Abstract
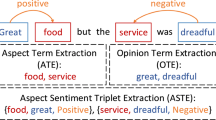
Aspect extraction and opinion extraction are two fundamental subtasks in aspect-based sentiment analysis. Many methods extract aspect terms or opinion terms but ignore the relationships between them. However, such relationships are crucial for downstream tasks, such as sentiment classification and commodity recommendation. Recently, methods have been proposed to extract both terms jointly; however, they fail to extract them as pairs. In this paper, we explore the aspect–opinion pair extraction task that aims to extract aspect and opinion terms in pairs. To carry out this task, we propose a span-based relational graph transformer network that consists of a span generator, a span classifier, and a relation detector. The span generator enumerates all possible spans to generate the candidates for aspect or opinion terms and filters non-aspects or non-opinions terms, while the relation classifier extracts aspect–opinion pairs. We propose a relational graph convolutional network to capture the dependent relationships between aspect and opinion terms. Extensive experiments show that the proposed model achieves the state-of-the-art performance using four benchmark datasets.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cambria E (2016) Affect computing and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell Syst 31(2):102–107
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Pavlopoulos J et al (2014) SemEval-2014 task 4: aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on semantic evaluation, pp 27–35
Liu K, Xu L, Zhao J (2015) Co-extracting opinion targets and opinion words from online reviews based on the word alignment model. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(3):636–650
He R, Lee WS, Ng HT et al (2017) An unsupervised neural attention model for aspect extraction. In: Proceedings of the 55th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 388–397
Xu H, Liu B, Shu L et al (2018) Double embeddings and CNN-based sequence labeling for aspect extraction. In: Proceedings of the 56th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 592–598
Fan Z, Wu Z, Dai XY, Huang S et al (2019) Target-oriented opinion words extraction with target-fused neural sequence labeling. In: Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies, pp 2509–2518
Wu Z, Zhao F, Dai XY et al (2020) Latent opinions transfer network for target-oriented opinion words extraction. In: The thirty-fourth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 9298–9305
Veyseh A, Nouri N, Dernoncourt F et al (2020) Introducing syntactic structures into target opinion word extraction with deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 8947–8956
Liu P, Joty S, Meng H (2015) Fine-grained opinion mining with recurrent neural networks and word embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 1433–1443
Pereg O, Korat D, Wasserblat M (2020) Syntactically aware cross-domain aspect and opinion terms extraction. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on computational linguistics, pp 1772–1777
Wang W, Pan SJ (2018) Recursive neural structural correspondence network for cross-domain aspect and opinion co-extraction. In: Proceedings of the 56th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 2171–2181
Yu J, Jiang J, Xia R (2019) Global inference for aspect and opinion terms co-extraction based on multi-task neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 27(1):168–177
Wang W, Pan S, Dahlmeier D et al (2017) Coupled multi-layer attentions for co-extraction of aspect and opinion terms. In: Thirty-first AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3316–3322
Zhao H, Huang L, Zhang R et al (2020) SpanMlt: a span-based multi-task learning framework for pair-wise aspect and opinion terms extraction. In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 3239–3248
Wang H, Zhang C, Yin H et al (2016) A unified framework for fine-grained opinion mining from online reviews. In: Hawaii international conference on system sciences. IEEE, pp 1134–1143
Hu M, Peng Y, Huang Z et al (2019) Open-domain targeted sentiment analysis via span-based extraction and classification. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 537–546
Wu Z, Ying C, Zhao F et al (2020) Grid tagging scheme for end-to-end fine-grained opinion extraction. In: Findings of the association for computational linguistics: EMNLP, pp 2576–2585
Liu B (2012) Sentiment analysis and opinion mining. Synth Lect Hum Lang Technol 5(1):1–167
Liang B, Su H, Gui L, Cambria E, Xu R (2022) Aspect-based sentiment analysis via affective knowledge enhanced graph convolutional network. Knowl Based Syst 235:107643
Kumar AJ, Trueman TE, Cambria E (2021) A convolutional stacked bidirectional LSTM with a multiplicative attention mechanism for aspect category and sentiment detection. Cogn Comput 13:1423–1432
Valdivia A, Luzón MV, Cambria E, Herrera F (2018) Consensus vote models for detecting and filtering neutrality in sentiment analysis. Inf Fusion 44:126–135
Wang Z, Ho SB, Cambria E (2020) Multi-level fine-scaled sentiment sensing with ambivalence handling. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 28(4):683–697
Cambria E, Li Y, Xing FZ, Poria S, Kwok K (2020) SenticNet 6: ensemble application of symbolic and subsymbolic AI for sentiment analysis. In: The 29th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, pp 105–113
Li W, Shao W, Ji S, Cambria E (2022) BiERU: bidirectional emotional recurrent unit for conversational sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing 467:73–82
Liu K, Xu L, Zhao J (2014) Extracting opinion targets and opinion words from online reviews with graph co-ranking. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 314–324
Kumar A, Kohail S, Kumar A et al (2016) IIT-TUDA at SemEval-2016 task 5: beyond sentiment lexicon: combining domain dependency and distributional semantics features for aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation, pp 1129–1135
Ma Y, Peng H, Cambria E (2018) Targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis via embedding common sense knowledge into an attentive LSTM. In: Proceedings of the thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 5876–5883
Movahedi S, Ghadery E, Faili H et al (2019) Aspect category detection via topic-attention network. Computing Research Repository (CoRR) arXiv:1901.01183
Qiu G, Liu B, Bu J et al (2011) Opinion word expansion and target extraction through double propagation. Comput Linguist 37(1):9–27
Chen S, Liu J, Wang Y et al (2020) Synchronous double-channel recurrent network for aspect-opinion pair extraction. In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 6515–6524
Li Z, Li X, Wei Y et al (2019) Transferable end-to-end aspect-based sentiment analysis with selective adversarial learning. In: Proceedings of the 2019 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing and the 9th international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 4589–4599
Eberts M, Ulges A (2020) Span-based joint entity and relation extraction with transformer pre-training. In: 24th European conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2006–2013
Velickovic P, Cucurull G, Casanova A et al (2018) Graph attention networks. In: 6th international conference on learning representations
Hamilton LW, Ying Z, Leskovec J (2017) Inductive representation learning on large graphs. In: Annual conference on neural information processing systems, pp 1024–1034
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and feedbacks. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1811264, 62062027, and 61966009), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (Nos. 2020GXNSFAA159012 and 2018GXNSFDA281049), the Science and Technology Major Project of Guangxi Province (No. AA19046004), the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (No. YCBZ2021069), and the project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Trusted Software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, C., Lin, Y. et al. Span-based relational graph transformer network for aspect–opinion pair extraction. Knowl Inf Syst 64, 1305–1322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-022-01675-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-022-01675-8