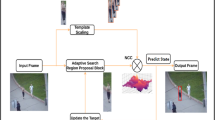
Abstract
A simple and elegant tracking algorithm called Centroid Iteration algorithm is proposed. It employs a new Background-Weighted similarity measure which can greatly reduce the influence from the pixels shared by the target template and background on localization. Experiments demonstrated the Background-Weighted measure performs much better than the other similarity measures like Kullback–Leibler divergence, Bhattacharyya coefficient and so on. It has been proved that this measure can compute the similarity value contribution of each pixel in the target candidate, based on which, a new target search method called Centroid Iteration is constructed. The convergence of the method has been demonstrated. Theory analysis and visual experiments both validated the new algorithm.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2003) Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 25(5):564–577
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2000) Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit II:142–149
Liu T, Chen H (2004) Real-time tracking using trust-region methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 26(3):397–402
Liu T, Chen H (2001) Trust-region methods for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of eighth IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2001. 2:717–722
Boykov Y, Huttenlocher D (2000) Adaptive Bayesian recognition in tracking rigid objects. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2:697–704
Rosales R, Sclaroff S (1999) 3D trajectory recovery for tracking multiple objects and trajectory guided recognition of actions. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, pp 117–123
MacCormick J, Blake A (2000) A probabilistic exclusion principle for tracking multiple objects. Int J Comput Vis 39(1):57–71
Li B, Chellappa R (2000) Simultaneous tracking and verification via sequential posterior estimation. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2:110–117
Bar-Shalom Y, Fortmann T (1988) Tracking and data association. Academic Press
Horn BKP, Schunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17:185–203
Duncan JH, Chou T (1992) On the detection of motion and computation of optical flow. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 14(3):346–352
Lim S, Apostolopoulos JG, Gamal AE (2005) Optical flow estimation using temporally oversampled video. IEEE Trans Image Process 14:1074–1087
Doucet A, Godsill S, Andrieu C (2000) On sequential Monte Carlo sampling methods for Bayesian filtering. Stat Comput 10(3):197–208
Isard M, Blake A (1998) Condensation-conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 29(1):5–28
Arulampalam S, Maskell S, Gordon N, Clapp T (2002) A tutorial on particle filters for on-line non-linear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 50(2):174–189
Julier S, Uhlmann J (1997) A new extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. Proc SPIE 3068:182–193
Yang C, Duraiswami R, Davis L (2005) Efficient mean-shift tracking via a new similarity measure. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:176–183
Wang L, Zhang Y, Feng J (2005) On the Euclidean distance of images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1334–1339
Acknowledgments
The paper is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61105034 and 60905044, Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant No. 20100201120040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, N., Feng, Z. Centroid Iteration algorithm for image tracking. Pattern Anal Applic 15, 163–174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-011-0252-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-011-0252-8