Abstract
Existing nonconvex statistical optimization theory and methods crucially rely on the correct specification of the underlying “true” statistical models. To address this issue, we take a first step towards taming model misspecification by studying the high-dimensional sparse phase retrieval problem with misspecified link functions. In particular, we propose a simple variant of the thresholded Wirtinger flow algorithm that, given a proper initialization, linearly converges to an estimator with optimal statistical accuracy for a broad family of unknown link functions. We further provide extensive numerical experiments to support our theoretical findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here we use the shorthand \([n] = \{1,2,\ldots , n\}\).
See, for example, Foucart and Rauhut [13] for the definition of the distributional derivative.
References
Ahmadi, A.A., Parrilo, P.A.: Some recent directions in algebraic methods for optimization and Lyapunov analysis. In: Laumond, J.P., Mansard, N., Lasserre, J.B. (eds.) Geometric and Numerical Foundations of Movements, pp. 89–112. Springer, Cham (2017)
Alquier, P., Biau, G.: Sparse single-index model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 14, 243–280 (2013)
Bolte, J., Sabach, S., Teboulle, M.: Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems. Math. Program. 146, 459–494 (2014)
Bühlmann, P., van de Geer, S.: Statistics for High-Dimensional Data: Methods, Theory and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Bunk, O., Diaz, A., Pfeiffer, F., David, C., Schmitt, B., Satapathy, D.K., van der Veen, J.F.: Diffractive imaging for periodic samples: retrieving one-dimensional concentration profiles across microfluidic channels. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 63, 306–314 (2007)
Cai, T.T., Li, X., Ma, Z.: Optimal rates of convergence for noisy sparse phase retrieval via thresholded Wirtinger flow. Ann. Stat. 44, 2221–2251 (2016)
Candès, E.J., Eldar, Y.C., Strohmer, T., Voroninski, V.: Phase retrieval via matrix completion. SIAM Rev. 57, 225–251 (2015)
Candès, E.J., Li, X., Soltanolkotabi, M.: Phase retrieval via Wirtinger flow: theory and algorithms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 61, 1985–2007 (2015)
Candès, E.J., Strohmer, T., Voroninski, V.: Phaselift: exact and stable signal recovery from magnitude measurements via convex programming. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 66, 1241–1274 (2013)
Chen, Y., Candès, E.: Solving random quadratic systems of equations is nearly as easy as solving linear systems. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2015)
Coene, W., Janssen, G., de Beeck, M.O., Van Dyck, D.: Phase retrieval through focus variation for ultra-resolution in field-emission transmission electron microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 3743 (1992)
Cook, R.D., Ni, L.: Sufficient dimension reduction via inverse regression: a minimum discrepancy approach. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 100, 410–428 (2005)
Foucart, S., Rauhut, H.: A Mathematical Introduction to Compressive Sensing. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Genzel, M.: High-dimensional estimation of structured signals from non-linear observations with general convex loss functions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 63, 1601–1619 (2017)
Ghadimi, S., Lan, G.: Stochastic first-and zeroth-order methods for nonconvex stochastic programming. SIAM J. Optim. 23, 2341–2368 (2013)
Ghadimi, S., Lan, G.: Accelerated gradient methods for nonconvex nonlinear and stochastic programming. Math. Program. 156, 59–99 (2016)
Goldstein, L., Minsker, S., Wei, X.: Structured signal recovery from non-linear and heavy-tailed measurements (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.01025
Golub, G.H., Van Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computations. Johns Hopkins University Press, Johns Hopkins University Press (2012)
Gonçalves, M.L., Melo, J.G., Monteiro, R.D.: Convergence rate bounds for a proximal admm with over-relaxation stepsize parameter for solving nonconvex linearly constrained problems (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.01850
Gu, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, H.: Sparse PCA with oracle property. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2014)
Han, A.K.: Non-parametric analysis of a generalized regression model: the maximum rank correlation estimator. J. Econ. 35, 303–316 (1987)
Harrison, R.: Phase problem in crystallography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. Part A Opt. Image Sci. 10, 1046–1055 (1993)
Hong, M., Luo, Z.-Q., Razaviyayn, M.: Convergence analysis of alternating direction method of multipliers for a family of nonconvex problems. SIAM J. Optim. 26, 337–364 (2016)
Horowitz, J.L.: Semiparametric and Nonparametric Methods in Econometrics. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Jaganathan, K., Eldar, Y.C. and Hassibi, B.: Phase retrieval: an overview of recent developments (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.07713
Jiang, B., Liu, J.S.: Variable selection for general index models via sliced inverse regression. Ann. Stat. 42, 1751–1786 (2014)
Johnstone, I.M., Lu, A.Y.: On consistency and sparsity for principal components analysis in high dimensions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 104, 682–693 (2009)
Kakade, S.M., Kanade, V., Shamir, O., Kalai, A.: Efficient learning of generalized linear and single index models with isotonic regression. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2011)
Kalai, A.T., Sastry, R.: The isotron algorithm: high-dimensional isotonic regression. In: Conference on Learning Theory (2009)
Kim, S., Kojima, M., Toh, K.-C.: A Lagrangian-DNN relaxation: a fast method for computing tight lower bounds for a class of quadratic optimization problems. Math. Program. 156, 161–187 (2016)
Li, K.-C.: Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 86, 316–327 (1991)
Li, K.-C.: On principal Hessian directions for data visualization and dimension reduction: another application of Stein’s lemma. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 87, 1025–1039 (1992)
Li, K.-C., Duan, N.: Regression analysis under link violation. Ann. Stat. 17, 1009–1052 (1989)
Li, X., Yang, L.F., Ge, J., Haupt, J., Zhang, T., Zhao, T.: On quadratic convergence of DC proximal Newton algorithm for nonconvex sparse learning in high dimensions (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.06066
Lin, Q., Zhao, Z., Liu, J.S.: On consistency and sparsity for sliced inverse regression in high dimensions (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.03895
Loh, P.-L., Wainwright, M.J.: Regularized \({M}\)-estimators with nonconvexity: statistical and algorithmic theory for local optima. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 16, 559–616 (2015)
Lu, Z., Xiao, L.: On the complexity analysis of randomized block-coordinate descent methods. Math. Program. 152, 615–642 (2015)
Marchesini, S., He, H., Chapman, H.N., Hau-Riege, S.P., Noy, A., Howells, M.R., Weierstall, U., Spence, J.C.: X-ray image reconstruction from a diffraction pattern alone. Phys. Rev. B 68, 140101 (2003)
McCullagh, P., Nelder, J.A.: Generalized Linear Models. Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton (1989)
Miao, J., Ishikawa, T., Shen, Q., Earnest, T.: Extending X-ray crystallography to allow the imaging of noncrystalline materials, cells, and single protein complexes. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 59, 387–410 (2008)
Millane, R.: Phase retrieval in crystallography and optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. 7, 394–411 (1990)
Netrapalli, P., Jain, P., Sanghavi, S.: Phase retrieval using alternating minimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2013)
Neykov, M., Wang, Z., Liu, H.: Agnostic estimation for misspecified phase retrieval models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2016)
Parrilo, P.A.: Semidefinite programming relaxations for semialgebraic problems. Math. Program. 96, 293–320 (2003)
Plan, Y., Vershynin, R.: The generalized lasso with non-linear observations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 62, 1528–1537 (2016)
Plan, Y., Vershynin, R., Yudovina, E.: High-dimensional estimation with geometric constraints (2014). arXiv preprint arXiv:1404.3749
Radchenko, P.: High dimensional single index models. J. Multivar. Anal. 139, 266–282 (2015)
Sahinoglou, H., Cabrera, S.D.: On phase retrieval of finite-length sequences using the initial time sample. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 38, 954–958 (1991)
Shechtman, Y., Eldar, Y.C., Cohen, O., Chapman, H.N., Miao, J., Segev, M.: Phase retrieval with application to optical imaging: a contemporary overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32, 87–109 (2015)
Stein, C.M.: Estimation of the mean of a multivariate normal distribution. Ann. Stat. 9, 1135–1151 (1981)
Sun, J., Qu, Q., Wright, J.: A geometric analysis of phase retrieval. In: IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (2016)
Sun, W., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Cheng, G.: Non-convex statistical optimization for sparse tensor graphical model. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2015)
Tan, K.M., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, T.: Sparse generalized eigenvalue problem: optimal statistical rates via truncated rayleigh flow (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.08697
Thrampoulidis, C., Abbasi, E., Hassibi, B.: Lasso with non-linear measurements is equivalent to one with linear measurements. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2015)
Waldspurger, I.: Phase retrieval with random gaussian sensing vectors by alternating projections (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.03088
Waldspurger, I., dÁspremont, A., Mallat, S.: Phase recovery, maxcut and complex semidefinite programming. Math. Program. 149, 47–81 (2015)
Wang, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, T.: Optimal computational and statistical rates of convergence for sparse nonconvex learning problems. Ann. Stat. 42, 2164–2201 (2014)
Wang, Z., Lu, H., Liu, H.: Tighten after relax: Minimax-optimal sparse PCA in polynomial time. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2014)
Weisser, T., Lasserre, J.-B., Toh, K.-C.: Sparse-BSOS: a bounded degree SOS hierarchy for large scale polynomial optimization with sparsity. Math. Program. Comput. 10, 1–32 (2017)
Xu, Y., Yin, W.: A globally convergent algorithm for nonconvex optimization based on block coordinate update. J. Sci. Comput. 72(2), 700–734 (2017)
Yang, Z., Balasubramanian, K., Liu, H.: High-dimensional non-gaussian single index models via thresholded score function estimation (2017)
Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Liu, H.: Estimating high-dimensional non-gaussian multiple index models via Stein’s lemma. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2017)
Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Eldar, Y.C., Zhang, T.: Sparse nonlinear regression: Parameter estimation and asymptotic inference. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (2015)
Yi, X., Wang, Z., Caramanis, C., Liu, H.: Optimal linear estimation under unknown nonlinear transform. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2015)
Zhang, H., Chi, Y., Liang, Y.: Provable nonconvex phase retrieval with outliers: median truncated Wirtinger flow. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (2016)
Zhao, T., Liu, H., Zhang, T.: Pathwise coordinate optimization for sparse learning: algorithm and theory. Ann. Stat. 46(1), 180–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1214/17-AOS1547
Zhu, L., Miao, B., Peng, H.: On sliced inverse regression with high-dimensional covariates. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101, 630–643 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 A Further simulations
We further investigate how the sparsity level of the estimator changes over iterations empirically. For the three link function \(h_1\), \(h_2\), and \(h_3\) defined in Eq. (4.1), we plot the sparsity of the TWF algorithm in Fig. 5 up to \(T = 1000\) iterations. Similar to our experimental study of the optimization error, here we set \(p = 1000\), \(s= 5\), and \(n = 864 \approx 5 s^2 \log p\). Moreover, the tuning parameters are set as \(\gamma = 2\), \(\kappa = 15\), and \(\eta = 0.005\). In this case, as we show in Sect. 4.1, our TWF algorithm converges geometrically to an estimator with high statistical accuracy. As shown in Fig. 5, our algorithm tends to over-estimate the sparsity. However, in all of these figures, the estimated sparsity gradually decreases as the algorithm proceeds. Furthermore, combining with the experiments in Sect. 4.1, although the estimator has more nonzero entries than the true parameter, the statistical error is satisfactory.
Plots of the sparsity of the TWF updates \(\beta ^{(t)}\). Here the link function is one of \(h_1\), \(h_2\), and \(h_3\). In addition, we set \(p = 1000 \), \(s = 5\), \(n = 864 \approx 5 s^2\cdot \log p\), and run the TWF algorithm for \(T = 1000\) iterations. These figures are generated based on 50 independent trials for each link function
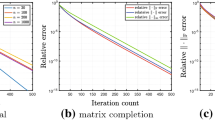
Plots of the statistical errors for the cubic model \(Y = (X^\top \beta ^*)^3 + \epsilon \) and the phase retrieval model \(Y = (X^\top \beta ^*)^2 + \epsilon \). We set \(p = 1000\), \(s= 5\), and let n vary. The plots are generated based on 100 independent trials for each (n, p, s). In a, we plot the two error curves together, which shows that the TWF algorithm incurs much larger error on the cubic model, whereas the error for the phase retrieval model becomes rather negligible in comparison. In b and c, we plot the two curves in a separately for presentation
In addition, we show a failed example, which violates Assumption 3.1, for the readers to better understand to what extent the proposed algorithm is robust to model misspecification. In particular, consider the cubic link function \(f(u, v) = u^3 + v\), which violates Assumption 3.1 since in this case we have \(\text {Cov} [ Y, (X ^\top \beta ^*)^2 ] = 0\). We compare this cubic model \(Y = (X^\top \beta ^*)^3 + \epsilon \) with the phase retrieval model \(Y = (X^\top \beta ^*)^2 + \epsilon \), where the link function is quadratic. We set \(p = 1000\), \(s = 5\), and let n vary. For each setting, we report the estimation error based on 100 independent trials. The statistical error of the TWF algorithm for these two models are plotted in Fig. 6a, which shows that our algorithm has nondecreasing estimation error for the cubic model even when n is very large. This is in sharp contrast with the phase retrieval model, where the estimation error is negligible. Moreover, we plot the two error curves separately in Fig. 6b and c to better see the details.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Yang, L.F., Fang, E.X. et al. Misspecified nonconvex statistical optimization for sparse phase retrieval. Math. Program. 176, 545–571 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-019-01364-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-019-01364-5