:155–163
Asada H, Slotine JJ (1986) Robot analysis and control. Wiley, New York
Chiang HK, Tseng CH (2004) Integral variable structure controller with grey prediction for synchronous reluctance motor drive. IEE Proc Elec Power Appl 151:349–358
Lin FJ, Wai RJ, Lin CH, Liu DC (2000) Decoupled stator-fluxoriented induction motor drive with fuzzy neural network uncertainty observer. IEEE Trans Indust Electron 47:356–367
Chen TC, Sheu TT (2002) Model reference neural network controller for induction motor speed control. IEEE Trans Energy Conversion 17:157–163
Lin Z, Reay DS, Williams BW, Xiangning H (2007) Online modeling for switched reluctance motors using B-spline neural networks. IEEE Trans Indust Electron 54:3317–3322
Jang JSR, Sun CT (1993) Functional equivalence between radial basis function networks and fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 4:156–159
Lin FJ, Teng LT, Shieh PH (2007) Intelligent sliding-mode control using RBFN for magnetic levitation system. IEEE Trans Indust Electron 54:1752–1762
Park JW, Venayagamoorthy GK, Harley RG (2005) MLP/RBF neural-networks-based online global model identification of synchronous generator. IEEE Trans Indust Electron 52:1685–1695
Huang SJ, Huang KS, Chiou KC (2003) Development and application of a novel radial basis function sliding mode controller. Mechatronics 13:313–329
Huang SJ, Lian RJ (1996) A combination of fuzzy logic and neural network algorithms for active vibration control. Proc Inst Mech Eng 210:153–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 14th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, February 5–7, 2009
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CA., Chiang, HK., Lin, WB. et al. Synchronous reluctance motor speed drive using sliding mode controller based on Gaussian radial basis function neural network. Artif Life Robotics 14, 53–57 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0627-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0627-8