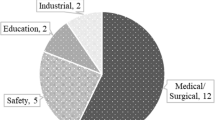
Abstract
Virtual reality (VR) provides the capability to train individuals to deal with complex situations by immersing them in a virtual environment. VR-based training has been used in many domains; however, in order to be effective, the training should be adapted based on user’s capabilities, performance, and needs. This study provided a framework for adaptive VR-based training including performance measures, adaptive logic, and adaptive variables. A systematic review of literature was conducted using Compendex, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases to identify the adaptive VR-based training approaches used in different domains. Results revealed that adaptive VR-based training can be improved by using real-time kinematic/kinetic data and physiological measures from the user, incorporating offline measures such as trainee’s profile information, providing adaptations on controlled elements in the simulation, adjusting feedback content, type, and timing, and using reinforcement learning algorithms. The recommendations provided in this study need to be further validated using longitudinal studies comparing adaptive and non-adaptive training approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abdessalem HB, Frasson C (2017) Real-time brain assessment for adaptive virtual reality game: a neurofeedback approach. Paper presented at the international conference on brain function assessment in learning
Adamovich SV, Fluet GG, Mathai A, Qiu Q, Lewis J, Merians AS (2009) Design of a complex virtual reality simulation to train finger motion for persons with hemiparesis: a proof of concept study. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation 6(1):28
Amat AZ, Swanson A, Weitlauf A, Warren Z, Sarkar N (2018) Design of an assistive avatar in improving eye gaze perception in children with ASD during virtual interaction. Paper presented at the international conference on universal access in human-computer interaction
Antonacopoulou EP (2001) The paradoxical nature of the relationship between training and learning. J Manage Stud 38(3):327–350
Aoki H, Oman CM, Buckland DA, Natapoff A (2008) Desktop-VR system for preflight 3D navigation training. Acta Astronaut 63(7–10):841–847
Barzilay O, Wolf A (2009) An adaptive virtual biofeedback system for neuromuscular rehabilitation. Paper presented at the world congress on medical physics and biomedical engineering, 7–12 Sept 2009, Munich, Germany
Barzilay O, Wolf A (2013) Adaptive rehabilitation games. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23(1):182–189
Bayart B, Pocheville A, Kheddar A (2005) An adaptive haptic guidance software module for i-touch: example through a handwriting teaching simulation and a 3D maze. Paper presented at the IEEE international workshop on haptic audio visual environments and their applications
Bekele E, Young M, Zheng Z, Zhang L, Swanson A, Johnston R, Davidson J, Warren Z, Sarkar N (2013) A step towards adaptive multimodal virtual social interaction platform for children with autism. Paper presented at the international conference on universal access in human-computer interaction
Bhagat KK, Liou W-K, Chang C-Y (2016) A cost-effective interactive 3D virtual reality system applied to military live firing training. Virtual Reality 20(2):127–140
Bian D, Wade J, Warren Z, Sarkar N (2016) Online engagement detection and task adaptation in a virtual reality based driving simulator for autism intervention. Paper presented at the international conference on universal access in human-computer interaction
Billings D (2012) Efficacy of adaptive feedback strategies in simulation-based training. Military Psychology 24(2):114
Birk MV, Mandryk RL (2019) Improving the efficacy of cognitive training for digital mental health interventions through avatar customization: crowdsourced quasi-experimental study. Journal of medical Internet research 21(1):e10133
Blankendaal RA, Bosse T (2018) Using run-time biofeedback during virtual agent-based aggression de-escalation training. Paper presented at the international conference on practical applications of agents and multi-agent systems
Bosse T, Gerritsen C, de Man, J, Tolmeijer S (2014a) Adaptive training for aggression de-escalation. Paper presented at the artificial life and intelligent agents symposium
Bosse T, Man JD, Gerritsen C (2014b) Agent-based simulation as a tool for the design of a virtual training environment. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/WIC/ACM international joint conferences on web intelligence (WI) and intelligent agent technologies (IAT), vol 03
Bulu ST (2012) Place presence, social presence, co-presence, and satisfaction in virtual worlds. Comput Educ 58(1):154–161
Cameirão MS, i Badia SB, Oller ED, Verschure PF (2008) Using a multi-task adaptive VR system for upper limb rehabilitation in the acute phase of stroke. Paper presented at the virtual rehabilitation, 2008
Cameirão MS, i Badia SB, Oller ED, Verschure PF (2010) Neurorehabilitation using the virtual reality based rehabilitation gaming system: methodology, design, psychometrics, usability and validation. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation 7(1):48
Carpentier K, Lourdeaux D (2013) Generation of learning situations according to the learner’s profile within a virtual environment. Paper presented at the international conference on agents and artificial intelligence
Cesta A, Cortellessa G, De Benedictis R (2014) Training for crisis decision making–an approach based on plan adaptation. Knowl-Based Syst 58:98–112
Chan CL, Ngai EK, Leung PK, Wong S (2010) Effect of the adapted virtual reality cognitive training program among Chinese older adults with chronic schizophrenia: a pilot study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry: A journal of the psychiatry of late life and allied sciences 25(6):643–649
Chemuturi R, Amirabdollahian F, Dautenhahn K (2013) Adaptive training algorithm for robot-assisted upper-arm rehabilitation, applicable to individualised and therapeutic human-robot interaction. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation 10(1):102
Chen Y, Baran M, Sundaram H, Rikakis T (2011) A low cost, adaptive mixed reality system for home-based stroke rehabilitation. Paper presented at the engineering in medicine and biology society, EMBC, 2011 annual international conference of the IEEE
Christie R (2001) The effectiveness of driver training as a road safety measure: an international review of the literature. Paper presented at the road safety research, policing and education conference, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Cosic K, Popovic S, Kostovic I, Judas M (2010) Virtual reality adaptive stimulation of limbic networks in the mental readiness training. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 154:14–19
Cox DJ, Brown T, Ross V, Moncrief M, Schmitt R, Gaffney G, Reeve R (2017) Can youth with autism spectrum disorder use virtual reality driving simulation training to evaluate and improve driving performance? An exploratory study. J Autism Dev Disord 47(8):2544–2555
Dey A, Chatourn A, Billinghurst M (2019) Exploration of an EEG-based cognitively adaptive training system in virtual reality. Paper presented at the 2019 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR)
Dhiman A, Solanki D, Bhasin A, Bhise A, Das A, Lahiri U (2016) Design of adaptive haptic-enabled virtual reality based system for upper limb movement disorders: a usability study. Paper presented at the 2016 6th IEEE international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics (BioRob)
Feidakis M (2016) A review of emotion-aware systems for e-learning in virtual environments. Formative assessment, learning data analytics and gamification. Elsevier, pp 217–242
Fricoteaux L, Thouvenin IM, Olive J (2011) Adaptive Guiding for Fluvial Navigation Training in Informed Virtual Environment. Paper presented at the Joint VR conference of euroVR and EGVE, 2011
Fricoteaux L, Thouvenin I, Olive J, George P (2012) Evidential network with conditional belief functions for an adaptive training in informed virtual environment. In: Belief functions: theory and applications. Springer, pp 417–424
Fricoteaux L, Thouvenin I, Mestre D (2014) GULLIVER: a decision-making system based on user observation for an adaptive training in informed virtual environments. Eng Appl Artif Intell 33:47–57
García-Vergara S, Chen Y-P, Howard AM (2013) Super pop VR TM: An adaptable virtual reality game for upper-body rehabilitation. Paper presented at the international conference on virtual, augmented and mixed reality
Gerbaud S, Gouranton V, Arnaldi B (2009) Adaptation in collaborative virtual environments for training. Paper presented at the International Conference on Technologies for E-Learning and Digital Entertainment
Grimm F, Naros G, Gharabaghi A (2016) Closed-loop task difficulty adaptation during virtual reality reach-to-grasp training assisted with an exoskeleton for stroke rehabilitation. Frontiers in neuroscience 10:518
Gurusamy K, Aggarwal R, Palanivelu L, Davidson B (2008) Systematic review of randomized controlled trials on the effectiveness of virtual reality training for laparoscopic surgery. Br J Surg 95(9):1088–1097
Gurusamy KS, Aggarwal R, Palanivelu L, Davidson BR (2009) Virtual reality training for surgical trainees in laparoscopic surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006575.pub2
Hancock P, Nourbakhsh I, Stewart J (2019) On the future of transportation in an era of automated and autonomous vehicles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 201805770
Heloir A, Nunnari F, Haudegond S, Havrez C, Lebrun Y, Kolski C (2014) Design and evaluation of a self adaptive architecture for upper-limb rehabilitation. Paper presented at the international workshop on ICTs for improving patients rehabilitation research techniques
Hernández Y, Ramírez MP (2016) Adaptive and blended learning for electrical operators training. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 8th international conference on computer supported education
Huang X, Naghdy F, Naghdy G, Du H, Todd C (2018) The combined effects of adaptive control and virtual reality on robot-assisted fine hand motion rehabilitation in chronic stroke patients: a case study. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 27(1):221–228
i Badia SB, Morgade AG, Samaha H, Verschure P (2013) Using a hybrid brain computer interface and virtual reality system to monitor and promote cortical reorganization through motor activity and motor imagery training. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 21(2):174–181
Jeelani I, Han K, Albert A (2017) Development of immersive personalized training environment for construction workers. Computing in civil engineering 2017, pp 407–415
Johnson A, Tang Y, Franzwa C (2014) kNN-based adaptive virtual reality game system. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 11th IEEE international conference on networking, sensing and control
Jones D, Dechmerowski S (2016) Measuring stress in an augmented training environment: approaches and applications. Paper presented at the international conference on augmented cognition
Jones N, Kiely J, Suraci B, Collins D, De Lorenzo D, Pickering C, Grimaldi K (2016) A genetic-based algorithm for personalized resistance training. Biology of sport 33(2):117
Kalyuga S, Ayres P, Chandler P, Sweller J (2003) Expertise reversal effect. Educ Psychol 38:23–31
Kelley CR (1969) What is adaptive training? Hum Factors 11(6):547–556
Kizony R, Katz N, Weiss PL (2003) Adapting an immersive virtual reality system for rehabilitation. The Journal of Visualization and Computer Animation 14(5):261–268
Knowles M (1990) The adult learner: A neglected species. Houston. Gulf Publishing, TX
Koenig A, Novak D, Omlin X, Pulfer M, Perreault E, Zimmerli L, Mihelj M, Riener R (2011) Real-time closed-loop control of cognitive load in neurological patients during robot-assisted gait training. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 19(4):453–464
Kommalapati R, Michmizos KP (2016) Virtual reality for pediatric neuro-rehabilitation: Adaptive visual feedback of movement to engage the mirror neuron system. Paper presented at the 2016 38th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC)
Kühnapfel U, Cakmak HK, Maaß H (2000) Endoscopic surgery training using virtual reality and deformable tissue simulation. Computers & graphics 24(5):671–682
Kumar D, González A, Das A, Dutta A, Fraisse P, Hayashibe M, Lahiri U (2018) Virtual reality-based center of mass-assisted personalized balance training system. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 5:85
Lafond I, Qiu Q, Adamovich S (2010) Design of a customized virtual reality simulation for retraining upper extremities after stroke. Paper presented at the bioengineering conference, Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 36th annual northeast
Lahiri U, Bekele E, Dohrmann E, Warren Z, Sarkar N (2013) Design of a virtual reality based adaptive response technology for children with autism. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 21(1):55–64
Lang Y, Wei L, Xu F, Zhao Y, Yu L-F (2018) Synthesizing personalized training programs for improving driving habits via virtual reality. Paper presented at the 2018 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR)
Larsen CR, Soerensen JL, Grantcharov TP, Dalsgaard T, Schouenborg L, Ottosen C, Schroeder TV, Ottesen BS (2009) Effect of virtual reality training on laparoscopic surgery: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 338:b1802
Liu P, Jiang G, Liu Y, An M (2016) The utility evaluation of the astronaut virtual training system in layout familiarization training. Paper presented at the 2016 6th international conference on IT convergence and security (ICITCS)
Loftin R, Kenney P (1994) Virtual environments in training: NASA’s hubble space telescope mission. 16th interservice. Paper presented at the industry training systems & education conference, Orlando, FL
Lopez-Garate M, Lozano-Rodero A, Matey L (2008) An adaptive and customizable feedback system for VR-based training simulators. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 7th international joint conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems, vol 3
Luo L, Yin H, Cai W, Lees M, Zhou S (2013) Interactive scenario generation for mission-based virtual training. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 24(3–4):345–354
Ma M, Bechkoum K (2008) Serious games for movement therapy after stroke. Paper presented at the 2008 IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics
Ma M, McNeill M, Charles D, McDonough S, Crosbie J, Oliver L, McGoldrick C (2007) Adaptive virtual reality games for rehabilitation of motor disorders. Paper presented at the international conference on universal access in human-computer interaction
Magerko B, Wray R, Holt L, Stensrud B (2005) Improving interactive training through individualized content and increased engagement. Paper presented at the the interservice/industry training, simulation & education conference (I/ITSEC)
Malik H, Larue GS, Rakotonirainy A, Maire F (2015) Fuzzy logic to evaluate driving maneuvers: an integrated approach to improve training. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 16(4):1728–1735
Mariani A, Pellegrini E, Enayati N, Kazanzides P, Vidotto M, De Momi E (2018) Design and evaluation of a performance-based adaptive curriculum for robotic surgical training: a pilot study. Paper presented at the 2018 40th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC)
Matthias H, Beckhaus S (2012) Adaptive generation of emotional impact using enhanced virtual environments. Presence Teleoperators and Virtual Environments 21(1):96–116
Merians AS, Tunik E, Adamovich SV (2009) Virtual reality to maximize function for hand and arm rehabilitation: exploration of neural mechanisms. Studies in health technology and informatics 145:109
Milgram P, Kishino F (1994) A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems 77(12):1321–1329
Mohamed F, Abdeslam J, Lahcen EB (2017) Personalization of learning activities within a virtual environment for training based on fuzzy logic theory. International association for development of the information society
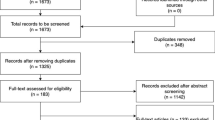
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS medicine 6(7):e1000097
Mourning R, Tang Y (2016) Virtual reality social training for adolescents with high-functioning autism. Paper presented at the 2016 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC)
NAE (2017) NAE grand challenges for engineering. Retrieved from http://www.engineeringchallenges.org/File.aspx?id=11574&v=34765dff. Accessed Mar 2019
Nazemi K, Bhatti N, Godehardt E, Hornung C (2007) Adaptive tutoring in virtual learning worlds. Paper presented at the EdMedia+ innovate learning
NIH (2019) Rehabilitation. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/rehabilitation.html. Accessed Dec 2019
Nirme J, Duff A, Verschure PF (2011) Adaptive rehabilitation gaming system: on-line individualization of stroke rehabilitation. Paper presented at the 2011 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society
Nowak K (2001) Defining and differentiating copresence, social presence and presence as transportation. Paper presented at the presence 2001 conference, Philadelphia, PA
Ohno N, Kageyama A (2007) Scientific visualization of geophysical simulation data by the CAVE VR system with volume rendering. Phys Earth Planet Inter 163(1–4):305–311
Padilla-Castaneda MA, Sotgiu E, Frisoli A, Bergamasco M, Orsini P, Martiradonna A, Olivieri S, Mazzinghi G, Laddaga C (2013) A virtual reality system for robotic-assisted orthopedic rehabilitation of forearm and elbow fractures. Paper presented at the 2013 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems
Pallavicini F, Argenton L, Toniazzi N, Aceti L, Mantovani F (2016) Virtual reality applications for stress management training in the military. Aerospace medicine and human performance 87(12):1021–1030
Peck RC (2011) Do driver training programs reduce crashes and traffic violations?—A critical examination of the literature. IATSS research 34(2):63–71
Peretz C, Korczyn AD, Shatil E, Aharonson V, Birnboim S, Giladi N (2011) Computer-based, personalized cognitive training versus classical computer games: a randomized double-blind prospective trial of cognitive stimulation. Neuroepidemiology 36(2):91–99
Pham T, Roland L, Benson KA, Webster RW, Gallagher AG, Haluck RS (2005) Smart tutor: a pilot study of a novel adaptive simulation environment. Studies in health technology and informatics 111:385–389
Popovic S, Horvat M, Kukolja D, Dropuljic B, Cosic K (2009) Stress inoculation training supported by physiology-driven adaptive virtual reality stimulation
Pozueco L, Tuero AG, Pañeda XG, Melendi D, García R, Pañeda AG, Rionda A, Díaz G, Mitre M (2015) Adaptive learning for efficient driving in urban public transport. Paper presented at the computer, information and telecommunication systems (CITS), 2015 international conference on
Pradhan A, Fisher D, Pollatsek A (2006) Risk perception training for novice drivers: evaluating duration of effects of training on a driving simulator. Transp Res Record J Transp Res Board 1969:58–64
Rezazadeh IM, Wang X, Firoozabadi M, Golpayegani MRH (2011) Using affective human–machine interface to increase the operation performance in virtual construction crane training system: a novel approach. Automation in Construction 20(3):289–298
Ritter FE, Baxter G, Kim JW, Srinivasmurthy S (2013) Learning and retention. In: Lee JD, Kirlik A (eds) The Oxford handbook of cognitive engineering. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 125–142
Roenker DL, Cissell GM, Ball KK, Wadley VG, Edwards JD (2003) Speed-of-processing and driving simulator training result in improved driving performance. Hum Factors 45(2):218–233
Rossol N, Cheng I, Bischof WF, Basu A (2011) A framework for adaptive training and games in virtual reality rehabilitation environments. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 10th international conference on virtual reality continuum and its applications in industry
Sarasin LC (1999) Learning style perspectives: impact in the classroom. Atwood Pub, Cambridge
Saurav K, Dash A, Solanki D, Lahiri U (2018) Design of a VR-based upper limb gross motor and fine motor task platform for post-stroke survivors. Paper presented at the 2018 IEEE/ACIS 17th international conference on computer and information science (ICIS)
Schatz S, Wray R, Folsom-Kovarik J, Nicholson D (2012) Adaptive perceptual training in a virtual environment. Paper presented at the proceedings of the human factors and ergonomics society annual meeting
Schwaninger A, Hofer F, Wetter OE (2007) Adaptive computer-based training increases on the job performance of x-ray screeners. Paper presented at the security technology, 2007 41st annual IEEE international Carnahan conference on
Serge SR, Priest HA, Durlach PJ, Johnson CI (2013) The effects of static and adaptive performance feedback in game-based training. Comput Hum Behav 29(3):1150–1158
Sharma DA, Chevidikunnan MF, Khan FR, Gaowgzeh RA (2016) Effectiveness of knowledge of result and knowledge of performance in the learning of a skilled motor activity by healthy young adults. Journal of physical therapy science 28(5):1482–1486
Sharples S, Cobb S, Moody A, Wilson JR (2008) Virtual reality induced symptoms and effects (VRISE): comparison of head mounted display (HMD), desktop and projection display systems. Displays 29(2):58–69
Sheridan TB (1992) Musings on telepresence and virtual presence. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environments 1(1):120–126
Shochat G, Maoz S, Stark-Inbar A, Blumenfeld B, Rand D, Preminger S, Sacher Y (2017) Motion-based virtual reality cognitive training targeting executive functions in acquired brain injury community-dwelling individuals: A feasibility and initial efficacy pilot. Paper presented at the 2017 international conference on virtual rehabilitation (ICVR)
Siu K-C, Best BJ, Kim JW, Oleynikov D, Ritter FE (2016) Adaptive virtual reality training to optimize military medical skills acquisition and retention. Mil Med 181(suppl_5):214–220
Slater M, Wilbur S (1997) A framework for immersive virtual environments (FIVE): speculations on the role of presence in virtual environments. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ 6(6):603–616
Slater M, Usoh M, Steed A (1995) Taking steps: the influence of a walking technique on presence in virtual reality. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction (TOCHI) 2(3):201–219
Stansfield S, Shawver D, Sobel A, Prasad M, Tapia L (2000) Design and implementation of a virtual reality system and its application to training medical first responders. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environments 9(6):524–556
Steed A, Pan Y, Zisch F, Steptoe W (2016) The impact of a self-avatar on cognitive load in immersive virtual reality. Paper presented at the 2016 IEEE virtual reality (VR)
Stetz MC, Long CP, Wiederhold BK, Turner DD (2008) Combat scenarios and relaxation training to harden medics against stress. Journal of CyberTherapy and Rehabilitation 1(3):239–247
Steuer J (1992) Defining virtual reality: dimensions determining telepresence. Journal of communication 42(4):73–93
Strickland D (1997) Virtual reality for the treatment of autism. Stud Health Technol Inform 44:81–86
Stroud KJ, Harm DL, Klaus DM (2005) Preflight virtual reality training as a countermeasure for space motion sickness and disorientation. Aviat Space Environ Med 76(4):352–356
Summa S, Basteris A, Betti E, Sanguineti V (2015) Adaptive training with full-body movements to reduce bradykinesia in persons with Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation 12(1):16
Sweller J (1988) Cognitive load during problem solving: effects on learning. Cognitive science 12(2):257–285
Tsiakas K, Huber M, Makedon F (2015) A multimodal adaptive session manager for physical rehabilitation exercising. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 8th ACM international conference on pervasive technologies related to assistive environments
Vaughan N, Dubey VN, Wainwright TW, Middleton RG (2016a) A review of virtual reality based training simulators for orthopaedic surgery. Med Eng Phys 38(2):59–71
Vaughan N, Gabrys B, Dubey VN (2016b) An overview of self-adaptive technologies within virtual reality training. Computer Science Review 22:65–87
Verma S, Kumar D, Kumawat A, Dutta A, Lahiri U (2017) A low-cost adaptive balance training platform for stroke patients: a usability study. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25(7):935–944
Waltemate T, Gall D, Roth D, Botsch M, Latoschik ME (2018) The impact of avatar personalization and immersion on virtual body ownership, presence, and emotional response. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graphics 24(4):1643–1652
Wang L, Du S, Liu H, Yu J, Cheng S, Xie P (2017) A virtual rehabilitation system based on EEG-EMG feedback control. Paper presented at the 2017 Chinese automation congress (CAC)
Wiederhold BK, Wiederhold MD (2008) Virtual reality for posttraumatic stress disorder and stress inoculation training. Journal of CyberTherapy & Rehabilitation 1(1):23–35
Wilkerson W, Avstreih D, Gruppen L, Beier KP, Woolliscroft J (2008) Using immersive simulation for training first responders for mass casualty incidents. Acad Emerg Med 15(11):1152–1159
Wu W, Wang D, Wang T, Liu M (2016) A personalized limb rehabilitation training system for stroke patients. Paper presented at the robotics and biomimetics (ROBIO), 2016 IEEE international conference on
Yang X, Wang D, Zhang Y (2016) An adaptive strategy for an immersive visuo-haptic attention training game. Paper presented at the international conference on human haptic sensing and touch enabled computer applications
Yerkes RM, Dodson JD (1908) The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation. J Comp Neurol Psychol 18(5):459–482
Yovanoff M, Pepley D, Mirkin K, Moore J, Han D, Miller S (2017) Personalized learning in medical education: designing a user interface for a dynamic haptic robotic trainer for central venous catheterization. Paper presented at the proceedings of the human factors and ergonomics society annual meeting
Yovanoff MA, Chen H-E, Pepley DF, Mirkin KA, Han DC, Moore JZ, Miller SR (2018) Investigating the Effect of Simulator Functional Fidelity and Personalized Feedback on Central Venous Catheterization Training. Journal of surgical education 75(5):1410–1421
Zahabi M, Park J, Abdul Razak M, McDonald A (2019) Adaptive driving simulation-based training: framework, status, and needs. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/1463922X.2019.1698673
Zhu X, Liu Y, Zhou B, An M, Chen X, Hu F, Jiang G (2015) Design of a virtual training system and application of an evaluation scheme for orientation in a spacecraft cabin. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 15th international conference on man-machine-environment system engineering
Zhu B, Kaber D, Zahabi M, Ma W (2019) Effects of feedback type and modality on motor skill learning and retention. Behaviour Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2019.1599068
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahabi, M., Abdul Razak, A.M. Adaptive virtual reality-based training: a systematic literature review and framework. Virtual Reality 24, 725–752 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-020-00434-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-020-00434-w