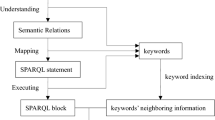
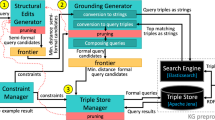
Abstract
SPARQL, the W3C standard for RDF query languages, has gained significant popularity in recent years. An increasing amount of effort is currently being exerted to improve the functionality and usability of SPARQL-based search engines. However, explaining missing items in the results of SPARQL queries or the so-called why-not question has not received sufficient attention. In this study, we first formalize why-not questions on SPARQL queries and then propose a novel explanation model, called answering why-not questions on SPARQL (ANNA) to answer why-not questions using a divide-and-conquer strategy. ANNA adopts a graph-based approach and an operator-based approach to generate logical explanations at the triple pattern level and the query operator level, respectively, which helps users refine their initial queries. Extensive experimental results on two real-world RDF datasets show that the proposed model and algorithms can provide high-quality explanations in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency.























Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Batman was released in 1989. The Nightmare Before Christmas was written and produced by Tim Burton, but its director was Henry Selick.
A demo system of ANNA has been presented at ISWC 2015.
http://wiki.dbpedia.org/Datasets, released in September, 2015.
References
Baget JF, Benferhat S, Bouraoui Z, Croitoru M, Mugnier ML, Papini O, Rocher S, Tabia K (2016) A general modifier-based framework for inconsistency-tolerant query answering. In: KR, pp 513–516
Bhowmick SS, Sun A, Truong BQ (2013) Why not, wine? towards answering why-not questions in social image search. In: Proceedings of the ACMMM. ACM, pp 917–926
Bidoit N, Herschel M, Tzompanaki K (2014) Query-based why-not provenance with nedexplain. In: Proceedings of the EDBT
Bienvenu M, Bourgaux C, Goasdoué F (2016) Explaining inconsistency-tolerant query answering over description logic knowledge bases. In: AAAI, pp 900–906
Bienvenu M, Rosati R (2013) Tractable approximations of consistent query answering for robust ontology-based data access. In: IJCAI, pp 775–781
Calvanese D, Ortiz M, Simkus M, Stefanoni G (2013) Reasoning about explanations for negative query answers in dl-lite. J Artif Intell Res 48:635–669
Chapman A, Jagadish H (2009) Why not? In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD. ACM, pp 523–534
Chen L, Lin X, Hu H, Jensen CS, Xu J (2015) Answering why-not questions on spatial keyword top-k queries. In: Proceedings of the ICDE. IEEE, pp 279–290
Cui Y, Widom J (2003) Lineage tracing for general data warehouse transformations. VLDB J 12(1):41–58
Damásio CV, Analyti A, Antoniou G (2012) Provenance for sparql queries. In: Proceedings of the ISWC. Springer, pp 625–640
Dividino R, Sizov S, Staab S, Schueler B (2009) Querying for provenance, trust, uncertainty and other meta knowledge in RDF. Web Semant Sci Serv Agents World Wide Web 7(3):204–219
Eiter T, Fink M, Schüller P, Weinzierl A (2014) Finding explanations of inconsistency in multi-context systems. Artif Intell 216:233–274
Elbassuoni S, Ramanath M, Schenkel R, Sydow M, Weikum G (2009) Language-model-based ranking for queries on RDF-graphs. In: Proceedings of the CIKM. ACM, pp 977–986
Elbassuoni S, Ramanath M, Weikum G (2011) Query relaxation for entity-relationship search. In: Proceedings of the ESWC. Springer, pp 62–76
Gallego MA, Fernández JD, Martínez-Prieto MA, de la Fuente P (2011) An empirical study of real-world sparql queries. In: Proceedings of the USEWOD2011, Hydebarabad, India
Gao Y, Liu Q, Chen G, Zheng B, Zhou L (2015) Answering why-not questions on reverse top-k queries. In: Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, vol. 8. VLDB Endowment, pp 738–749
Group, W.C.S.W. (2013) Sparql 1.1 overview. http://www.w3.org/TR/sparql11-overview/
He Z, Lo E (2014) Answering why-not questions on top-k queries. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(6):1300–1315
Herschel M, Hernández MA (2010) Explaining missing answers to spjua queries. In: Proceedings of the VLDB endowment, vol. 3. VLDB Endowment, pp 185–196
Huang J, Chen T, Doan A, Naughton JF (2008) On the provenance of non-answers to queries over extracted data. In: Proceedings of the VLDB endowment, vol. 1. VLDB Endowment, pp 736–747
Huang H, Liu C, Zhou X (2008) Computing relaxed answers on RDF databases. In: Proceedings of the WISE. Springer, pp 163–175 (2008)
Hurtado CA, Poulovassilis A, Wood PT (2006) A relaxed approach to RDF querying. In: Proceedings of the ISWC. Springer, pp 314–328
Islam MS, Zhou R, Liu C (2013) On answering why-not questions in reverse skyline queries. In: Proceedings of the ICDE. IEEE, pp 973–984
Islam MS, Liu C, Li J (2015) Efficient answering of why-not questions in similar graph matching. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(10):2672–2686
Kiefer C, Bernstein A, Lee HJ, Klein M, Stocker M (2007) Semantic process retrieval with iSPARQL. In: Proceedings of the ESWC. Springer, pp 609–623
Lembo D, Lenzerini M, Rosati R, Ruzzi M, Savo DF (2015) Inconsistency-tolerant query answering in ontology-based data access. Web Semant Sci Serv Agents World Wide Web 33:3–29
Miltersen PB, Radhakrishnan J, Wegener I (2005) On converting CNF to DNF. Theor Comput Sci 347(1):325–335
Pérez J, Arenas M, Gutierrez C (2009) Semantics and complexity of sparql. ACM Trans Database Syst 34:1–45
Saleem M, Ali MI, Hogan A, Mehmood Q, Ngomo ACN (2015) LSQ: the linked SPARQL queries dataset. In: ISWC, pp 121–131
Schmidt M, Meier M, Lausen G (2010) Foundations of SPARQL query optimization. In: Proceedings of the ICDT. ACM, pp 4–33
ten Cate B, Civili C, Sherkhonov E, Tan WC (2015) High-level why-not explanations using ontologies. In: Proceedings of the ACM PODS. ACM, pp 31–43
Theoharis Y, Fundulaki I, Karvounarakis G, Christophides V (2011) On provenance of queries on semantic web data. IEEE Internet Comput 15(1):31–39
Tran QT, Chan CY (2010) How to conquer why-not questions. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD. ACM, pp 15–26
Vidal ME, Ruckhaus E, Lampo T, Martínez A, Sierra J, Polleres A (2010) Efficiently joining group patterns in sparql queries. In: Proceedings of the ESWC. Springer, pp 228–242
Wang M, Chen W, Wang S, Liu J, Li X, Stantic B (2017) Answering why-not questions on semantic multimedia queries. Multimed Tools Appl 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/11042-017-5151-6
Yao S, Liu J, Wang M, Wei B, Chen X (2015) Anna: answering why-not questions for SPARQL. In Proceedings of the ISWC (Demos)
Zhang X, Xiao G, Lin Z, Van den Bussche J (2014) Inconsistency-tolerant reasoning with OWL DL. Int J Approx Reason 55(2):557–584
Zhou X, Gaugaz J, Balke WT, Nejdl W (2007) Query relaxation using malleable schemas. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD. ACM, pp 545–556
Acknowledgements
This work is sponsored by the Fundamental Theory and Applications of Big Data with Knowledge Engineering under the National Key Research and Development Program of China with Grant No. 2016YFB1000903; National Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61721002, 61672419, 61672418, 61532004 and 61532015; MOE Research Center for Online Education Funds under Grant No.2016YB165; Ministry of Education Innovation Research Team No. IRT17R86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Liu, J., Wei, B. et al. Answering why-not questions on SPARQL queries. Knowl Inf Syst 58, 169–208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-018-1155-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-018-1155-4