Abstract
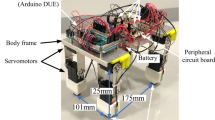
In this paper, we will compare the walking behavior of quadruped and hexapod walking MEMS robots. These robots are fabricated by connecting same modules, which are composed of a couple of independent leg mechanisms. Independent leg mechanisms can actuate the single leg by a single artificial muscle wire. The neural networks IC that mimics real living organisms controls the mechanical systems. The length and weight of the quadruped MEMS robot were 7.2 mm and 95.8 mg, respectively. The quadruped robot showed the walking speed of 24.6 mm/min. The robot tended to lose its balance and the weight balance is quite important for the moving quadruped. On the other hand, the length and weight of the hexapod MEMS robot were 9.0 mm and 162 mg, respectively. The hexapod robot showed stable walking. The speed was 27.0 mm/min.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Baisch AT, Sreetharan PS, Wood RJ, Miller EH (2010) Biologically-inspired locomotion of a 2 g hexapod robot. In: Proc. int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems, 10 conference, pp 5360–5365
Habib MK (1993) Innovations and robotics. Int J Mechatron Manuf Syst 4(2):123–135
Hollar S, Flynn A, Bellew C, Pister KSJ (2002) Solar powered 10 mg silicon robot. In: Proc. of the IEEE the sixteenth annual international conference on micro electro mechanical systems, Kyoto, pp 706–711. https://doi.org/10.1109/MEMSYS.2003.1189847
Vogtmann D, Pierre RS, Bergbreiter S, Paprotny I (2017) A 25 mg magneyically actuated microrobot walking at> 5 body lengths/sec. In: MEMS 2017, Las Vegas, January 22–26
Qi M, Zhu Y, Liu Z, Zhang X, Yan X, Lin L (2017) A fast-moving electrostatic crawling insect. In: MEMS 2017, Las Vegas, January 22–26
Saito K, Takato M, Sekine Y, Uchikoba F (2012) Biomimetics micro robot with active hardware neural networks locomotion control and insect-like switching behaviour. Int J Adv Robot Syst 9:1–6
Sugita K, Tanaka D, Ono S, Chiba S, Iwata K, Han Y, Takato M, Saito K, Uchikoba F (2016) SMA actuator and pulse-type hardware neural networks IC for fast walking motion of insect-type MEMS microrobot. In: IEEE international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics, pp 431–435
Sugita K, Tanaka T, Nakata Y, Takato M, Saito K, Uchikoba F (2017) Hexapod type MEMS microrobot equipped with an artificial neural networks IC. In: International conference on artificial life and robotics, pp 225–228
Tanaka D, Uchiumi Y, Kawamura S, Takato M, Saito K, Uchikoba F (2017) Four-leg independent mechanism for MEMS microrobot. Artif Life Robot 22(3):380–384
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kawamura, S., Tanaka, D., Tanaka, T. et al. Neural networks IC controlled multi-legged walking MEMS robot with independent leg mechanism. Artif Life Robotics 23, 380–386 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-018-0445-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-018-0445-y