Abstract.
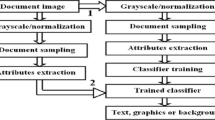
This paper proposes an integrated system for the processing and analysis of highly degraded printed documents for the purpose of recognizing text characters. As a case study, ancient printed texts are considered. The system is comprised of various blocks operating sequentially. Starting with a single page of the document, the background noise is reduced by wavelet-based decomposition and filtering, the text lines are detected, extracted, and segmented by a simple and fast adaptive thresholding into blobs corresponding to characters, and the various blobs are analyzed by a feedforward multilayer neural network trained with a back-propagation algorithm. For each character, the probability associated with the recognition is then used as a discriminating parameter that determines the automatic activation of a feedback process, leading the system back to a block for refining segmentation. This block acts only on the small portions of the text where the recognition cannot be relied on and makes use of blind deconvolution and MRF-based segmentation techniques whose high complexity is greatly reduced when applied to a few subimages of small size. The experimental results highlight that the proposed system performs a very precise segmentation of the characters and then a highly effective recognition of even strongly degraded texts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts E, Korst J (1989) Simulated annealing and Boltzmann machines. Wiley, New York
Aas K, Eikvil L (1996) Text page recognition using grey-level features and hidden Markov models. Patt Recog 29:977-985
Aloimonos Y, Shulman D (1989) Integration of visual modules: an extension of the Marr paradigm. Academic, Boston
Ayers GR, Dainty JG (1988) Iterative blind deconvolution method and its applications. Opt Lett 13:547-549
Avi-Itzhak HI, Diep TA, Garland H (1995) High accuracy optical character recognition using neural networks with centroid dithering. IEEE Trans PAMI 17:218-224
Bedini L, Gerace I, Salerno E, Tonazzini A (1996) Models and algorithms for edge-preserving image reconstruction. In: Hawkes PW (ed) Advances in imaging and electron physics, 97:86-189, Academic, San Diego
Bedini L, Cannata A, Ferraro M, Salerno E, Tonazzini A (1998) Visual module integration for optical flow estimation. In: Theodoridis S, Pitas I, Stouraitis A, Kalouptsidis N (eds) Signal processing IX: Theories and applications. Proceedings of EUSIPCO-98, Rhodes, Greece, 8-11 September 1998, 3:1577-1580
Cohen A (1995) Wavelets and multiscale signal processing. Chapman and Hall, New York
Cohen A, Daubechies I, Jawerth B, Vial P (1993) Multiresolution analysis, wavelets, and fast algorithms on an interval. Comptes Rendus Acad Sci Paris A 316:417-421
Demoment G (1989) Image reconstruction and restoration: overview of common estimation structures and problems. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 37(12):2024-2036
Denker JS, Gardner WR, Graf HP, Henderson D, Howard RE, Hubbard W, Jackel LD, Baird HS, Guyon I (1989) Neural network recognizer for handwritten zip code digits. In: Touretzky D (ed) Advances in neural information processing systems 1 (NIPS ‘88), pp 323-331, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA
Donoho DL (1995) Denoising by soft-tresholding. IEEE Trans Inf Technol 41:613-627
Fukushima K, Miyake S (1982) Neocognitron: a new algorithm for pattern recognition tolerant to deformations and shifts in position. Patt Recog 15:455-469
Gamble E, Poggio T (1987) Visual integration and detection of discontinuities: the key role of intensity edges. MIT-AI Memo No. 970
Geman S, Geman D (1984) Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans PAMI 6:721-740
Kanungo T, Haralick RM, Baird HS, Stuezle W, Madigan D (2000) A statistical, nonparametric methodology for document degradation model validation. IEEE Trans PAMI 22(11):1209-1223
Katsaggelos AK, Lay KT (1991) Maximum likelihood blur identification and image restoration using the EM algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 39:729-732
Kopec GE, Chou PA (1994) Document image decoding using Markov source models. IEEE Trans PAMI 16(6):602-617
Kundur D, Hatzinakos D (1996) Blind image deconvolution. IEEE Signal Process Mag 13(3):43-64
Lagendijk RL, Tekalp AM, Biemond J (1990) Maximum likelihood image and blur identification: a unifying approach. Opt Eng 29:422-435
Li SZ (1995) Markov random field modeling in computer vision. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Liang S, Shridhar M, Ahmadi M (1994) Segmentation of touching characters in printed document recognition. Patt Recog 27:825-840
Nguyen D, Widrow B (1990) Improving the learning speed of two layer neural networks by choosing initial values of the adaptive weights. In: Proceedings of the 1st international joint conference on neural networks, San Diego, June 1990, 3:21-26
Poggio T, Torre V, Koch C (1985) Computational vision and regularization theory. Nature 317:314-319
Rocha J, Pavlidis T (1994) A shape analysis model with applications to a character recognition system. IEEE Trans PAMI 16(4):393-404
Rocha J, Pavlidis T (1995) Character recognition without segmentation. IEEE Trans PAMI 17(9):903-909
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning internal representations by error propagation. In: Rumelhart DE, McClelland JL (eds) Parallel distributed processing, vol 1. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 318-362
Sezan MI, Tekalp AM (1990) Survey of recent developments in digital image restoration. Opt Eng 29(5):393-404
Strang G, Nguyen T (1996) Wavelets and filter banks. Wellesley-Cambridge Press, Wellesley, MA
Taxt T, Flynn PJ, Jain AK (1989) Segmentation of document images. IEEE Trans PAMI 11:1322-1329
Tonazzini A, Bedini L (1999) Character segmentation in highly blurred ancient printed documents. In: Proceedings of the 10th IAPR international conference on image analysis and processing, Venice, Italy, 27-29 September 1999, pp 836-841
Tonazzini A, Bedini L (2000) Segmentation of printed characters in ancient degraded documents through blind image restoration and labeling. Patt Recog Image Anal 10:273-287
Trier OD, Taxt T (1995) Evaluation of binarization methods for document images. IEEE Trans PAMI 17:312-315
Vogl TP, Mangis JK, Rigler AK, Zink WT, Alkon DL (1988) Accelerating the convergence of the back propagation method. Biol Cybern 59:256-264
Yanowitz SD, Bruckstein AM (1989) A new method for image segmentation. Comput Vision Graph Image Process 46:82-95
You Y, Kaveh M (1996) A regularization approach to joint blur identification and image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 5:416-428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received: 4 January 2003, Accepted: 22 June 2003, Published online: 17 November 2003
This work has been supported by the Italian CNR Special Project “Safeguard of Cultural Heritage”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonazzini, A., Vezzosi, S. & Bedini, L. Analysis and recognition of highly degraded printed characters. IJDAR 6, 236–247 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10032-003-0115-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10032-003-0115-y