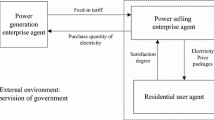
Abstract
With growing great interest in the energy problems, real-time pricing (RTP) for power systems has attracted attention in the world. In our research, a new distributed optimization method is proposed for RTP. It is based on negotiations between players (consumers, suppliers and distributors) through information networks. Then we developed a graphical and scalable multi-agent simulator for RTP which is named “RTPsim” for further investigations. RTPsim enables us to conduct numerical simulations in various conditions and various scales. This paper shows the new distributed optimization method based on negotiations, the features of our graphical and scalable RTP simulator and examples of simulation results.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bitar E, Khargonekar PP, Poolla K (2011) Systems and control opportunities in the integration of renewable energy into the smart grid, in The 18th IFAC World Congress, 2011
Berger W, Schweppe FC (1989) Real time pricing to assist in load frequency control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst 4(3):920–926
Rosenfeld AH, Bulleit DA, Peddie RA (1986) Smart meters and spot pricing: experiments and potential. IEEE Technol Soc Mag 5(1):23–28
Gans W, Alberini A, Longo A (2013) Smart meter devices and the effect of feedback on residential electricity consumption: evidence from a natural experiment in northern ireland. Energy Econ 36:729–743
Sakurama K, Miura M (2015) Complete distributed optimization with constraints on networked multi-agent systems, The 14th European control conference, 2015
Luenberger DG (2003) Ye Y (2003) Linear and Nonlinear Programming, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, USA
Olfati-Saber R, Murray R (2004) Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Trans. Automatic Control 49(9):1520–1533
Yamakage S (2009) Modeling and expanding artificial societies: introduction to multi-agent simulation with artisoc, Kozo Keikaku Engineering Inc., 2009
Kazuya Y (2007) International relations and agent-based modeling: A New User-friendly Simulator? Artisoc, Proceedings of annual meeting of the International Studies Association 48th Annual Convention, Chicago, 2007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, M., Tokunaga, Y. & Sakurama, K. Graphical and scalable multi-agent simulator for real-time pricing in electric power grid. Artif Life Robotics 21, 181–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0268-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0268-7