Abstract
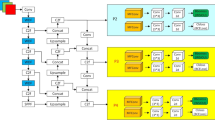
UAV small object detection has essential applications in the military, search and rescue, and smart cities, providing critical support for target recognition in complex environments. However, the existing UAV small object detection models usually have many parameters and high computational complexity, limiting their deployment and application in practical scenarios to some extent. In this study, we propose a UAV detector with Lightweight Multidimensional Feature Network (LMF-UAV), aiming to reduce the number of parameters and computation of the model while guaranteeing accuracy, which constructs the Lightweight Multidimensional Feature Network (LMF-Net) for lightweight feature extraction, and Efficient Expressive Network (EENet) for efficient feature fusion. Neural architecture search utilizes the Dual-branch Cross-stage Universal Inverted Bottleneck to enable the network to select the most suitable structure at different layers according to requirements, thereby improving the computational efficiency of LMF-Net while maintaining performance. EENet uses the Channel-wise Partial Convolution Stage to reduce redundant computation and memory access and fuse spatial features more effectively. First, LMF-Net extracts features from the images collected by UAV and obtains three multi-scale feature maps. Second, EENet performs feature fusion on three feature maps of different scales to obtain three feature representatives. Finally, the decoupled head detects the feature map and outputs the final result. The bounding box regression loss function uses Wasserstein distance to evaluate box similarity and enhance the model’s sensitivity to small targets. The experimental results demonstrate that on the VisDrone dataset, mAP50-95 of LMF-UAV reaches 24.6%, while parameters are only 14.7M, FLOPs are only 61.8G, showing a good balance between performance and efficiency.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data, models, and code generated and utilized in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
The codes will upload on https://github.com/yangwygithub/PaperCode/tree/main/, Branch: WenyuanYang_LMF-UAV.
References
Xue Y, Jin G, Shen T, Tan L, Wang N, Gao J, Wang L (2023) Smalltrack: Wavelet pooling and graph enhanced classification for uav small object tracking. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 5:9
Xue Y, Jin G, Shen T, Tan L, Wang L (2023) Template-guided frequency attention and adaptive cross-entropy loss for uav visual tracking. Chin J Aeronaut 36(9):299–312
Xue Y, Jin G, Shen T, Tan L, Yang J, Hou X (2022) Mobiletrack: Siamese efficient mobile network for high-speed uav tracking. IET Image Proc 16(12):3300–3313
Karanwal S (2024) Discriminative binary pattern descriptor for face recognition. Pattern Anal Appl 27(3):1–25
Thomine S, Snoussi H (2024) Dual model knowledge distillation for industrial anomaly detection. Pattern Anal Appl 27(3):77
Wang Z, Liu Y, Lei L, Shi P (2024) Smoking-yolov8: a novel smoking detection algorithm for chemical plant personnel. Pattern Anal Appl 27(3):72
Xue Y, Jin G, Shen T, Tan L, Wang N, Gao J, Wang L (2024) Consistent representation mining for multi-drone single object tracking. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol
Xue Y, Shen T, Jin G, Tan L, Wang N, Wang L, Gao J (2024) Handling occlusion in uav visual tracking with query-guided redetection. IEEE Trans Instr Meas
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2:8
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2961–2969
Cai Z, Vasconcelos N (2018) Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6154–6162
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu CY, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21–37
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A (2016) You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 779–788
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2017) Yolo9000: better, faster, stronger. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7263–7271
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2018) Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767
Bochkovskiy A, Wang CY, Liao HYM (2020) Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934
Jocher G YOLOv5 by Ultralytics. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3908559 . https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
Li C, Li L, Jiang H, Weng K, Geng Y, Li L, Ke Z, Li Q, Cheng M, Nie W, et al (2022) Yolov6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.02976
Wang CY, Bochkovskiy A, Liao HYM (2023) Yolov7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7464–7475
Jocher G, Chaurasia A, Qiu J, Ultralytics YOLO. https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
Wang CY, Yeh IH, Liao HYM (2024) Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.13616
Wang A, Chen H, Liu L, Chen K, Lin Z, Han J, Ding G (2024) Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14458
Lin TY, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988
Sayed AN, Ramahi OM, Shaker G (2024) Rdiws: An efficient beamforming-based method for uav detection and classification. IEEE Sens J 24(9):15230–15240
Hu N, Yang J, Pan W, Xu Q, Shao S, Tang Y (2024) Uav detection based on the variance of higher-order cumulants. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 5:1–14
Hao C, Zhang H, Song W, Liu F, Wu E (2024) Slinet: Slicing-aided learning for small object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 31:790–794
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6848–6856
Ma N, Zhang X, Zheng HT, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 116–131
Han K, Wang Y, Tian Q, Guo J, Xu C, Xu C (2020) Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1580–1589
Howard AG, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, Andreetto M, Adam H (2017) Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen LC (2018) Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520
Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen LC, Chen B, Tan M, Wang W, Zhu Y, Pang R, Vasudevan V, et al (2019) Searching for mobilenetv3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1314–1324
Qin D, Leichner C, Delakis M, Fornoni M, Luo S, Yang F, Wang W, Banbury C, Ye C, Akin, B, et al (2024) Mobilenetv4-universal models for the mobile ecosystem. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.10518
Chen J, Kao Sh, He H, Zhuo W, Wen S, Lee CH, Chan SHG (2023) Run, don’t walk: chasing higher flops for faster neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12021–12031
Girshick R (2015) Fast r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1440–1448
Yu J, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Cao Z, Huang T (2016) Unitbox: An advanced object detection network. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 516–520
Rezatofighi H, Tsoi N, Gwak J, Sadeghian A, Reid I, Savarese S (2019) Generalized intersection over union: a metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 658–666
Zheng Z, Wang P, Liu W, Li J, Ye R, Ren D (2020) Distance-iou loss: faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 12993–13000
Gevorgyan Z (2022) Siou loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12740
Wang J, Xu C, Yang W, Yu L (2021) A normalized gaussian wasserstein distance for tiny object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.13389
Song G, Du H, Zhang X, Bao F, Zhang Y (2024) Small object detection in unmanned aerial vehicle images using multi-scale hybrid attention. Eng Appl Artif Intell 128:107455
Jiang L, Yuan B, Du J, Chen B, Xie H, Tian J, Yuan Z (2024) Mffsodnet: Multi-scale feature fusion small object detection network for uav aerial images. IEEE Trans Instr Meas
Li Z, He Q, Yang W (2024) E-fpn: an enhanced feature pyramid network for uav scenarios detection. Vis Comput 3:1–19
Li X, Wang W, Wu L, Chen S, Hu X, Li J, Tang J, Yang J (2020) Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:21002–21012
Du D, Zhu P, Wen L, Bian X, Lin H, Hu Q, Peng T, Zheng J, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al (2019) Visdrone-det2019: The vision meets drone object detection in image challenge results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops
Suo J, Wang T, Zhang X, Chen H, Zhou W, Shi W (2023) Hit-uav: A high-altitude infrared thermal dataset for unmanned aerial vehicle-based object detection. Scientific Data 10(1):227
Du D, Qi Y, Yu H, Yang Y, Duan K, Li G, Zhang W, Huang Q, Tian Q (2018) The unmanned aerial vehicle benchmark: Object detection and tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 370–386
Sun Y, Cao B, Zhu P, Hu Q (2022) Drone-based rgb-infrared cross-modality vehicle detection via uncertainty-aware learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(10):6700–6713
Wang Z, Li C, Xu H, Zhu X (2024) Mamba yolo: Ssms-based yolo for object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.05835
Li Y, Chen Y, Wang N, Zhang Z (2019) Scale-aware trident networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6054–6063
Zhu C, He Y, Savvides M (2019) Feature selective anchor-free module for single-shot object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 840–849
Zhang S, Chi C, Yao Y, Lei Z, Li SZ (2020) Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9759–9768
Zhou X, Wang D, Krähenbühl P (2019) Objects as points. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07850
Tian Z, Shen C, Chen H, He T (2020) Fcos: A simple and strong anchor-free object detector. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(4):1922–1933
Chen Z, Yang C, Li Q, Zhao F, Zha ZJ, Wu F (2021) Disentangle your dense object detector. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 4939–4948
Feng C, Zhong Y, Gao Y, Scott MR, Huang W (2021) Tood: Task-aligned one-stage object detection. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3490–3499
Zhang H, Wang Y, Dayoub F, Sunderhauf N (2021) Varifocalnet: An iou-aware dense object detector. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8514–8523
Zhao Y, Lv W, Xu S, Wei J, Wang G, Dang Q, Liu Y, Chen J (2024) Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16965–16974
Ge Z, Liu S, Wang F, Li Z, Sun J (2021) Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.08430
Cai Z, Hong Z, Yu W, Zhang W (2023) Cnxresnet: A light-weight backbone based on pp-yoloe for drone-captured scenarios. In: 2023 8th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, pp. 460–464
Ding K, Li X, Guo W, Wu L (2022) Improved object detection algorithm for drone-captured dataset based on yolov5. In: 2022 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering, pp. 895–899
Hao C, Zhang H, Song W, Liu F, Wu E (2024) Slinet: Slicing-aided learning for small object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett
Su G, Zhu C (2024) An improved yolov8 algorithm for aerial image detection. In: 2024 7th International Conference on Computer Information Science and Application Technology, pp. 56–61
Jiang W, Wang L, Mao G, Sun M, Dharejo FA, Mallah GA (2023) Lf-yolov7: Improved yolov7 based on lightweight modules and novel feature fusion for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. In: 2023 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence, pp. 1152–1159
Wang J, Liu W, Zhang W, Liu B (2022) Lv-yolov5: A light-weight object detector of vit on drone-captured scenarios. In: 2022 16th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, vol. 1, pp. 178–183
Yang Y, Niu Z, Cao Z, Zhao M (2024) Small target detection with context fusion learning. In: 2024 9th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, pp. 61–66
Yang Y, Gao X, Wang Y, Song S (2022) Vamyolox: an accurate and efficient object detection algorithm based on visual attention mechanism for uav optical sensors. IEEE Sens J 23(11):11139–11155
Shi T, Ding Y, Zhu W (2023) Yolov5s_2e: improved yolov5s for aerial small target detection. IEEE Access
Perreault H, Bilodeau GA, Saunier N, Héritier M (2021) Ffavod: feature fusion architecture for video object detection. Pattern Recogn Lett 151:294–301
Perreault H, Bilodeau GA, Saunier N, Héritier M (2020) Spotnet: Self-attention multi-task network for object detection. In: 2020 17th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, pp. 230–237
Chen PY, Chang MC, Hsieh JW, Chen YS (2021) Parallel residual bi-fusion feature pyramid network for accurate single-shot object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:9099–9111
Chen L, Liu C, Li W, Xu Q, Deng H (2024) Dtssnet: dynamic training sample selection network for uav object detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 62(2):1–16
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62376114, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.12101289, the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province under Grant No.2022J01891. And it is supported by the Institute of Meteorological Big Data-Digital Fujian, and Fujian Key Laboratory of Data Science and Statistics (Minnan Normal University), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential Conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., He, Q. & Li, Z. A lightweight multidimensional feature network for small object detection on UAVs. Pattern Anal Applic 28, 29 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-024-01389-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-024-01389-3