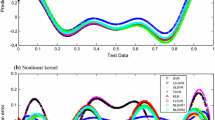
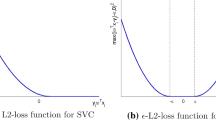
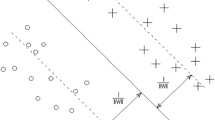
Abstract
In this paper, a novel root finding problem for the Lagrangian support vector regression in 2-norm (LSVR) is formulated in which the number of unknowns becomes the number of training examples. Further, it is proposed to solve it by functional iterative and Newton methods. Under sufficient conditions, we proved their linear rate of convergence. Experiments are performed on a number of synthetic and real-world benchmark datasets, and their results are compared with support vector regression (SVR) and its variants such as least squares SVR and LSVR. Similar generalization performance with improved or comparable learning speed to SVR and its variants demonstrates the usefulness of the proposed formulation solved by the iterative methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasundaram S, Gupta D, Kapil (2014) Lagrangian support vector regression via unconstrained convex minimization. Neural Netw 51:67–79
Balasundaram S, Kapil (2011) Finite Newton method for implicit Lagrangian support vector regression. Int J Knowl Based Intel Eng Syst 15:203–214
Balasundaram S, Kapil (2010) On Lagrangian support vector regression. Exp Syst Appl 37:8784–8792
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: Forecasting and Control. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Chen S, Wang M (2005) Seeking multi-threshold directly from support vectors for image segmentation. Neurocomputing 67:335–344
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel based learning method. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Demsar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2003) Finite Newton method for Lagrangian support vector machine. Neurocomputing 55:39–55
Golub GH, Van Loan CF (1996) Matrix computations, 3rd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Gretton A, Doucet A, Herbrich R, Rayner PJW, Scholkopf B (2001) Support vector regression for black-box system identification. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE workshop on statistical signal processing
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machine. Mach Learn 46:389–422
Hsieh C-J, Chang K-W, Lin C-J, Sathiya Keerthi S, Sundararajan S (2008) A dual coordinate descent method for large scale linear SVM. In: Proceedings of the 25th international conference on machine learning, ACM
Jayadeva, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 29(5):905–910
Joachims T, Ndellec C, Rouveriol (1998) Text categorization with support vector machines: learning with many relevant features. In: European conference on machine learning No. 10, Chemnitz, Germany, pp 137–142
Lee YJ, Hsieh WF, Huang CM (2005) \(\varepsilon \)-SSVR: a smooth support vector machine for \(\varepsilon \)-insensitive regression. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(5):678–685
Lee YJ, Mangasarian OL (2001) SSVM: a smooth support vector machine for classification. Comput Optim Appl 20(1):5–22
Mangasarian OL (2009) A generalized Newton method for absolute value equations. Optim Lett 3:101–108
Mangasarian OL, Musicant DR (2001) Lagrangian support vector machines. J Mach Learn Res 1:161–177
Mangasarian OL, Musicant DR (2001) Active set support vector machine classification. In: Leen TK, Dietterich TG, Tesp V (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 13. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 577–586
Murphy PM, Aha DW (1992) UCI repository of machine learning databases. University of California, Irvine. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn
Musicant DR, Feinberg A (2004) Active set support vector regression. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(2):268–275
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) Training support vector machines: an application to face detection. In: Proceedings of computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 130–136
Pardalos PM, Hansen P (2008) Data mining and mathematical programming, CRM vol 45, AMS
Peng X (2010) Primal twin support vector regression and its sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 73:2846–2858
Peng X (2010) TSVR: An efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Networks 23(3):365–372
Ribeiro B (2002) Kernelized based functions with Minkovsky’s norm for SVM regression. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks, IEEE press, pp 2198–2203
Rockafellar RT (1974) Conjugate duality and optimization. SIAM, Philadelphia
Shalev-Shwartz S, Zhang T (2013) Stochastic dual coordinate ascent methods for regularized loss minimization. J Mach Learn Res 14:567–599
Shawe-Taylor J, Sun S (2011) A review of optimization methodologies in support vector machines. Neurocomputing 74(17):3609–3618
Sjoberg J, Zhang Q, Ljung L, Berveniste A, Delyon B, Glorennec P, Hjalmarsson H, Juditsky A (1995) Nonlinear black-box modeling in system identification: a unified overview. Automatica 31:1691–1724
Souza LGM, Barreto GA (2006) Nonlinear system identification using local ARX models based on the self-organizing map. In: Learning and Nonlinear Models-Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Redes Neurais (SBRN) 4(2):112–123
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Vapnik VN (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Xanthopoulos P, Pardalos PM, Trafalis TB (2013) Robust data mining. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgments
The authors are extremely thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. Mr. Yogendra Meena acknowledges the financial assistance awarded by Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasundaram, S., Meena, Y. A new approach for training Lagrangian support vector regression. Knowl Inf Syst 49, 1097–1129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-016-0928-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-016-0928-x