Abstract
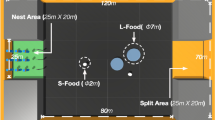
This paper mainly discussed the generation of collective behaviors with raw camera images as the primary information input. The swarm robotic system exhibits considerable advantages when faced with individual-level failure or the lack of global information. Spatial information has always been a necessity in generating collective transport behavior. The rise of deep neural network technology makes it possible for a robot to perceive the environment from its visual input. In this paper, the use of deep reinforcement learning in training a robotic swarm to generate collective foraging behavior is shown. The collective foraging behavior is evaluated in a transportation task, where robots need to learn to process image information while cooperatively transport foods to the nest. We applied a deep Q-Learning algorithm and several improved versions to develop controllers for robotic swarms. The results of computer simulations show that using images as the main information input can successfully generate collective foraging behavior. Besides, we also combine the advantages of several algorithms to improve performance and perform experiments to examine the flexibility of the developed controllers.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Şahin E (2004) Swarm robotics: from sources of inspiration to domains of application. International workshop on swarm robotics, pp. 10–20
Stephan C, Wilkinson A (2012) Have we met before? Pigeons recognise familiar human faces. Avian Biol Res 5(2):75–80
Yu H, Yang J (2001) A direct LDA algorithm for high-dimensional data-with application to face recognition. Pattern Recogn 34(10):2067–2070
LeCun Y, Yoshua B (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436
Hsu K, Gupta HV (1995) Artificial neural network modeling of the rainfall-runoff process. Water Resour Res 31(10):2517–2530
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K (2013) Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv:1312.5602
Mnih V et al (2015) Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540):529
Mnih V, Badia AP (2016) Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. Int Conf Mach Learn 2017:1928–1937
Hasselt V (2016) Hado and Guez. In: Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning, Thirtieth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Brambilla M et al (2013) Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. Swarm Intell 7(1):1–41
Liu W, Winfield AFT (2010) Modeling and optimization of adaptive foraging in swarm robotic systems. Int J Robot Res 29(14):1743–1760
Wei Y, Toshiyuki Y, Kazuhiro O (2017) Collective cognition: a case study of evolutionary swarm robotics in the collective foraging problem with poison. In: 2017 IEEE/SICE international symposium on system integration (SII), pp 865–868
Angeline PJ, Saunders GM, Pollack JB (1994) An evolutionary algorithm that constructs recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(1):54–65
OpenAI Five Website (2018) https://openai.com/five/
AlphaGo Website (2017) https://deepmind.com/research/alphago/
BayndIr L (2016) A review of swarm robotics tasks. Neurocomputing 172:292–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, B., Liang, Y., Han, Z. et al. Generating collective foraging behavior for robotic swarm using deep reinforcement learning. Artif Life Robotics 25, 588–595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00642-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00642-2