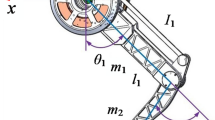
Abstract
It is known that the gait changes in accordance with the travel velocity by exploiting the body dynamics in the study of quadruped robots. For instance, some studies attained passive dynamic quadruped gaits such as a pace with a rigid trunk and a trot with a roll joint. The quadruped gait by the decentralized phase oscillator was reported, which exhibited a gait transition due to the intrinsic oscillator frequency. The robots had relatively short legs, which provides a stable upright posture, and the locomotion would not be influenced strongly by body dynamics. In this study, the quadruped RW06-Duo based on the passive dynamic walking mechanism, in which CoM is located at a high position, is developed and attains quadruped locomotion by the phase oscillator. The limb joints except for the knee (elbow) can rotate freely and passively; therefore, intralimb coordination is attained passively, and the phase oscillator and spine stiffness provide interlimb coordination. RW06-Duo exhibits different gaits according to travel velocity and demonstrates the gait transition from pace to trot or DS walk for the same oscillator frequency and stiffness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Remy CD et al (2009) Stability analysis of passive dynamic walking of quadrupeds. Intl J Robot Res 29(9):1173–1185
Nakatani K et al (2009) Demonstration and analysis of quadrupedal passive dynamic walking. Adv Robot 23:483–501
Remy CD et al (2010) Passive dynamic walking with quadrupeds—extensions towards 3D. In: Proc Intl Conf Robot Autom
Kito Y et al (2014) Design of multi-layered spine unit with 3-d.o.f. flexibility. In: Proc of the 2014 JSME Conf on Robotics and Mechatronics, 2A1-107
Owaki D et al (2012) Simple robot suggests physical interlimb communication is essential for quadruped walking. J R Soc Interface 10(78). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2012.0669
Owaki Dai, Ishiguro Akio (2017) A quadruped robot exhibiting spontaneous gait transitions from walking to trotting to galloping. Sci Rep 7:277
McGeer T (1988) Passive dynamic walking, CSS-IS TR, 88-02
Smith AC, Berkemeier MD (1997) Passive dynamic quadrupedal walking. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 34–39
Li L et al (2020) Energy-efficient locomotion generation and theoretical analysis of a quasi-passive dynamic walker. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 5(2):4305–4312
Li L et al (2021) Synergetic effect between limbs and spine dynamics in quadruped walking robots. In: Proc of IEEE Intl Conf on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2021), 6818–6823
Kibayashi T et al (2013) Realization of quadrupedal quasi-passive dynamic walking driven by rocking motion and motion analysis based on a nonholonomic model. J Robot Soc Jpn 31(8):730–738
Sugimoto Y et al (2017) Walking analysis of quadruped quasi-passive dynamic walking robot “Duke-II” focusing on trunk structure. In: Proc on Climbing and Walking Robots 2017, paper ID 34
Fukuhara A et al (2020) A bio-inspired quadruped robot exploiting flexible shoulder for stable and efficient walking. In: Proc on IEEE/RSJ Intl Conf on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS2020), 7832–7839
Kinugasa T et al (2019) Three-dimensional dynamic bipedal walking based on passive dynamic walking mechanism using telescopic knee via phase oscillator with ground reaction force. Artif Life Robot 24(2):172–177
Kinugasa T et al (2015) 3D dynamic biped walker with flat feet and ankle springs: passive gait analysis and extension to active walking. J Robot Mechatron 27(4):444–452
Kinugasa T et al (2011) Passive dynamic quadruped walker with feet and ankle springs. In: Proc of Climbing and Walking Robots CLAWAR2011, 517–524
Osuka K, Saruta Y (2000) Development and control of new legged robot QUARTET III-from active walking to passive walking. In: Proc of IEEE/RSJ Intl Conf on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS2000), 991–995
Sugimoto Y, Osuka K (2004) Walking control of quasi passive dynamic walking robot “Quartet III” based on continuous delayed feedback control. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Robotics and Biometrics, pp 606–611
Kuramoto Y (1984) Chemical oscillators, waves, and turbulence. Springer, New York
Cartmill M et al (2002) Support polygons and symmetrical gaits in mammals. Zool J Linnean Soc 136:401–420
Univ. of Pennsylvania, Animal locomotion: the Muybridge Work at the Univ. of Pennsylvania: The Method and the Result, Philadelphia : J.B. Lippincott Co., (1888)
Hoyt DF, Taylor CR (1981) Gait and the energetics of locomotion in horses. Nature 292:239–240
Alexander RM (1976) Estimates of speeds of dinosaurs. Nature 261:129–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Miwa, S., Kinugasa, T., Oba, K. et al. Various gait pattern generation and analysis of semi-passive quadruped walker with telescopic knee based on phase oscillator. Artif Life Robotics 28, 540–546 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-023-00862-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-023-00862-2