Abstract
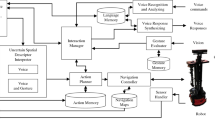
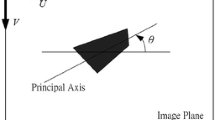
This article proposes a method for understanding user commands based on visual attention. Normally, fuzzy linguistic terms such as “very little” are commonly included in voice commands. Therefore, a robot’s capacity to understand such information is vital for effective human-robot interaction. However, the quantitative meaning of such information strongly depends on the spatial arrangement of the surrounding environment. Therefore, a visual attention system (VAS) is introduced to evaluate fuzzy linguistic information based on the environmental conditions. It is assumed that the corresponding distance value for a particular fuzzy linguistic command depends on the spatial arrangement of the surrounding objects. Therefore, a fuzzy-logic-based voice command evaluation system (VCES) is proposed to assess the uncertain information in user commands based on the average distance to the surrounding objects. A situation of object manipulation to rearrange the user’s working space is simulated to illustrate the system. This is demonstrated with a PA-10 robot manipulator.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Crangle C, Suppes P (1994) Language and learning for robots. CSLI Publications, Stanford
Menzel P, D’Aluisio F (2000) Robosapiens. MIT Press, London
Pulasinghe K, Watanabe K, Izumi K, et al (2004) A modular fuzzy-neuro controller driven by spoken language commands. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B, Cybern 34:293–302
Jayawardena C, Watanabe K, Izumi K (2004) Knowledge acquisition by a sub-coach in a coach player system for controlling a robot. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Mechatronics, Hokkaido, Japan, October 2004, JSME, Hokkaido, pp 601–606
Jayawardena C, Watanabe K, Izumi K (2006) Learning of object identification by robots commanded by natural language. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems, Tokyo, Japan, March 2006, IOS Press, Tokyo, pp 913–920
Kragic D, Bjorkman M, Christensen HI, et al (2005) Vision for robotic object manipulation in domestic settings. Robotics Auton Syst 52:85–100
Jayasekara B, Watanabe K, Izumi K (2008) Controlling a robot manipulator with fuzzy voice commands guided by visual motor coordination learning. Proceedings of the International Conference on Instrumentation, Control and Information Technology, Tokyo, Japan, August 2008, SICE, Tokyo, pp 2540–2544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 14th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, February 5–7, 2009
About this article
Cite this article
Jayasekara, A.G.B.P., Watanabe, K. & Izumi, K. Understanding user commands by evaluating fuzzy linguistic information based on visual attention. Artif Life Robotics 14, 48–52 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0716-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-009-0716-8