Abstract
Recent years have witnessed the development of large knowledge bases (KBs). Due to the lack of information about the content and schema semantics of KBs, users are often not able to correctly formulate KB queries that return the intended result. In this paper, we consider the problem of failing RDF queries, i.e., queries that return an empty set of answers. Query relaxation is one cooperative technique proposed to solve this problem. In the context of RDF data, several works proposed query relaxation operators and ranking models for relaxed queries. But none of them tried to find the causes of an RDF query failure given by Minimal Failing Subqueries (MFSs) as well as successful queries that have a maximal number of triple patterns named Ma \(\underline{x}\) imal Succeeding Subqueries (XSSs). Inspired by previous work in the context of relational databases and recommender systems, we propose two complementary approaches to fill this gap. The lattice-based approach (LBA) leverages the theoretical properties of MFSs and XSSs to efficiently explore the subquery lattice of the failing query. The matrix-based approach computes a matrix that records alternative answers to the failing query with the triple patterns they satisfy. The skyline of this matrix directly gives the XSSs of the failing query. This matrix can also be used as an index to improve the performance of LBA. The practical interest of these two approaches are shown via a set of experiments conducted on the LUBM benchmark and a comparative study with baseline and related work algorithms.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Numbers current as of February 2015.
For readability, we use names instead of URIs to identify the query elements.
Given a set of objects described by a list of criteria, a skyline is a subset of objects that are not dominated (in the sense of Pareto) by any other object with respect to some criteria of interest.
To ensure that subqueries of an MFS are successful, it is defined that \([[\emptyset ]]_{D} \ne \emptyset \).
As the semantics of SPARQL is never null-rejecting, contrary to the relational algebra, this expression is not equivalent to:
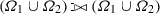 .
.The coalesce function returns the first non-null expression in the list of parameters.
For readability, we shorten the URIs.
MFSs which are only poorly satisfied, i.e., that do not return any answer with at least a satisfaction degree equals to \(\alpha \) (a user-defined threshold).
References
Hoffart J, Suchanek FM, Berberich K, Weikum G (2013) YAGO2: a spatially and temporally enhanced knowledge base from Wikipedia. Artif Intell 194:28–61
Bizer C, Lehmann J, Kobilarov G, Auer S, Becker C, Cyganiak R, Hellmann S (2009) DBpedia—a crystallization point for the web of data. J Web Semant 7(3):154–165
Dong X, Gabrilovich E, Heitz G, Horn W, Lao N, Murphy K, Strohmann T, Sun S, Zhang W (2014) Knowledge vault: a web-scale approach to probabilistic knowledge fusion. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD’14), pp 601–610
Deshpande O, Lamba DS, Tourn M, Das S, Subramaniam S, Rajaraman A, Harinarayan V, Doan A (2013) Building, maintaining, and using knowledge bases: a report from the trenches. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data (SIGMOD’13), pp 1209–1220
Cyganiak R, Wood D, Lanthaler M (2014) RDF 1.1 concepts and abstract syntax. W3C Recommendation 25 February 2014. http://www.w3.org/TR/2014/REC-rdf11-concepts-20140225/
Prud’hommeaux E, Seaborne A (2008) SPARQL query language for RDF. W3C Recommendation 15 January 2008. http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-sparql-query/
Brickley D, Guha R (2014) RDF schema 1.1. W3C recommendation 25 February 2014. http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-schema/
Bechhofer S, van Harmelen F, Hendler J, Horrocks I, McGuinness DL, Patel-Schneider PF, Stein LA (2004) OWL web ontology language reference. W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004. http://www.w3.org/TR/owl-ref
Bollacker KD, Evans C, Paritosh P, Sturge T, Taylor J (2008) Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data (SIGMOD’08), pp 1247–1250
Guo Y, Pan Z, Heflin J (2005) LUBM: a benchmark for OWL knowledge base systems. Web Semant 3(2–3):158–182
Hurtado CA, Poulovassilis A, Wood PT (2008) Query relaxation in RDF. J Data Semant X 10:31–61
Hurtado CA, Poulovassilis A, Wood PT (2009) Ranking approximate answers to semantic web queries. In: Proceeding of the 6th extended semantic web conference (ESWC’09), pp 263–277
Huang H, Liu C, Zhou X (2008) Computing relaxed answers on RDF databases. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on web information systems engineering (WISE’08), pp 163–175
Huang H, Liu C, Zhou X (2012) Approximating query answering on RDF databases. World Wide Web 15(1):89–114
Fokou G, Jean S, Hadjali A (2014) Endowing semantic query languages with advanced relaxation capabilities. In: Proceeding of the 21st international symposium on methodologies for intelligent systems (ISMIS 2014), Roskilde, Denmark, pp 512–517
Poulovassilis A, Wood PT (2010) Combining Approximation and relaxation in semantic web path queries. In: Proceedings of the 9th international semantic web conference (ISWC’10), pp 631–646
Calí A, Frosini R, Poulovassilis A, Wood P (2014) Flexible querying for SPARQL. In: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on ontologies, databases, and applications of semantics (ODBASE’14), pp 473–490
Hogan A, Mellotte M, Powell G, Stampouli D (2012) Towards fuzzy query-relaxation for RDF. In: Proceeding of the 9th extended semantic web conference (ESWC’12), pp 687–702
Elbassuoni S, Ramanath M, Weikum G (2011) Query relaxation for entity-relationship search. In: Proceeding of the 8th extended semantic web conference (ESWC’11), pp 62–76
Dolog P, Stuckenschmidt H, Wache H, Diederich J (2009) Relaxing RDF queries based on user and domain preferences. J Intell Inf Syst 33(3):239–260
Godfrey P (1997) Minimization in cooperative response to failing database queries. Int J Coop Inf Syst 6(2):95–149
Jannach D (2009) Fast computation of query relaxations for knowledge-based recommenders. AI Commun 22(4):235–248
Pérez J, Arenas M, Gutierrez C (2009) Semantics and complexity of SPARQL. ACM Trans Database Syst 34(3):16:1–16:45
Fokou G, Jean S, Hadjali A, Baron M (2015) Cooperative techniques for SPARQL query relaxation in RDF databases. In: Proceeding of the 12th extended semantic web conference (ESWC 2015), pp 237–252
Sakr S, Al-Naymat G (2009) Relational processing of RDF queries: a survey. SIGMOD Rec 38(4):23–28
Galindo-Legaria CA (1992) Algebraic optimization of outerjoin queries. PhD thesis, Harvard University
Gallego MA, Fernández JD, Martínez-Prieto MA, de la Fuente P (2011) An empirical study of real-world SPARQL queries. In: Proceedings of the USEWOD workshop co-located with WWW’11
Cyganiak R (2005) A relational algebra for SPARQL. HP-Labs Technical Report, HPL-2005-170. http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/2005/HPL-2005-170.html
Hose K, Vlachou A (2012) A survey of skyline processing in highly distributed environments. VLDB J 21(3):359–384
Chambi S, Lemire D, Kaser O, Godin R (2014) Better bitmap performance with Roaring bitmaps. CoRR abs/1402.6407
Gombos G, Kiss A (2014) SPARQL query writing with recommendations based on datasets. In: Yamamoto S (ed) Human interface and the management of information. Information and knowledge design and evaluation. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 310–319
Lehmann J, Bühmann L (2011) AutoSPARQL: let users query your knowledge base. In: Proceeding of the 8th Extended Semantic Web Conference (ESWC’11), pp 63–79
Campinas S (2014) Live SPARQL auto-completion. In: Proceedings of the 13th international semantic web conference (ISWC’14 Posters & Demos), pp 477–480
Möller K, Ambrus O, Josan L, Handschuh S (2008) A visual interface for building SPARQL queries in Konduit. In: Proceedings of the 7th international semantic web conference (ISWC’08 Posters & Demos)
Clark L (2010) SPARQL views: a visual SPARQL query builder for Drupal. In: Proceedings of the 9th international semantic web conference (ISWC’10 Posters & Demos)
Bosc P, Hadjali A, Pivert O (2009) Incremental controlled relaxation of failing flexible queries. J Intell Inf Syst 33(3):261–283
Pivert O, Smits G, Hadjali A, Jaudoin H (2011) Efficient detection of minimal failing subqueries in a fuzzy querying context. In: Proceedings of the 15th East-European conference on advances in databases and information systems (ADBIS’11), pp 243–256
Pivert O, Smits G (2015) How to efficiently diagnose and repair fuzzy database queries that fail. In: Fifty years of fuzzy logic and its applications, studies in fuzziness and soft computing, pp 499–517
McSherry D (2004) Incremental relaxation of unsuccessful queries. In: Advances in case-based reasoning, volume 3155, pp 131–148
Bidoit N, Herschel M, Tzompanaki K (2014) Query-based why-not provenance with NedExplain. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on extending database technology (EDBT 2014), pp 145–156
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers as well as Patrice Naudin and Pascal Richard for their very useful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fokou, G., Jean, S., Hadjali, A. et al. Handling failing RDF queries: from diagnosis to relaxation. Knowl Inf Syst 50, 167–195 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-016-0941-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-016-0941-0





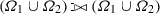 .
.