Abstract
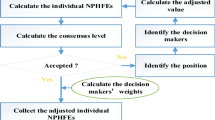
The purposes of the study: to address the situation where multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problems with hesitant fuzzy elements (HFEs), this study develops group decision-making method considering the individuals best and worst consensus levels simultaneously. Procedures: first, the concepts of individual best and worst consensus levels are proposed, and then, the concept of acceptable consensus level is developed. Second, several optimization models are constructed for improving the consensus levels. Third, the proposed consensus checking and improving processes are extended to incomplete evaluation information. Fourth, an algorithm is designed for deriving the priority weights of decision-makers. Finally, an illustrative example in conjunction with comparative analysis is provided. Findings: the concept of acceptable individual consensus level with HFEs not only overcomes the shortcoming of difficult to achieve owing to too restricted, but also the loss of information owing to too loose. The consensus improving process considers all the evaluation information and avoids the loss of information. Conclusions: Several programming models are constructed to improve the consensus level with HFEs. This provides the direction of the decision-makers to revise their evaluation values, and the consensus improving process is time-saving and easy to extend to incomplete evaluation information.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram M, Luqman A, Kahraman C (2021) Hesitant pythagorean fuzzy ELECTRE-II method for multi-criteria decision-making problems. Appl Soft Comput 108:107479
Atanassov K, Pasi G, Yager R (2005) Intuitionistic fuzzy interpretations of multi-criteria multi-person and multi-measurement tool decision making. Int J Syst Sci 14:859–868
Büyüközkan G, Güler M (2021) A combined hesitant fuzzy MCDM approach for supply chain analytics tool evaluation. Appl Soft Comput 112:107812
Bustince H, Kacprzyk J, Mohedano V (2000) Intuitionistic fuzzy generators application to intuitionistic fuzzy complementation. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114:485–504
Deveci M, Oner S, Ciftci M et al (2022) Interval type-2 hesitant fuzzy entropy-based WASPAS approach for aircraft type selection. Appl Soft Comput 114:108076
Dombi J, Jónás T (2020) Ranking trapezoidal fuzzy numbers using a parametric relation pair. Fuzzy Sets Syst 399:20–43
Dong Y, Xu Y, Li H et al (2010) The OWA-based consensus operator under linguistic representation models using position indexes. Eur J Oper Res 203:455–463
Li C, Rodríguez RM, Martínez L et al (2018) Consistency of hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations: an interval consistency index. Inf Sci 432:347–361
Li H, Ji Y, Gong Z et al (2021a) Two-stage stochastic minimum cost consensus models with asymmetric adjustment costs. Inf Fusion 71:77–96
Li J, Chen Q (2020) An outranking method for multicriteria decision making with probabilistic hesitant information. Expert Syst 37:e12513
Li J, Niu L, Chen Q et al (2021b) Approaches for multicriteria decision-making based on the hesitant fuzzy best–worst method. Complex Intell Syst 7:2617–2634
Li J, Niu L, Chen Q et al (2022a) Group decision making method with hesitant fuzzy preference relations based on additive consistency and consensus. Complex Intell Syst 8:2023–2225
Li J, Niu L, Ye J et al (2022b) Decision-making models based on satisfaction degree with incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relation. Soft Comput 26:3129–3145
Li J, Wang J, Hu J (2019) Consensus building for hesitant fuzzy preference relations with multiplicative consistency. Comput Ind Eng 128:387–400
Liang D, Darko A, Xu Z et al (2019a) Aggregation of dual hesitant fuzzy heterogenous related information with extended Bonferroni mean and its application to MULTIMOORA. Comput Ind Eng 135:156–176
Liang W, Zhao G, Wang X et al (2019b) Assessing the rockburst risk for deep shafts via distance-based multi-criteria decision making approaches with hesitant fuzzy information. Eng Geol 260:105211
Liao Z, Liao H, Tang M et al (2020) A Choquet integral-based hesitant fuzzy gained and lost dominance score method for multi-criteria group decision making considering the risk preferences of experts: case study of higher business education evaluation. Inf Fusion 62:121–133
Liu H, Jiang L (2020) Optimizing consistency and consensus improvement process for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations and the application in group decision making. Inf Fusion 56:114–127
Liu H, Xu Z, Liao H (2016) The multiplicative consistency index of hesitant fuzzy preference relation. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 24:82–93
Liu P, Zhang X, Pedrycz W (2021a) A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy linguistic group decision-making in the framework of Dempster–Shafer evidence theory. Knowl-Based Syst 212:106559
Liu X, Wang Z, Zhang S et al (2021b) Novel correlation coefficient between hesitant fuzzy sets with application to medical diagnosis. Expert Syst Appl 183:115393
Liu X, Xu Y, Gong Z et al (2022) Democratic consensus reaching process for multi-person multi-criteria large scale decision making considering participants’ individual attributes and concerns. Inf Fusion 77:220–232
Lu Y, Xu Y, Huang J et al (2022) Social network clustering and consensus-based distrust behaviors management for large-scale group decision-making with incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl Soft Comput 117:108373
Meng F, An Q (2017) A new approach for group decision making method with hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 127:1–15
Meng F, Chen S, Tang J (2020) Group decision making based on acceptable multiplicative consistency of hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Inf Sci 524:77–96
Mishra A, Rani P, Pardasani K et al (2019) A novel hesitant fuzzy WASPAS method for assessment of green supplier problem based on exponential information measures. J Clean Prod 238:117901
Mo X, Zhao H, Xu Z (2020) Feature-based hesitant fuzzy aggregation method for satisfaction with life scale. Appl Soft Comput 94:106493
Mu Z, Zeng S, Baležentis T (2015) A novel aggregation principle for hesitant fuzzy elements. Knowl-Based Syst 84:134–143
Phu N, Hung N, Ahmadian A et al (2022) Limit properties in the metric semi-linear space of picture fuzzy numbers. Soft Comput 26:5481–5496
Rodríguez R, Labella Á, Sesma-Sara M et al (2021) A cohesion-driven consensus reaching process for large scale group decision making under a hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets environment. Comput Ind Eng 155:107158
Sen S, Patra K, Mondal S (2016) Fuzzy risk analysis in familial breast cancer using a similarity measure of interval-valued fuzzy numbers. Pac Sci Rev A Nat Sci Eng 18:203–221
Song Y, Li G (2019) Handling group decision-making model with incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations and its application in medical decision. Soft Comput 23:6657–6666
Tan X, Zhu J, Palomares I et al (2022) On consensus reaching process based on social network analysis in uncertain linguistic group decision making: exploring limited trust propagation and preference modification attitudes. Inf Fusion 78:180–198
Tang J, An Q, Meng F et al (2017) A natural method for ranking objects from hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 16:1611–1646
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Fuzz-Ieee
Vassilev P, Atanassov K (2019) Extensions and modifications of intuitionistic fuzzy sets. "Prof. Marin Drinov" Academic Publishing House, Sofia
Wan S, Yan J, Dong J (2022a) Personalized individual semantics based consensus reaching process for large-scale group decision making with probabilistic linguistic preference relations and application to COVID-19 surveillance. Expert Syst Appl 191:116328
Wan S, Zou W, Dong J et al (2022b) A consensual method for multi-criteria group decision-making with linguistic intuitionistic information. Inf Sci 582:797–832
Wang F (2021) Preference degree of triangular fuzzy numbers and its application to multi-attribute group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 178:114982
Wang Z, Rodríguez R, Wang Y et al (2021) A two-stage minimum adjustment consensus model for large scale decision making based on reliability modeled by two-dimension 2-tuple linguistic information. Comput Ind Eng 151:106973
Wu J, Dai L, Chiclana F et al (2018a) A minimum adjustment cost feedback mechanism based consensus model for group decision making under social network with distributed linguistic trust. Inf Fusion 41:232–242
Wu N, Xu Y, Liu X et al (2020) Water–energy–food nexus evaluation with a social network group decision making approach based on hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl Soft Comput 93:106363
Wu Q, Liu X, Qin J et al (2021) Multi-criteria group decision-making for portfolio allocation with consensus reaching process under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Inf Sci 570:668–688
Wu Z, Xu J (2018b) A consensus model for large-scale group decision making with hesitant fuzzy information and changeable clusters. Inf Fusion 41:217–231
Xia M, Xu Z (2011) Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision making. Int J Approx Reason 52:395–407
Xiao J, Wang X, Zhang H (2022) Coping with diversity ratings in prioritizing design requirements in quality function deployment: a consensus-based approach with minimum-maximum adjustments. Comput Ind Eng 163:107799
Xu Y, Cabrerizo F, Herrera-Viedma E (2017) A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy preference relations and its application in water allocation management. Appl Soft Comput 58:265–284
Xu Y, Dai W, Huang J et al (2022) Some models to manage additive consistency and derive priority weights from hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Inf Sci 586:450–467
Xu Y, Liu X, Xu L (2020) A dynamic expert contribution-based consensus model for hesitant fuzzy group decision making with an application to water resources allocation selection. Soft Comput 24:4693–4708
Zeng W, Cui H, Liu Y et al (2022) Novel distance measure between intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application in pattern recognition. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 19:127–137
Zhang H, Zhao S, Kou G et al (2020a) An overview on feedback mechanisms with minimum adjustment or cost in consensus reaching in group decision making: research paradigms and challenges. Inf Fusion 60:65–79
Zhang X, Li J, Mi J (2022a) Dynamic updating approximations approach to multi-granulation interval-valued hesitant fuzzy information systems with time-evolving attributes. Knowl-Based Syst 238:107809
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gao L et al (2022b) Consensus reaching with trust evolution in social network group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 188:116022
Zhang Z (2016) Deriving the priority weights from incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations based on multiplicative consistency. Appl Soft Comput 46:37–59
Zhang Z, Kou X, Dong Q (2018a) Additive consistency analysis and improvement for hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Expert Syst Appl 98:118–128
Zhang Z, Kou X, Yu W et al (2018b) On priority weights and consistency for incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 143:115–126
Zhang Z, Pedrycz W (2020b) Iterative algorithms to manage the consistency and consensus for group decision-making with hesitant multiplicative preference relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28:2944–2957
Zhang Z, Wang C, Tian X (2015a) A decision support model for group decision making with hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 86:77–101
Zhang Z, Wang C, Tian X (2015b) Multi-criteria group decision making with incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl Soft Comput 36:1–23
Zhou X, Wang L, Liao H et al (2019) A prospect theory-based group decision approach considering consensus for portfolio selection with hesitant fuzzy information. Knowl-Based Syst 168:28–38
Zhu B, Xu Z (2014a) Analytic hierarchy process-hesitant group decision making. Eur J Oper Res 239:794–801
Zhu B, Xu Z, Xu J (2014b) Deriving a ranking from hesitant fuzzy preference relations under group decision making. IEEE Trans Cybern 44:1328–1337
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their insightful and constructive comments and suggestions that have led to an improved version of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.72061026), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No. 2020GXNSFAA297239), the Science and Technology Plan of Guangxi (No. gui ke AD20238006) and Young Teachers’ Basic Scientific Research Ability in Universities of Guangxi (Nos. 2022KY0387, 2021KY1563 and 2021KY1560).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Jian Li, Li-li Niu, Qiongxia Chen, Feilong Li, Limei Wei and Zhong-xing Wang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Niu, Ll., Chen, Q. et al. A consensus reaching process with hesitant fuzzy elements considers the individuals best and worst consensus levels. Knowl Inf Syst 65, 3665–3693 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-023-01874-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-023-01874-x