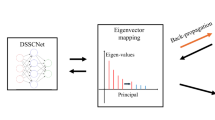
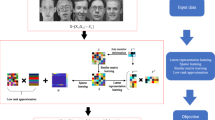
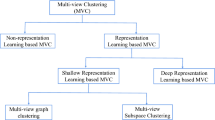
Abstract
High-dimensional data that lies on several subspaces tend to be highly correlated and contaminated by various noises, and its affinities across different subspaces are not always reliable, which impedes the effectiveness of subspace clustering. To alleviate the deficiencies, we propose a novel subspace learning model via adaptive-loss regularized representation learning with latent affinities (ALRLA). Specifically, the robust least square regression with nonnegative constraint is firstly proposed to generate more interpretable reconstruction coefficients in low-dimensional subspace and specify the weighted self-representation capability with adaptive loss norm for better robustness and discrimination. Moreover, an adaptive latent graph learning regularizer with an initialized affinity approximation is considered to provide more accurate and robust neighborhood assignment for low-dimensional representations. Finally, the objective model is solved by an alternating optimization algorithm, with theoretical analyses on its convergence and computational complexity. Extensive experiments on benchmark databases demonstrate that the ALRLA model can produce clearer structured representation under redundant and noisy data environment. It achieves competing clustering performance compared with the state-of-the-art clustering models.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bouhlel N, Feki G, Ben Amar C (2021) Adaptive weighted least squares regression for subspace clustering. Knowl Inf Syst 63(11):2883–2900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-021-01612-1
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends Mach Learn 3(1):1–122. https://doi.org/10.1561/2200000016
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2009) Sparse subspace clustering. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2790–2797. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206547
Fang X, Xu Y, Li X, Fan Z, Liu H, Chen Y (2014) Locality and similarity preserving embedding for feature selection. Neurocomputing 128:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.08.040
Fang X, Xu Y, Li X, Lai Z, Wong WK (2016) Robust semi-supervised subspace clustering via non-negative low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(8):1828–1838. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2454521
Fang X, Zhang R, Li Z, Shao X (2021) Subspace clustering with block diagonal sparse representation. Neural Process Lett 53(6):4293–4312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10597-5
Guo X (2015) Robust subspace segmentation by simultaneously learning data representations and their affinity matrix. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI’15, pp 3547–3553. AAAI Press
Hu H, Lin Z, Feng J, Zhou J (2014) Smooth representation clustering. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3834–3841. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.484
Huang J, Nie F, Huang H (2015) A new simplex sparse learning model to measure data similarity for clustering. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI’15, pp 3569–3575. AAAI Press
Kang Z, Pan H, Hoi SCH, Xu Z (2020) Robust graph learning from noisy data. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(5):1833–1843. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2887094
Kanungo T, Mount D, Netanyahu N, Piatko C, Silverman R, Wu A (2002) An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):881–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017616
Lee DD, Seung HS (1999) Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401(6755):788–791. https://doi.org/10.1038/44565
Li S, Tang C, Liu X, Liu Y, Chen J (2019) Dual graph regularized compact feature representation for unsupervised feature selection. Neurocomputing 331:77–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.060
Li X, Zhang H, Zhang R (2022) Matrix completion via non-convex relaxation and adaptive correlation learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3157083
Lin Z, Chen M, Ma Y (2009) The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. ArXiv abs/1009.5055
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88
Liu J, Chen Y, Zhang J, Xu Z (2014) Enhancing low-rank subspace clustering by manifold regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(9):4022–4030. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2343458
Lu C, Feng J, Lin Z, Mei T, Yan S (2019) Subspace clustering by block diagonal representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(2):487–501. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2794348
Lu CY, Min H, Zhao ZQ, Zhu L, Huang DS, Yan S (2012) Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer vision–ECCV 2012. Springer, Berlin, pp 347–360
Lu X, Wang Y, Yuan Y (2013) Graph-regularized low-rank representation for destriping of hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51(7):4009–4018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2012.2226730
Luo M, Chang X, Nie L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG, Zheng Q (2018) An adaptive semisupervised feature analysis for video semantic recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(2):648–660. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2647904
Luxburg U (2007) A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat Comput 17(4):395–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z
Maier M, Luxburg Uv, Hein M (2008) Influence of graph construction on graph-based clustering measures. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on neural information processing systems, NIPS’08, pp 1025–1032. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA
Nie F, Huang H, Cai X, Ding C (2010)Efficient and robust feature selection via joint \(\ell \)2,1-norms minimization. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on neural information processing systems, Vol 2, NIPS’10, pp 1813–1821. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA
Nie F, Wang H, Huang H, Ding C (2013)Adaptive loss minimization for semi-supervised elastic embedding. In: Proceedings of the twenty-third international joint conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI ’13, pp 1565–1571. AAAI Press
Nie F, Wang X, Huang H (2014)Clustering and projected clustering with adaptive neighbors. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’14, pp 977–986. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623726
Nie F, Wang X, Jordan MI, Huang H (2016) The constrained laplacian rank algorithm for graph-based clustering. In: Proceedings of the thirtieth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI’16, pp 1969–1976. AAAI Press
Qian M, Zhai C (2015) Joint adaptive loss and \(l_2/l_0\)-norm minimization for unsupervised feature selection. In: 2015 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), pp 1–8 https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2015.7280307
Roweis ST, Saul LK (2000) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290(5500):2323–2326. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5500.2323
Shah SA, Koltun V (2017) Robust continuous clustering. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(37):9814–9819. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700770114
Shi J, Malik J (2000) Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(8):888–905. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.868688
Wang J, Shi D, Cheng D, Zhang Y, Gao J (2016) Lrsr: low-rank-sparse representation for subspace clustering. Neurocomputing 214:1026–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.07.015
Wang L, Huang J, Yin M, Cai R, Hao Z (2020) Block diagonal representation learning for robust subspace clustering. Inf Sci 526:54–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.103
Wei L, Zhang F, Chen Z, Zhou R, Zhu C (2022) Subspace clustering via adaptive least square regression with smooth affinities. Knowl-Based Syst 239:107950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107950
Wen J, Fang X, Xu Y, Tian C, Fei L (2018) Low-rank representation with adaptive graph regularization. Neural Netw 108:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.08.007
Wen J, Zhang B, Xu Y, Yang J, Han N (2018) Adaptive weighted nonnegative low-rank representation. Pattern Recogn 81:326–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.04.004
Wu Z, Yin M, Zhou Y, Fang X, Xie S (2018) Robust spectral subspace clustering based on least square regression. Neural Process Lett 48(3):1359–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9726-z
Xu J, An W, Zhang L, Zhang D (2019) Sparse, collaborative, or nonnegative representation: which helps pattern classification? Pattern Recogn 88:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.12.023
Yang J, Liang J, Wang K, Rosin PL, Yang MH (2020) Subspace clustering via good neighbors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(6):1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913863
Yang M, Zhang L, Yang J, Zhang D (2013) Regularized robust coding for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(5):1753–1766. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2235849
Yang Y, Shen HT, Nie F, Ji R, Zhou X (2011) Nonnegative spectral clustering with discriminative regularization. In: Proceedings of the twenty-fifth aaai conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI’11, pp 555–560. AAAI Press
Yi Y, Wang J, Zhou W, Fang Y, Kong J, Lu Y (2019) Joint graph optimization and projection learning for dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recogn 92:258–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.03.024
Yin M, Gao J, Lin Z (2016) Laplacian regularized low-rank representation and its applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(3):504–517. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2462360
Yin M, Wu Z, Zeng D, Li P, Xie S (2018) Sparse subspace clustering with jointly learning representation and affinity matrix. J Franklin Inst 355(8):3795–3811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.02.024
Yin M, Xie S, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Gao J (2018) Subspace clustering via learning an adaptive low-rank graph. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(8):3716–3728. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2825647
Zheng J, Lu C, Yu H, Wang W, Chen S (2018) Iterative reconstrained low-rank representation via weighted nonconvex regularizer. IEEE Access 6:51693–51707. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870371
Zhuang L, Gao S, Tang J, Wang J, Lin Z, Ma Y, Yu N (2015) Constructing a nonnegative low-rank and sparse graph with data-adaptive features. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3717–3728. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2441632
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province, China (No. 2021JM-339, 2020JQ-647) and Shaanxi Province Key Research and Development Program (No. 2022ZDLSF07-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, K., Zhu, L., Liu, Z. et al. Subspace clustering via adaptive-loss regularized representation learning with latent affinities. Pattern Anal Applic 27, 15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-024-01226-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-024-01226-7