Abstract
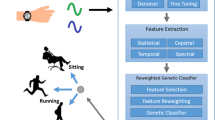
Human motion has already deeply affected many aspects of psychological and social research. On the other hand, because of the huge challenges and new dimensions of its increasingly extreme applications, this field remains an inspiring area in which to explore rich possibilities in the fields of artificial intelligence and bio-informatics. In this research, we investigated a novel approach to identify individuals based on their gaits. Furthermore, we investigated a new avenue of the research toward the biometric identification of humans that involves the classification of human gait using the power of genetic programming (GP). Moreover, we also propose an approach that applies collaborative filter using multiple evolved classifiers to address the challenges of non-determinism and insufficient generality of GP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Montepare JM, Goldstein SB, Clausen A (1987) The identification of emotions from gait information. J Nonverbal Behav 11(1):33–42
Torje NF (2002) Decomposing biological motion: a framework for analysis and synthesis of human gait patterns. J Vis 2(5):371–387
Johannson G (1973) Visual perception of biological motion and a model for its analysis. Percept Psychophys 14(2):201–211
Levitan IB, Kaczmarek LK (2002) The neuron cell and molecular biology, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 509
Wang L, Hu W, Tan T (2003) Recent developments in human motion analysis. Pattern Recognit 36(3):585–601
Hofmann M, Bachmann S, Rigoll G (2012) 2.5D gait biometrics using the depth gradient histogram energy image. In: Biometrics: theory, applications and systems (BTAS), IEEE fifth international conference, Dec. 2012, pp 399–403
Ng H, Ton HL, Tan WH et al (2011) Human identification based on extracted gait features. Int J New Comput Archit Appl 1(2):358–370
Wang L, Tan T, Ning H et al (2003) Silhouette analysis based gait recognition for human identification. Patt Anal Mach 25(12):1505–1518
Sharma DG, Yusuf R, Tanev I et al (2014) Human recognition based on gait features and genetic programming. J Robot Netw Artif Life 1(3):194–197
Microsoft (2012) https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh438998.aspx. Accessed 22 Feb 2016
Tanev I, Shimohara K (2010) XML-based genetic programming framework: design philosophy, implementation, and applications. Artif Life Robot 15(4):376–380
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, D.G., Yusuf, R., Tanev, I. et al. Human gait analysis based on biological motion and evolutionary computing. Artif Life Robotics 21, 188–194 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0267-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0267-8