Abstract
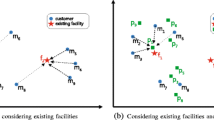
In this paper, we propose a new type of queries to retrieve the top-k most influential locations from a candidate set \(C\) given sets of customers \(M\) and existing facilities \(F\). The influence models the popularity of a facility. Such queries have wide applications in decision support systems. A naive solution sequentially scans (SS) all data sets, which is expensive, and hence, we investigate two branch-and-bound algorithms for the query, namely Estimate Expanding Pruning (EEP) and Bounding Influence Pruning (BIP). Both algorithms follow the best first traverse. On determining the traversal order, while EEP leverages distance metrics between nodes, BIP relies on half plane pruning which avoids the repetitive estimations in EEP. As our experiments shown, BIP is much faster than SS which outperforms EEP, while the worst-case complexity of EEP and BIP is worse than that of SS. To improve the efficiency, we further propose a Nearest Facility Circle Join (NFCJ) algorithm. NFCJ builds an influence R-tree on the influence relationship between customers and existing facilities and joins the candidate R-tree with the influence R-tree to obtain the results. We compare all algorithms and conclude that NFCJ is the best solution, which outperforms SS, EEP, and BIP by orders of magnitude.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtert E, Kriegel HP, Krger P, Renz M, Zfle A (2009) Reverse k-nearest neighbor search in dynamic and general metric databases. In: Proceedings of EDBT
ANNLibrary (2011) http://www.cs.umd.edu/~mount/ann/
Aronovich L, Spiegler I (2009) Bulk construction of dynamic clustered metric trees. Knowl Inf Syst 22(2):211–244
Brinkhoff T, Kriegel HP, Seeger B (1993) Efficient processing of spatial joins using r-trees. In: Proceedings of SIGMOD
Cabello S, Díaz-Báñez JM, Langerman S, Seara C, Ventura I (2006) Reverse facility location problems. In: Proceedings of CCCG
Cheema MA, Lin X, Wang W, Zhang W, Pei J (2010) Probabilistic reverse nearest neighbor queries on uncertain data. IEEE TKDE 22(4):550–564
Cheema MA, Lin X, Zhang W, Zhang Y (2011) Influence zone : efficiently processing reverse k nearest neighbors queries. In: Proceedings of ICDE
Cheema MA, Zhang W, Lin X, Zhang Y (2012) Efficiently processing snapshot and continuous reverse k nearest neighbors queries. VLDB J
Chen H, Liu J, Furuse K, Yu JX, Ohbo N (2010) Indexing expensive functions for efficient multi-dimensional similarity search. Knowl Inf Syst 27(2):165–192
CloudMade (2013) http://downloads.cloudmade.com/
Du Y, Zhang D, Xia T (2005) The optimal-location query. Adv Sp Temp Databases 3633:163–180
Gao Y, Zheng B, Chen G, Li Q (2009) Optimal-location-selection query processing in spatial databases. IEEE TKDE 68(8):1162–1177
Ghaemi P, Shahabi K, Wilson JP, Banaei-Kashani F (2010) Optimal network location queries. In: Proceedings of GIS
Guttman A (1984) R-trees: a dynamic index structure for spatial searching. In: Proceedings of SIGMOD, pp 47–57
Huang J, Wen Z, Qi J, Zhang R, Chen J, He Z (2011) Top-k most influential location selection. In: Proceedings of CIKM
Korn F, Muthukrishnan S (2000) Influence sets based on reverse nearest neighbor queries. In: Proceedings of SIGMOD
Mouratidis K, Papadias D, Papadimitriou S (2005) Medoid queries in large spatial databases. In: Proceedings of SSTD, pp 55–72
OpenStreetMap (2013) http://www.openstreetmap.org/
Qi J, Zhang R, Kulik L, Lin D, Xue Y (2012) The min-dist location selection query. In: Proceedings of ICDE
Roussopoulos N, Kelley S, Vincent F (1995) Nearest neighbor queries. In: Proceedings of SIGMOD, pp 71–79
Shang S, Yuan B, Deng K, Xie K, Zhou X (2011) Finding the most accessible locations-reverse path nearest neighbor query in road networks categories and subject descriptors. In: Proceedings of GIS
SouFang (2013) http://www.soufun.com
Stanoi I, Riedewald M, Agrawal D, Abbadi AE (2001) Discovery of influence sets in frequently updated database. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Sun Y, Huang J, Chen Y, Zhang R, Du X (2012) Location selection for utility maximization with capacity constraints. In: Proceedings of CIKM
Tao Y, Lian X (2004) Reverse kNN search in arbitrary dimensionality. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Trulia (2013) http://trulia.com
Vaidya PM (1989) AnO(n logn) algorithm for the all-nearest-neighbors problem. Discret Comput Geom 4(1):101–115
Wong RCW, Özsu MT, Fu AWC, Yu PS, Liu L, Liu Y (2011) Maximizing bichromatic reverse nearest neighbor for L p -norm in two- and three-dimensional spaces. VLDB J 20(6):893–919
Wong RCW, Ozsu MT, Yu PS, Fu AWC, Liu L (2009) Efficient method for maximizing bichromatic reverse nearest neighbor. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Wu W, Yang F, Chan CY, Tan KL (2008) FINCH: evaluating reverse k-nearest-neighbor queries on location data. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Xia T, Zhang D, Kanoulas E, Du Y (2005) On computing top-t most influential spatial sites. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Yan D, Wong RCW, Ng W (2011) Efficient methods for finding influential locations with adaptive grids. In: Proceedings of CIKM, pp 1475–1484
Yang C, Lin KI (2001) An index structure for efficient reverse nearest neighbor queries. In: Proceedings of ICDE, pp 485–492
Zhang D, Du Y, Xia T, Tao Y (2006) Progressive computation of the min-dist optimal location query. In: Proceedings of VLDB
Zhang J, Mamoulis N, Papadias D, Tao Y (2004) All-nearest-neighbors queries in spatial databases. In: Proceedings of SSDM, pp 297–306
Zheng K, Huang Z, Zhou A, Zhou X (2011) Discovering the most influential sites over uncertain data: a rank based approach. IEEE TKDE
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61272065) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No. S2012010009311), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, SCUT(Grant No. 2012ZZ0088), and the Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery Project DP130104587. Dr. Rui Zhang was supported by the ARC Future Fellowships Project FT120100832. Zeyi Wen was supported by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Huang, J., Wen, Z. et al. Analysis and evaluation of the top-\(k\) most influential location selection query. Knowl Inf Syst 43, 181–217 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-013-0720-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-013-0720-0