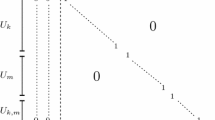
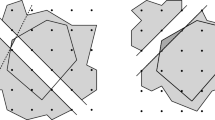
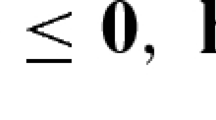Abstract
One method which has been used very successfully for finding optimal and provably good solutions for large instances of the symmetric travelling salesman problem (STSP) is the branch and cut method. This method requires knowledge of classes of useful valid inequalities for the polytope associated with the STSP, as well as efficient separation routines for these classes of inequalities. Recently a new class of valid inequalities called the domino-parity inequalites were introduced for the STSP. An efficient separation routine is known for these constraints if certain conditions are satisfied by the point to be separated. This separation routine has never been implemented or tested. We present several performance enhancements for this separation routine, and discuss our implementation of this improved algorithm. We test our implementation and provide results which we believe demonstrate the practical usefulness of these constraints and the separation routine for the STSP within a branch and cut framework.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applegate D., Bixby R., Chvátal V., Cook W. (1995): Finding cuts in the TSP (A Preliminary Report). DIMACS Technical Report 95-05, Rutgers University, New Brunswick
Applegate, D., Bixby, R., Chvátal, V., Cook, W., CONCORDE, a code for the solution of the TSP, http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/concorde/.
Boyd S., Cockburn S. (2001): A family of facet-inducing domino-parity inequalities for the STSP. Technical Report TR-2001-09, SITE, University of Ottawa, Ottawa
Boyd S., Cockburn S. (2002): Distinctness of the twisted comb constraints. Technical Report TR-2002-01, SITE, University of Ottawa, Ottawa
Caprara A., Fischetti M., Letchford A.N. (2000): On the separation of maximally violated mod-k cuts. Math. Prog. 87, 37–56
Carr R. (1997): Separating clique trees and bipartition inequalities having a fixed number of handles and teeth in polynomial time. Math. Oper. Res. 22(2): 257–265
Cockburn S. (2001): On DP-constraints for the Traveling Salesman Polytope. Master’s Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa
Fleischer L., Tardos É (1999): Separating maximally violated comb inequalities in planar graphs. Math. Oper. Res. 24, 130–148
Goemans M., Talluri K. (1991): 2-change for k-connected networks. Oper. Res. Lett. 10, 113–117
Grötschel M., Padberg M. (1979): On the symmetric travelling salesman problem I: Inequalities. Math. Prog. 16, 265–280
Grötschel M., Padberg M. (1979): On the symmetric travelling salesman problem II: Lifting theorems and facets. Math. Prog. 16, 281–302
Henzinger M., Klein P., Rao S., Subramanian S.(1997): Faster shortest-path algorithms for planar graphs. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 55(1): 3–23
Johnson D.S., Papadimitriou C.H. (1985): Performance guarantees for heuristics. In: Lawler et al. (eds). The Traveling Salesman Problem. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 37–85
Jünger M., Reinelt G., Rinaldi G. (1995): The travelling salesman problem. In: Ball et al. (eds). Network Models. Handbooks on Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 7, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 225–330
Letchford A.N. (2001): Separating a superclass of comb inequalities in planar graphs. Math. Oper. Res. 25(3): 443–454
Naddef D. (2001): The domino inequalities for the Symmetric Traveling Salesman Problem. Technical Report, Laboratoire ID-IMAG, France
Naddef D., Thienel S. (2002): Efficient separation routines for the symmetric traveling salesman problem I: general tools and comb separation. Math. Prog. 92(2): 237–255
Padberg M.W., Grötschel M. (1985): Polyhedral computations. In: Lawler et al. (eds). The Traveling Salesman Problem. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 307–360
Padberg M.W., Rao G. (1982): Odd minimum cut-sets and b-matchings. Math. Oper. Res. 7, 67–80
Padberg M.W., Rinaldi G. (1990): Facet identification for the symmetric traveling salesman polytope. Math. Prog. 47, 219–257
Padberg M.W., Rinaldi G. (1991): A branch-and-cut algorithm for the resolution of large-scale symmetric traveling salesman problems. SIAM Rev. 33, 60–100
Reinelt G. (1991): TSPLIB–A traveling salesman problem library. ORSA J. Comput. 3, 376–384
Vella D. (2001): Using DP-constraints to obtain improved TSP solutions. Master’s Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was partially supported by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyd, S., Cockburn, S. & Vella, D. On the domino-parity inequalities for the STSP. Math. Program. 110, 501–519 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-006-0011-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-006-0011-6