Abstract
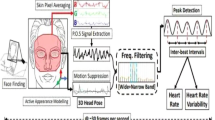
In this paper, we propose a method to remove the influence of light on the face from display in imaging photoplethysmography (iPPG) to measure blood flow of the face when watching a video with an RGB camera. We propose a simple method which is used to correct the pixel values of the face by the pixel values of a standard white plate. The proposed method is evaluated by simulation and actual measurement. As a result, it is shown that it is possible to reduce the influence of light on the face from display in iPPG and measure variation in blood flow of face when watching a video.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDuff D, Gontarek S, Picard R (2014) Remote measurement of cognitive stress via heart rate variability. In: 36th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, Chicago, IL, 2014, pp 2957–2960
Poh MZ, McDuff DJ, Picard RW (2011) Advancements in noncontact, multiparameter physiological measurements using a webcam. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):7–11
Alghoul K, Alharthi S, Osman Al et al (2017) Heart rate variability extraction from videos signals: ICA vs. EVM comparison. IEEE Access 5:4711–4719
Okada G, Yonezawa T, Kurita K, Tsumura N (2018) Monitoring emotion by remote measurement of physiological signals using an RGB camera. ITE Trans Media Technol Appl 6(1):131–137
Weenk M, Alken A, Engelen L et al (2018) Stress measurement in surgeons and residents using a smart patch. Am J Surg 216:361–368
Pereira T, Almeida P, Cunha J et al (2017) Heart rate variability metrics for fine-grained stress level assessment. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 148:71–80
Kashima H, Hayashi N (2011) Basic taste stimuli elicit unique responses in facial skin blood flow. PLoS One 6(12):e28236
Guazzi AR, Villarroel M, Jorge J et al (2015) Non-contact measurement of oxygen saturation with an RGB camera. Biomed Opt Express 6(9):2228–3320
Petrov GI, Doronin A, Whelan HT et al (2012) Human tissue color as viewed in high dynamic range optical spectral transmission measurements. Biomed Opt Express 3(9):2154–2161
Acknowledgements
We thank Adam Przywecki, B.Eng, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Iuchi, K., Mitsuhashi, R., Goto, T. et al. Removing the influence of light on the face from display in iPPG. Artif Life Robotics 25, 377–382 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00625-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00625-3