Abstract
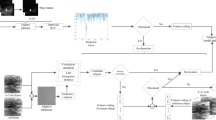
This paper presents a new small target detection method using scale invariant feature. Detecting small targets whose sizes are varying is very important to automatic target detection in infrared search and track (IRST). The conventional spatial filtering methods with fixed sized kernel show limited target detection performance for incoming targets. The scale invariant target detection can be defined as searching for maxima in the 3D (x, y, and scale) representation of an image with the Laplacian function. The scale invariant feature can detect different sizes of targets robustly. Experimental results with real FLIR images show higher detection rate and lower false alarm rate than conventional methods. Furthermore, the proposed method shows very low false alarms in scan-based IR images than conventional filters.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warren RC (2002) Detection of distant airborne targets in cluttered backgrounds in infrared image sequences, Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Australia
Barnett J (1989) Statistical analysis of median subtraction filtering with application to point target detection in infrared backgrounds. Proc SPIE 1050:10–15
Tom VT et al (1993) Morphology-based algorithm for point target detection in infrared backgrounds. Proc SPIE 1954:2–11
Leung H, Young A (2000) Small target detection in clutter using recursive nonlinear prediction. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 36(2):713–718
Deshpande SD et al (1999) Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small-targets. Proc SPIE 3809:74–83
Nitzberg R et al (1979) Spatial filtering techniques for infrared (IR) sensors. Proc SPIE 178:40–58
Schmidt WAC (1990) Modified matched filter for cloud clutter suppression. Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(6):594–600
Gregoris DJ et al (1994) Detection of dim targets in FLIR imagery using multiscale transforms. Proc SPIE 2269:62–71
Boccignone G, Chianese A, Picariello A (2000) Using Renyi’s information and wavelets for target detection: an application to mammograms. Pattern Anal Appl 3(4):303–313
Lindeberg T (1998) Feature detection with automatic scale selection. Int J Comput Vis 30(2):77–116
Ardouin JP (1993) Point source detection based on point spread function symmetry. Opt Eng 32(9):2156–2164
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C Indexing based on scale invariant interest points. In: 8th IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV’01), vol 1, pp 525–531
Kim S, Kweon IS (2006) Biologically motivated perceptual feature: generalized robust invariant feature (ACCV’06), LNCS, vol 3852, pp 305–314
Lowe DG (1999) Object recognition from scale invariant features. In: 7th IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV’99), pp 1150–1157
Se S et al (2001) Vision-based mobile robot localization using scale-invariant features. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA’01), pp 2051–2058
Cadieu C et al (2007) A model of V4 shape selectivity and invariance. J Neurophysiol 98:1733–1750
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Li J, Shen Z, Yang W Small target detection in noisy image sequences. In: IEEE aerospace and electronics conference, vol 2, pp 868–872
da Silva Tavares PJ (2007) Accurate subpixel corner detection on planar camera calibration targets. Opt Eng. doi:10.1117/1.2790926
Gerald CF, Wheatley PO (1994) Applied numerical analysis, 5th edn. Addison-Wesley, New York
Comaniciu D, Meer P (2002) Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 24(5):603–619
Agarwal S, Roth D (2002) Learning a sparse representation for object detection. In: European conference on computer vision (ECCV’02), pp 113–130
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Yeungnam University research grants in 210-A-054-014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Lee, JH. Robust scale invariant target detection using the scale-space theory and optimization for IRST. Pattern Anal Applic 14, 57–66 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-010-0190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-010-0190-x