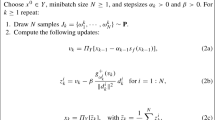Abstract
This paper deals with iterative gradient and subgradient methods with random feasibility steps for solving constrained convex minimization problems, where the constraint set is specified as the intersection of possibly infinitely many constraint sets. Each constraint set is assumed to be given as a level set of a convex but not necessarily differentiable function. The proposed algorithms are applicable to the situation where the whole constraint set of the problem is not known in advance, but it is rather learned in time through observations. Also, the algorithms are of interest for constrained optimization problems where the constraints are known but the number of constraints is either large or not finite. We analyze the proposed algorithm for the case when the objective function is differentiable with Lipschitz gradients and the case when the objective function is not necessarily differentiable. The behavior of the algorithm is investigated both for diminishing and non-diminishing stepsize values. The almost sure convergence to an optimal solution is established for diminishing stepsize. For non-diminishing stepsize, the error bounds are established for the expected distances of the weighted averages of the iterates from the constraint set, as well as for the expected sub-optimality of the function values along the weighted averages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronszajn N.: Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 68(3), 337–404 (1950)
Bauschke, H.H.: Projection algorithms and monotone operators. Ph.D. thesis, Simon Frazer University, Canada (1996)
Bauschke H.H.: Projection algorithms: results and open problems. In: Butnariu, D., Censor, Y., Reich, Y. (eds) Inherently Parallel Algorithms in Feasibility and Optimization and their Applications, pp. 11–22. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Bauschke H.H., Borwein J.M.: On projection algorithms for solving convex feasibility problems. SIAM Rev. 38(3), 367–426 (1996)
Bauschke H.H., Combettes H.H., Luke D.R.: Hybrid projection-reflection method for phase retrieval. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 20(6), 1025–1034 (2003)
Beck A., Teboulle M.: A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2, 183–202 (2009)
Beck A., Teboulle M.: Gradient-based algorithms with applications to signal-recovery problems. In: Eldar, Y., Palomar, D. (eds) Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications, pp. 42–88. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Bertsekas D.P.: A hybrid incremental gradient method for least squares. SIAM J. Optim. 7, 913–926 (1997)
Bertsekas D.P.: A note on error bounds for convex and nonconvex programs. Comp. Optim. Appl. 12, 41–51 (1999)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Incremental Gradient, Subgradient and Proximal Methods for Convex Optimization: A Survey. Technical report, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010, Lab. for Info. and Decision Systems, Report LIDS-P-2848, MIT (2010)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Incremental Proximal Methods for Large Scale Convex Optimization. Technical report, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010, Lab. for Info. and Decision Systems, Report LIDS-P-2847 (2010)
Bertsekas D.P., Nedić A., Ozdaglar A.E.: Convex Analysis and Optimization. Athena Scientific, Cambridge (2003)
Bertsekas D.P., Tsitsiklis J.N.: Gradient convergence in gradient methods. SIAM J. Optim. 10(3), 627–642 (2000)
Borkar V.S.: Stochastic Approximation: A Dynamical Systems Viewpoint. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Burke J.V., Ferris M.C.: Weak sharp minima in mathematical programming. SIAM J. Control Optim. 31(6), 1340–1359 (1993)
Burke J.V., Tseng P.: A unified analysis of Hoffman’s bound via Fenchel duality. SIAM J. Optim. 6(2), 265–282 (1996)
Capricelli T.D., Combettes P.L.: A convex programming algorithm for noisy discrete tomography. In: Herman, G.T., Kuba, A. (eds) Advances in Discrete Tomography and Its Applications, pp. 207–226. Birkháuser, Boston (2007)
Cegielski A., Suchocka A.: Relaxed alternating projection methods. SIAM J. Optim. 19(3), 1093–1106 (2008)
Combettes P.L.: Convex set theoretic image recovery by extrapolated iterations of parallel subgradient projections. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(4), 493–506 (1997)
Deutsch F.: Rate of convergence of the method of alternating projections. In: Brosowski, B., Deutsch, F. (eds) Parametric Optimization and Approximation, vol. 76, pp. 96–107. Birkhäuser, Basel (1983)
Deutsch F., Hundal H.: The rate of convergence for the cyclic projections algorithm I: Angles between convex sets. J. Approx. Theory 142, 36–55 (2006)
Deutsch F., Hundal H.: The rate of convergence for the cyclic projections algorithm II: Norms of nonlinear operators. J. Approx. Theory 142, 56–82 (2006)
Deutsch F., Hundal H.: The rate of convergence for the cyclic projections algorithm III: regularity of convex sets. J. Approx. Theory 155, 155–184 (2008)
Ermoliev Y.: Stochastic Programming Methods. Nauka, Moscow (1976)
Ermoliev Y.: Stochastic quasi-gradient methods and their application to system optimization. Stochastics 9(1), 1–36 (1983)
Ermoliev Y.: Stochastic quazigradient methods. In: Ermoliev, Y., Wets, R.J.-B. (eds) Numerical Techniques for Stochastic Optimization, pp. 141–186. Springer, NY (1988)
Eryilmaz A., Srikant R.: Fair resource allocation in wireless networks using queue-length-based scheduling and congestion control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 15, 1333–1344 (2007)
Fabian M.J., Henrion R., Kruger A.Y., Outrata J.: Error bounds: necessary and sufficient conditions. Set-Valued Anal. 18, 121–149 (2010)
Facchinei F., Pang J.-S.: Finite-dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems, vol. I and II. Springer, New York (2003)
Georgiadis L., Neely M.J., Tassiulas L.: Resource allocation and cross-layer control in wireless networks. Found. Trends Netw. 1(1), 1–149 (2006)
Gubin L.G., Polyak B.T., Raik E.V.: The method of projections for finding the common point of convex sets. U.S.S.R. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 7(6), 1211–1228 (1967)
Halperin I.: The product of projection operators. Acta Scientiarum Mathematicarum 23, 96–99 (1962)
Huang J., Subramanian V.G., Agrawal R., Berry R.: Joint scheduling and resource allocation in uplink OFDM systems for broadband wireless access networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., special issue on “Broadband Area Networks” 27(2), 226–234 (2009)
Kibardin V.M: Decomposition into functions in the minimization problem. Autom. Remote Control 40(9), 1311–1323 (1980)
Kiwiel K.C.: Convergence of approximate and incremental subgradient methods for convex optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 14(3), 807–840 (2003)
Knopp K.: Theory and Applications of Infinite Series. Blackie & Son Limited, Glasgow (1954)
Lewis A., Pang J.-S.: Error bounds for convex inequality systems. In: Crouzeix, J.-P., Martinez-Legaz, J.-E., Volle, M. (eds) Generalized Convexity, Generalized Monotonicity, pp. 75–110. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Luo Z.-Q.: New error bounds and their applications to convergence analysis of iterative algorithms. Math. Program. Ser. B 88, 341–355 (2000)
Luo Z.-Q., Tseng P.: Analysis of an approximate gradient projection method with applications to the backpropagation algorithm. Optim. Methods Softw. 4(2), 85–101 (1994)
Mangasarian, O.L.: Error Bounds for Nondifferentiable Convex Inequalities Under Strong Slater Constraint Qualification. Technical report, University of Wisconsin, Wisconsin (1996)
Nedić A., Bertsekas D.P.: Incremental subgradient method for nondifferentiable optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 12, 109–138 (2001)
Nesterov Yu.: Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Math. Program. Ser. A 103, 127–152 (2005)
Nesterov Yu.: A method of solving a convex programming problem with convergence rate of o(1/k 2). Sov. Math. Dokl. 27(2), 372–376 (1983)
Polyak B.T.: Minimization of unsmooth functionals. U.S.S.R. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 9, 14–29 (1969)
Polyak B.T.: Introduction to Optimization. Optimization Software Inc., New York (1987)
Polyak B.T.: Random algorithms for solving convex inequalities. In: Butnariu, D., Censor, Y., Reich, S. (eds) Inherently Parallel Algorithms in Feasibility and Optimization and their Applications, pp. 409–422. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Ram S.S., Nedić A., Veeravalli V.V.: Incremental stochastic sub-gradient algorithms for convex optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 20(2), 691–717 (2009)
Robbins H., Siegmund D.: A convergence theorem for nonnegative almost supermartingales and some applications. In: Rustagi, J.S. (ed.) Optimizing Methods in Statistics, pp. 233–257. Academic Press, New York (1971)
Solodov M.V.: Incremental gradient algorithms with stepsizes bounded away from zero. Comput. Optim. Algorithms 11(1), 23–35 (1998)
Stolyar A.L.: On the asymptotic optimality of the gradient scheduling algorithm for multiuser throughput allocation. Oper. Res. 53(1), 12–25 (2005)
Tseng, P.: Successive Projection Under a Quasi-cyclic Order. Technical report, LIDS-P-1938, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MA (1990)
Tseng P.: An incremental gradient(-projection) method with momentum term and adaptive stepsize rule. SIAM J. Optim. 8(2), 506–531 (1998)
Tseng, P.: On accelerated proximal gradient methods for convex-concave optimization. submitted to SIAM J. Optim. (2008)
von Neumann J.: Functional Operators. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1950)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nedić, A. Random algorithms for convex minimization problems. Math. Program. 129, 225–253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-011-0468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-011-0468-9