Abstract
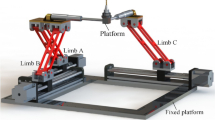
A tripod parallel mechanism consists of three links of fixed length and a rigid platform, and these are connected by revolute joints. The platform can achieve sixdegrees-of-freedom (6-DOF) motion by the coordinated movement of the bottom ends of the three links on a horizontal plane. This mechanism has advantages over the more common six extendible parallel manipulators. It has a much larger work space and a simple structure. In this article, we show that the vector analysis for this tripod parallel mechanism and the derivation of the positions of the three bottom ends of the links in an arbitrary attitude of platform can be found by inverse kinematics and the conditions of geometrical constraint. Then, by a numerical simulation, the trajectories of the bottom ends of the three links are shown.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Stewart D (1965–1966) A platform with 6 degrees of freedom. Proc Inst Mech Eng, vol 180, part 1, No 15, pp 371–386
Ben-Horin R, Shoham M, Djerassi S (1998) Kinematics, dynamics and construction of a planarly actuated parallel robot. Robotics Computer-Integrated Manuf 14:163–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 14th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, February 5–7, 2009
About this article
Cite this article
Hitaka, Y., Tanaka, Y., Tanaka, Y. et al. Motion analysis of a tripod parallel mechanism. Artif Life Robotics 14, 494–497 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0707-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0707-9