Abstract
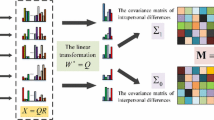
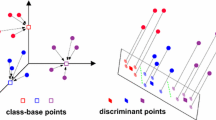
Person Re-Identification (PRe-ID) or person retrieval is a challenging task of computer vision, aiming to identify a specific person across disjoint cameras distributed over different locations. Designing discriminant features parts as well as learning distance metrics are critical issues for improving the performances of the PRe-ID system. To deal with these critical problems, this paper proposes a new semi-supervised subspace approach named Multilinear Cross-view Quadratic Discriminant Analysis based on Cholesky decomposition (MXQDA-CD). In which, a new multidimensional discriminant representation is designed to increase the discrimination between different persons using third order tensor data that combines several features parts. Since the matching process yields heterogeneous scores, resulting from subjects captured through multiple cameras under different conditions, score normalization is applied to map these scores into a common space which led to improved performances of our approach. Experimental results achieved on four challenging person re-identification datasets, namely, PRID450S , CUHK01, GRID and VIPeR, show high competitiveness of the proposed method.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in VIPeRhttps://vision.soe.ucsc.edu/user/login?destination=node%2F178, GRID https://personal.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/~ccloydownloads_qmul_underground_reid.html, PRID450Shttps://www.tugraz.at/institute/icg/research/team-bischof/lrs/downloads/prid450s/ and CUHK01 datasets http://www.ee.cuhk.edu.hk/~xgwang/CUHK_identification.html.
References
Bessaoudi M, Chouchane A, Ouamane A, Boutellaa E (2021) Multilinear subspace learning using handcrafted and deep features for face kinship verification in the wild. Appl Intell 51(6):3534–3547
Chu H, Qi M, Liu H, Jiang J (2019) Local region partition for person re-identification. Multimed Tools Appl 78(19):27067–27083
Deng X, Liao K, Zheng Y, Lin G, Lei H (2021) A deep multi-feature distance metric learning method for pedestrian re-identification. Multimed Tools Appl 80(15):23113–23131
Franco A, Oliveira L (2017) Convolutional covariance features: conception, integration and performance in person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 61:593–609
Gou M, Wu Z, Rates-Borras A, Camps O, Radke RJ et al (2018) A systematic evaluation and benchmark for person re-identification: features, metrics, and datasets. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(3):523–536
Gray D, Tao H (2008) Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 262–275. Springer
Guo R, Li CG, Li Y, Lin J, Guo J (2020) Density-adaptive kernel based efficient reranking approaches for person reidentification. Neurocomputing 411:91–111
Hirzer M, Roth PM, Köstinger M, Bischof H (2012) Relaxed pairwise learned metric for person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 780–793. Springer
Hirzer M, Roth PM, Köstinger M, Bischof H (2012) Relaxed pairwise learned metric for person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 780–793. Springer
Jia J, Ruan Q, Jin Y, An G, Ge S (2020) View-specific subspace learning and re-ranking for semi-supervised person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 108:107568
Klaser A, Marszałek M, Schmid C (2008) A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In: BMVC 2008-19th British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 275–1. British Machine Vision Association
Koestinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Roth PM, Bischof H (2012) Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2288–2295. IEEE
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 25
Laiadi O, Ouamane A, Benakcha A, Taleb-Ahmed A, Hadid A (2020) Tensor cross-view quadratic discriminant analysis for kinship verification in the wild. Neurocomputing 377:286–300
Li H, Xu J, Yu Z, Luo J (2020) Jointly learning commonality and specificity dictionaries for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:7345–7358
Li R, Zhang B, Teng Z, Fan J (2021) A divide-and-unite deep network for person re-identification. Appl Intell 51(3):1479–1491
Li W, Zhao R, Wang X (2012) Human reidentification with transferred metric learning. In: Asian conference on computer vision, pp. 31–44. Springer
Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X (2014) Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 152–159
Li X, Liu L, Lu X (2017) Person reidentification based on elastic projections. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(4):1314–1327
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X, Li SZ (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2197–2206
Liao S, Zhao G, Kellokumpu V, Pietikäinen M, Li SZ (2010) Modeling pixel process with scale invariant local patterns for background subtraction in complex scenes. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1301–1306. IEEE
Liu H, Xiao Z, Fan B, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Jiang G (2021) Prgcn: Probability prediction with graph convolutional network for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 423:57–70
Loy CC, Xiang T, Gong S (2010) Time-delayed correlation analysis for multi-camera activity understanding. Int J Comput Vision 90(1):106–129
Martinel N, Micheloni C, Foresti GL (2015) Kernelized saliency-based person re-identification through multiple metric learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5645–5658
Matsukawa T, Okabe T, Suzuki E, Sato Y (2016) Hierarchical gaussian descriptor for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1363–1372
Moghaddam B, Jebara T, Pentland A (2000) Bayesian face recognition. Pattern Recogn 33(11):1771–1782
Nautsch A, Patino J, Treiber A, Stafylakis T, Mizera P, Todisco M, Schneider T, Evans N (2019) Privacy-preserving speaker recognition with cohort score normalisation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.03454
Ouamane A, Chouchane A, Boutellaa E, Belahcene M, Bourennane S, Hadid A (2017) Efficient tensor-based 2d+ 3d face verification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(11):2751–2762
Prasad MV, Balakrishnan R et al (2022) Spatio-temporal association rule based deep annotation-free clustering (star-dac) for unsupervised person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 122:108287
Prates R, Schwartz WR (2019) Kernel cross-view collaborative representation based classification for person re-identification. J Vis Commun Image Represent 58:304–315
Roth PM, Hirzer M, Köstinger M, Beleznai C, Bischof H (2014) Mahalanobis distance learning for person re-identification. In: Person re-identification, pp. 247–267. Springer
Song J, Yang Y, Song YZ, Xiang T, Hospedales TM (2019) Generalizable person re-identification by domain-invariant mapping network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 719–728
Su C, Zhang S, Xing J, Gao W, Tian Q (2016) Deep attributes driven multi-camera person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 475–491. Springer
Sun C, Wang D, Lu H (2016) Person re-identification via distance metric learning with latent variables. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(1):23–34
Sun J, Kong L, Qu B (2022) Sparse and low-rank joint dictionary learning for person re-identification. Mathematics 10(3):510
Tao D, Guo Y, Yu B, Pang J, Yu Z (2017) Deep multi-view feature learning for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(10):2657–2666
Wei L, Zhang S, Yao H, Gao W, Tian Q (2017) Glad: Global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia, pp. 420–428
Wu L, Shen C, Van Den Hengel A (2017) Deep linear discriminant analysis on fisher networks: A hybrid architecture for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 65:238–250
Wu W, Tao D, Li H, Yang Z, Cheng J (2021) Deep features for person re-identification on metric learning. Pattern Recogn 110:107424
Yan S, Xu D, Yang Q, Zhang L, Tang X, Zhang HJ (2006) Multilinear discriminant analysis for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(1):212–220
Yang X, Wang M, Tao D (2017) Person re-identification with metric learning using privileged information. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(2):791–805
Yang Y, Tiwari P, Pandey HM, Lei Z et al (2021) Pixel and feature transfer fusion for unsupervised cross-dataset person reidentification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Ye M, Shen J, Lin G, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi SC (2021) Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Zhang C, Wu L, Wang Y (2019) Crossing generative adversarial networks for cross-view person re-identification. Neurocomputing 340:259–269
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Wang X (2013) Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3586–3593
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Wang X (2014) Learning mid-level filters for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 144–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest in the submission of this article for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chouchane, A., Bessaoudi, M., Boutellaa, E. et al. A new multidimensional discriminant representation for robust person re-identification. Pattern Anal Applic 26, 1191–1204 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-023-01144-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-023-01144-0