Abstract
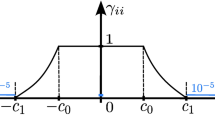
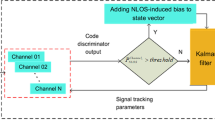
We propose a method to improve the state estimation accuracy of mobile robots placed near high-rise buildings using the statistical property of the reflected and diffracted waves of global positioning system (GPS) signals. First, it is assumed that a GPS signal that contains a reflected and diffracted wave is denoted by the sum of the true position information and noise that follows a time-varying Gaussian distribution. On the basis of this assumption, the time-varying bias of a GPS signal is tracked using a Kalman filter. In addition, a particle filter, which executes sampling and likelihood evaluation using the estimated bias, is developed. With the proposed method, a GPS signal that contains the rejected noise introduced by the conventional method can be used efficiently, and the state estimation accuracy of the robot in a shadow area of GPS satellite can be improved. Furthermore, a control system for an autonomous mobile robot incorporating the proposed state estimation mechanism is developed, and its effectiveness is evaluated via simulation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H, Collins J (2001) GPS: theory and practice, 5th revised edn. Springer, NewYork, pp 125–129
Yamazaki M, Takeuchi E, Ohono K, Tadokoro S (2011) GPS based particle filter localization method with multipath model using 3D-Map. JRSJ 29(8):702–709
Thrun S, Burgard W, Fox D (2005) Probabilistic robotics. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 117–234
Maier D, Kleiner A (2010) Improved GPS sensor model for mobile robots in urban terrain. In: International conference on robotics and automation
Bekey GA (2005) Autonomous robots: from biological inspiration to implementation and control. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 57–71
Kitagawa G (1998) Monte Carlo filter and smoother for non-Gaussian nonlinear state space models. J Comput Graph Stat 5:1–25
Doucet A, Freitas N, Gordon N (eds) (2001) Sequential Monte Carlo methods in practice. Springer, Berlin
Tomono M (2011) Probabilistic approaches to localization and mapping for mobile robots. JRSJ 29(5):423–426
Corke P (2011) Robotics, vision and control fundamental algorithms in MATLAB. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–130
Liu JS, Chen R (1998) Sequential Monte Carlo methods for dynamic systems. J Am Stat Assoc 93(443):1032–1044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nishida, T., Inoue, S. & Sagara, S. State estimation of mobile robot using GPS signal that includes reflected and diffracted waves. Artif Life Robotics 18, 178–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-013-0115-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-013-0115-z