Abstract:
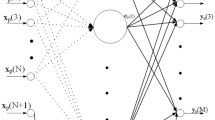
We introduce a mechanism for constructing and training a hybrid architecture of projection-based units and radial basis functions. In particular, we introduce an optimisation scheme which includes several steps and assures a convergence to a useful solution. During network architecture construction and training, it is determined whether a unit should be removed or replaced. The resulting architecture often has a smaller number of units compared with competing architectures. A specific overfitting resulting from shrinkage of the RBF radii is addressed by introducing a penalty on small radii. Classification and regression results are demonstrated on various benchmark data sets and compared with several variants of RBF networks [1,2]. A striking performance improvement is achieved on the vowel data set [3].
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 03 November 2000, Received in revised form: 25 October 2001, Accepted: 04 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, S., Intrator, N. A Hybrid Projection-based and Radial Basis Function Architecture: Initial Values and Global Optimisation. Pattern Anal Appl 5, 113–120 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100440200010
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100440200010