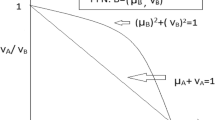
Abstract
Urgency of fresh items is increasing day by day everywhere. During transportation over a long distance, the rate of deterioration is also increasing for perishable items, and if the items are not reaching at destination within a specified time, then they are no longer fresh. Based on the fact, the customers loose the quality and quantity of items; as a result, suppliers are penalized for the occurrence of any such a situation. This problem is resolved by introducing two criteria such as time window restrictions and preservation technology in the proposed study. To prevent the deterioration rate, we find a strategy by formulating a model for multi-objective fixed-charge solid transportation problem with two criteria and then finalize one of them. To ensure that the necessary fresh items are to reached at the destination just in time, we introduce several objectives such as transportation cost, transportation time, preservation cost, penalty charge for time window, carbon emission with cap policy, deterioration, etc., such that these are optimized simultaneously. Again source, demand and conveyance capacity are not precisely estimated for different real-life situations. Here, we address such situation by choosing type-2 zigzag uncertain variable. Expected value operator is initiated to convert such uncertainty into crisp form, and then three approaches, namely, fuzzy programming, Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy programming and global criterion method are utilized to find Pareto-optimal solution. Finally two numerical examples are put to check the appropriateness of the formulated study. The results along with discussions and conclusions are described at last. The main contribution is that the deterioration of transported perishable items is reduced by imposing one of the proposed criteria according to the economical or other conditions of systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhami AY, Ahmad F (2020) Interactive Pythagorean-hesitant fuzzy computational algorithm for multi-objective transportation problem under uncertainty. International Journal of Management Science and Engineering Management 15(4):288–297
Ali SS, Kaur R, Ersöz F, Altaf B, Basu A, Weber G-W (2020) Measuring carbon performance for sustainable green supply chain practices: a developing country scenario. CEJOR 28(4):1389–1416
Das SK, Roy SK, Weber G-W (2020) Application of type-2 fuzzy logic to a multi-objective green solid transportation-location problem with dwell time under carbon tax, cap, and offset policy: fuzzy versus nonfuzzy techniques. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(11):2711–2725
Das SK, Roy SK, Weber G-W (2020) Heuristic approaches for solid transportation-p-facility location problem. CEJOR 28:939–961
Fügenschuh A (2006) The vehicle routing problem with coupled time windows. CEJOR 14(2):157–176
Ghosh S, Roy SK (2020) Fuzzy-rough multi-objective product blending fixed-charge transportation problem with truck load constraints through transfer station. RAIRO-Operations Research 55:S2923–S2952
Ghosh S, Roy SK, Ebrahimnejad A, Verdegay JL (2020) Multi-objective fully intuitionistic fuzzy fixed-charge solid transportation problem. Complex & Intelligent Systems 7(2):1009–1023
Ghosh S, Küfer K-H, Roy SK, Weber G-W (2022) Carbon mechanism on sustainable multi-objective solid transportation problem for waste management in pythagorean hesitant fuzzy environment. Complex & Intelligent Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-022-00686-w
Giri B, Pal H, Maiti T (2017) A vendor-buyer supply chain model for time-dependent deteriorating item with preservation technology investment. International Journal of Mathematics in Operational Research 10(4):431–449
Haley K (1962) New methods in mathematical programming-the solid transportation problem. Oper Res 10(4):448–463
He Y, Huang H (2013) Optimizing inventory and pricing policy for seasonal deteriorating products with preservation technology investment. Journal of Industrial Engineering 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/793568
Hirsch WM, Dantzig GB (1968) The fixed charge problem. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 15(3):413–424
Hitchcock FL (1941) The distribution of a product from several sources to numerous localities. J Math Phys 20(1–4):224–230
Hsu P, Wee H, Teng H (2010) Preservation technology investment for deteriorating inventory. Int J Prod Econ 124(2):388–394
Khanna A, Yadav S et al (2020) Effect of carbon-tax and cap-and-trade mechanism on an inventory system with price-sensitive demand and preservation technology investment. Yugoslav Journal of Operations Research 30(3):361–380
Kropat E, Weber G-W, Belen S (2011) Dynamical gene-environment networks under ellipsoidal uncertainty: set-theoretic regression analysis based on ellipsoidal OR. Dynamics, Games and Science I:545–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11456-4_35
Liang D, Xu Z (2017) The new extension of TOPSIS method for multiple criteria decision making with hesitant Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 60:167–179
Liu B (2007) Uncertainty theory, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 205–234
Liu B (2010) Uncertainty Theory: A branch of mathematics for modeling human uncertainty. Heidelberg, Springer, Berlin
Liu Y, Ha M (2010) Expected value of function of uncertain variables. Journal of Uncertain Systems 4(3):181–186
Maity G, Roy SK, Verdegay JL (2019) Time variant multi-objective interval-valued transportation problem in sustainable development. Sustainability 11(21):6161
Midya S, Roy SK (2020) Multi-objective fixed-charge transportation problem using rough programming. International Journal of Operational Research 37(3):377–395
Miettinen K (1999) Non-linear multi-objective optimization, vol 33. Kluwer Academic Publishers, USA
Oberthür S, Ott HE (1999) The Kyoto Protocol: International Climate policy for the 21st century. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Pervin M, Roy SK, Weber GW (2020) Deteriorating inventory with preservation technology under price-and stock-sensitive demand. Journal of Industrial & Management Optimization 16(4):1585–1612
Rosario ED, Vitoriano B, Weber G-W (2020) Editorial: OR for sustainable development. CEJOR 28(4):1179–1186
Roy SK, Maity G, Weber G-W (2017) Multi-objective two-stage grey transportation problem using utility function with goals. CEJOR 25(2):417–439
Roy SK, Midya S, Weber G-W (2019) Multi-objective multi-item fixed-charge solid transportation problem under two-fold uncertainty. Neural Comput Appl 31(12):8593–8613
Sengupta D, Das A, Dutta A, Bera UK (2020) A carbon emission optimization model with reduction method of type-2 zigzag uncertain variable. Neural Comput Appl 32(15):10895–10914
Shell E (1955) Distribution of a product by several properties, directorate of management analysis. Proceedings of the 2nd symposium on linear programming 2:615–642
Shen L, Tao F, Wang S (2018) Multi-depot open vehicle routing problem with time windows based on carbon trading. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(9):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15092025
Tirkolaee EB, Goli A, Bakhsi M, Mahdavi I (2017) A robust multi-trip vehicle routing problem of perishable products with intermediate depots and time windows. Numerical Algebra, Control & Optimization 7(4):417–433
Tirkolaee EB, Abbasian P, Soltani M, Ghaffarian SA (2019) Developing an applied algorithm for multi-trip vehicle routing problem with time windows in urban waste collection: A case study. Waste Management & Research 37(1):4–13
Wang YM, Yin HL (2018) Cost-optimization problem with a soft time-window based on an improved fuzzy genetic algorithm for fresh food distribution. Math Probl Eng 2018(2):1–16
Wu H, Tao F, Qiao Q, Zhang M (2020) A chance-constrained vehicle routing problem for wet waste collection and transportation considering carbon emissions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(2):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020458
Yager RR, Abbasov AM (2013) Pythagorean membership grades, complex numbers, and decision making. Int J Intell Syst 28(5):436–452
Yan Q, Zhang Q (2015) The optimization of transportation costs in logistics enterprises with time-window constraints. Discret Dyn Nat Soc 2015(1):1–10
Yan B, Chen X, Yuan Q, Zhou X (2020) Sustainability in fresh agricultural product supply chain based on radio frequency identification under an emergency. CEJOR 28(4):1343–1361
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zimmermann H-J (1978) Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1(1):45–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
We the authors announce that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Küfer, KH., Roy, S.K. et al. Type-2 zigzag uncertain multi-objective fixed-charge solid transportation problem: time window vs. preservation technology. Cent Eur J Oper Res 31, 337–362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-022-00811-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-022-00811-7
Keywords
- Multi-objective solid transportation problem
- Time window
- Preservation technology and carbon emission
- Type-2 zigzag variable
- Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy programming
- Global criterion method