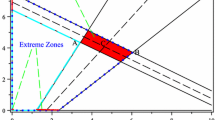
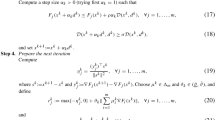Abstract
In this paper, we present a novel sequential convex bilevel programming algorithm for the numerical solution of structured nonlinear min–max problems which arise in the context of semi-infinite programming. Here, our main motivation are nonlinear inequality constrained robust optimization problems. In the first part of the paper, we propose a conservative approximation strategy for such nonlinear and non-convex robust optimization problems: under the assumption that an upper bound for the curvature of the inequality constraints with respect to the uncertainty is given, we show how to formulate a lower-level concave min–max problem which approximates the robust counterpart in a conservative way. This approximation turns out to be exact in some relevant special cases and can be proven to be less conservative than existing approximation techniques that are based on linearization with respect to the uncertainties. In the second part of the paper, we review existing theory on optimality conditions for nonlinear lower-level concave min–max problems which arise in the context of semi-infinite programming. Regarding the optimality conditions for the concave lower level maximization problems as a constraint of the upper level minimization problem, we end up with a structured mathematical program with complementarity constraints (MPCC). The special hierarchical structure of this MPCC can be exploited in a novel sequential convex bilevel programming algorithm. We discuss the surprisingly strong global and locally quadratic convergence properties of this method, which can in this form neither be obtained with existing SQP methods nor with interior point relaxation techniques for general MPCCs. Finally, we discuss the application fields and implementation details of the new method and demonstrate the performance with a numerical example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitescu, M.: Nonlinear programs with unbounded Lagrange multiplier sets. Technical report, Preprint ANL/MCS-P796-0200, Mathematics and Computer Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL (2000)
Anitescu, M.: Global convergence of an elastic mode approach for a class of mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. SIAM J. Optim. 16, 120–145 (2005)
Bard, J.F.: Practical Bilevel Optimization: Algorithms and Applications. Kluwer, Boston MA (1999)
Ben-Tal, A., Boyd, S., Nemirovski, A.: Extending scope of robust optimization: comprehensive robust counterparts of uncertain problems. Math. Program. (Ser. B) 107, 63–89 (2006)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: Robust truss topology design via semidefinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 7, 991–1016 (1997)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: Robust convex optimization. Math. Oper. Res 23, 769–805 (1998)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: Robust solutions of uncertain linear programs. Oper. Res. 25, 1–13 (1999)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A., Roos, C.: Robust solutions of uncertain quadratic and conic-quadratic problems. SIAM J. Optim. 13(2), 535–560 (2002)
Benson, H.Y., Sen, A., Shanno, D.F., Vanderbei, R.J.: Interior-point algorithms, penalty methods and equilibrium problems. Computat. Optim. Appl. 34, 155–182 (2006)
Bhattacharjee, B., Lemonidis, P., Green, W.H., Barton, P.I.: Global solution of semi-infinite programs. Math. Program. (Ser. B) 103(2), 283–307 (2005)
Chamberlain, R., Lemaréchal, C., Pedersen, H.C., Powell, M.J.D.: The watchdog technique for forcing convergence in algorithms for constrained optimization. Math. Program. 16, 1–17 (1982)
Chen, L., Goldfarb, D.: An active set method for mathematical programs with linear complementarity constraint. Manuscript, Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University (2007)
Coleman, T.F., Conn, A.R.: Non-linear programming via an exact penalty function: asymptotic analysis. Math. Program. 24, 123–136 (1982)
Conn, A.R., Gould, N., Toint, P.L.: Trust-Region Methods. MPS/SIAM Series on Optimization. SIAM, Philadelphia, USA (2000)
Diehl, M., Bock, H.G., Kostina, E.: An approximation technique for robust nonlinear optimization. Math. Program. 107, 213–230 (2006)
Diehl, M., Jarre, F., Vogelbusch, C.: Loss of superlinear convergence for an SQP-type method with conic constraints. SIAM J. Optim. 16(4), 1201–1210 (2006)
El-Ghaoui, L., Lebret, H.: Robust solutions to least-square problems to uncertain data matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. 18, 1035–1064 (1997)
Facchinei, F., Jiang, H., Qi, L.: A smoothing method for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. Math. Program. 85, 107–134 (1999)
Fletcher, R.: Second order corrections for non-differentiable optimization. In: Griffiths, D. (ed.) Numerical Analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp. 85–114 (1982)
Fletcher, R., Leyffer, S., Ralph, D., Scholtes, S.: Local convergence of SQP methods for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. SIAM J. Optim. 17, 259–286 (2006)
Floudas, C.A.: Deterministic Global Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1999)
Floudas, C.A., Stein, O.: The adaptative convexification algorithm: a feasible point method for semi-infinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 18(4), 1187–1208 (2007)
Han, S.P.: A globally convergent method for nonlinear programming. JOTA 22, 297–310 (1977)
Hettich, R., Jongen, H.T.: Semi-infinite programming: conditions of optimality and applications. In: Stoer, J. (ed.) Optimization Techniques, Part 2, Lecture Notes in Control and Inform. Sci., vol. 7. Springer, Berlin (1978)
Hettich, R., Kortanek, K.: Semi infinite programming: theory, methods, and application. SIAM Rev. 35(3), 380–429 (1993)
Hettich, R., Still, G.: Second order optimality conditions for generalized semi-infinite programming problems. Optimization 34, 195–211 (1995)
Houska, B.: Robustness and stability optimization of open-loop controlled power generating kites. University of Heidelberg, Master’s thesis (2007)
Houska, B., Ferreau, H.J., Diehl, M.: ACADO toolkit—an open source framework for automatic control and dynamic optimization. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 32(3), 298–312 (2011)
Houska, B., Logist, F., Van Impe, J., Diehl, M.: Approximate robust optimization of time-periodic stationary states with application to biochemical processes. In: Proceedings of the 48th Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 6280–6285. Shanghai, China (2009)
Jongen, H.T., Rückmann, J.J., Stein, O.: Generalized semi-infinite optimization: a first order optimality condition and examples. Math. Program. 83, 145–158 (1998)
Liu, G.S., Zhang, J.Z.: A new branch and bound algorithm for solving quadratic programs with linear complementarity constraints. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 146, 77–87 (2002)
Luo, Z., Pang, J.S., Ralph, D.: Piecewise sequential quadratic programming for mathematical programs with nonlinear complementarity constraints. In: Migdalas, A., Pardalos, P.M., Värbrand, P. (eds.) Multilevel Optimization: Algorithms and Applications, pp. 209–229. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands (1998)
Maratos, N.: Exact penaly function algorithms for finite-dimensional and control optimization problems. PhD thesis, Imperial College, London (1978)
Mayne, D.Q., Polak, E.: A quadratically convergent algorithm for solving infinite dimensional inequalities. J. Appl. Math. Optim. 9, 25–40 (1982)
Nagy, Z.K., Braatz, R.D.: Open-loop and closed-loop robust optimal control of batch processes using distributional and worst-case analysis. J. Process Control 14, 411–422 (2004)
Nagy, Z.K., Braatz, R.D.: Distributional uncertainty analysis using power series and polynomial chaos expansions. J. Process Control 17, 229–240 (2007)
Necoara, I., Savorgnan, C., Tran Dinh, Q., Suykens, J.A.K., Diehl, M.: Distributed nonlinear optimal control using sequential convex programming and smoothing techniques. In: Proceedings of the 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Shanghai, China (2009) (Accepted for publication)
Neumaier, A.: Complete Search in Continuous Global Optimization and Constraint Satisfaction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 271–369 (2004)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer Series in Operations Research and Financial Engineering, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Polak, E., Mayne, D.Q., Higgins, J.E.: Superlinearly convergent algorithm for min-max problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 69, 407–439 (1991)
Polak, E., Qi, L., Sun, D.: First-order algorithms for generalized semi-infinite min-max problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 13, 137–161 (1999)
Polak, E., Qi, L., Sun, D.: Second-order algorithms for generalized finite and semi-infinite min-max problems. SIAM J. Optim. 11, 937–961 (2001)
Polak, E., Tits, A.: A recursive quadratic programming algorithm for semi-infinite optimization problems. J. Appl. Math. Optim. 8, 325–349 (1982)
Powell, M.J.D.: The convergence of variable metric methods for nonlinear constrained optimization calculations. Academic Press, New York (1978)
Powell, M.J.D.: Convergence properties of algorithms for nonlinear optimization. SIAM Rev. 28, 487–500 (1984)
Ralph, D.: Sequential quadratic programming for mathematical programs with linear complementarity constraints. In: May, R.L., Eston, A.K. (eds). Proceedings of the seventh conference on computational techniques and applications, pp. 663–668. Scienctific Press, Singapore (1996)
Robinson, S.M.: First order conditions for general nonlinear optimization. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 30(4), 597–607 (1976)
Robinson, S.M.: Strongly regular generalized equations. Math. Oper. Res. 5(1), 43–62 (1980)
Rückmann, J.J., Stein, O.: On linear and linearized generalized semi-infinite optimization problems. Ann. Oper. Res., 101, 191–208 (2001)
Scheel, H., Scholtes, S.: Mathematical programs with complementarity constraints: stationarity, optimality, and sensitivity. Math. Oper. Res. 25, 1–22 (2000)
Sherali, H.D., Tuncbilek, C.H.: A Reformulation-Convexification Approach for Solving Nonconvex Quadratic Programming Problems. J. Glob. Optim. 7, 1–31 (1995)
Sherali, H.D., Tuncbilek, C.H.: New reformulation linearization/convexification relaxations for univariate and multivariate polynomial programming problems. Oper. Res. Lett. 21, 1–9 (1997)
Shimizu, K., Lu, M.: A global optimization method for the Stackelberg problem with convex functions via problem transformation and concave programming. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 25(23), 1635–1640 (1995)
Stein, O.: The feasible set in generalized semi-infinite programming. In: Lassonde, M. (ed.) Approximation, Optimization, and Mathematical Economics, pp. 313–331. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg (2001)
Stein, O.: Bilevel Strategies in Semi Infinite Optimization. Kluwer, Boston (2003)
Stein, O., Still, G.: On optimality conditions for generalized semi-infinite programming problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 104(2), 443–458 (2000)
Stein, O., Still, G.: Solving semi-infinite optimization problems with interior point techniques. SIAM J. Control Optim. 42(3), 769–788 (2003)
Still, G.: Discretization in semi-infinite programming: the rate of convergence. Math. Program. 91, 53–69 (2001)
Still, G.: Generalized semi-infinite programming: numerical aspects. Optimization 49, 223–242 (2001)
Voorhis, T.V.: A global optimization algorithm using Lagrangian underestimates and the interval Newton method. J. Glob. Optim. 24, 349–370 (2002)
Weber, G.W.: Generalized semi-infinite optimization and related topics. Habilitation Thesis , Darmstadt University of Technology, Darmstadt, Germany (1999)
Wright, S.J.: Modifying SQP for degenerate problems. SIAM J. Optim. 13, 470–497 (2002)
Yakubovich, V.A.: S-procedure in nonlinear control theory. Vestnik Leningrad University 4, 73–93 (1977)
Zhang, J., Liu, G.: A new extreme point algorithm and its application in PSQP algorithms for solving mathematical programs with linear complementarity constraints. J. Glob. Optim. 19(4), 345–361 (2001)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Quoc Tran Dinh for fruitful discussions on sequential convex programming [37]. Additionally, we thank two anonymous referees and the associate editor for substantial remarks which significantly improved this paper. This research was supported by the Research Council KUL via the Center of Excellence on Optimization in Engineering EF/05/006 (OPTEC, http://www.kuleuven.be/optec/), GOA AMBioRICS, IOF-SCORES4CHEM and PhD/postdoc/fellow grants, the Flemish Government via FWO (PhD/postdoc grants, projects G.0452.04, G.0499.04, G.0211.05,G.0226.06, G.0321.06, G.0302.07, G.0320.08, G.0558.08, G.0557.08, research communities ICCoS, ANMMM, MLDM) and via IWT (PhD Grants, McKnow-E, Eureka-Flite+), Helmholtz Gemeinschaft via vICeRP, the EU via ERNSI, Contract Research AMINAL, as well as the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office: IUAP P6/04 (DYSCO, Dynamical systems, control and optimization, 2007–2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houska, B., Diehl, M. Nonlinear robust optimization via sequential convex bilevel programming. Math. Program. 142, 539–577 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-012-0591-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-012-0591-2
Keywords
- Robust optimization
- Mathematical programming with complementarity constraints
- Bilevel optimization
- Semi-infinite optimization
- Sequential convex programming