Abstract
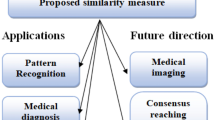
This article proposes novel cosine and weighted cosine similarity measures based on intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy rough sets and examines their fundamental characteristics. Similarity measures are crucial and advantageous tools that have a broad range of applications in decision making, data mining, medical diagnosis, and pattern recognition. To demonstrate the validity of the proposed similarity measures, an illustrative example in the evaluation of volatile currency in Pakistan is presented to verify the efficacy of our approach. Additionally, the rankings of suggested similarity measures are compared to those identified in the literature. The findings demonstrate that the innovative similarity measures lead in consistent patterns of ranking. The comparison confirms that the suggested similarity measures methodologies may achieve precise classification results and are applicable to real-world challenges involving hesitancy and uncertainty.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are available in the manuscript.
References
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Nakamura A (1988) Fuzzy rough sets. Note Mult Valued Log Jpn 9(8):1–8
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17(2–3):191–209
Cornelis C, De Cock M, Kerre EE (2003) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets: at the crossroads of imperfect knowledge. Expert Syst 20(5):260–270
Hung WL, Yang MS (2004) Similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets based on Hausdorff distance. Pattern Recogn Lett 25(14):1603–1611
Yong D, Wenkang S, Feng D, Qi L (2004) A new similarity measure of generalized fuzzy numbers and its application to pattern recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 25(8):875–883
Mitchell HB (2003) On the Dengfeng–Chuntian similarity measure and its application to pattern recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(16):3101–3104
Liang Z, Shi P (2003) Similarity measures on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(15):2687–2693
Xu Z (2007) Some similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to multiple attribute decision making. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 6(2):109–121
Mahmood T, Ur Rehman U (2022) A novel approach towards bipolar complex fuzzy sets and their applications in generalized similarity measures. Int J Intell Syst 37(1):535–567
Ali Z, Mahmood T, Yang MS (2020) TOPSIS method based on complex spherical fuzzy sets with Bonferroni mean operators. Mathematics 8(10):1739
Rehman UU, Mahmood T (2021) Picture fuzzy N-soft sets and their applications in decision making problems. Fuzzy Inf Eng 13(3):335–367
Mahmood T (2022) The generalized dice similarity measures for bipolar complex fuzzy set and its applications to pattern recognition and medical diagnosis. Comput Appl Math 41(6):1–30
Jiang H, Hu BQ (2021) A decision-theoretic fuzzy rough set in hesitant fuzzy information systems and its application in multi-attribute decision making. Inf Sci 579:103–127
Xu ZS, Chen J (2008) An overview of distance and similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 16(04):529–555
Xu Z, Yager RR (2009) Intuitionistic and interval-valued intutionistic fuzzy preference relations and their measures of similarity for the evaluation of agreement within a group. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 8(2):123–139
Yang X, Song X, Qi Y, Yang J (2014) Constructive and axiomatic approaches to hesitant fuzzy rough set. Soft Comput 18(6):1067–1077
Zhang H, Shu L, Liao S (2017) Hesitant fuzzy rough set over two universes and its application in decision making. Soft Comput 21(7):1803–1816
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In: 2009 IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems. IEEE, pp 1378–1382
Atanassov KT (1999) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets, vol 35. ISBN : 978-3-7908-2463-6
Beg I, Rashid T (2014) Group decision making using intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Fuzzy Log Intell Syst 14(3):181–187
Chinram R, Hussain A, Mahmood T, Ali MI (2021) EDAS method for multi-criteria group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy rough aggregation operators. IEEE Access 9:10199–10216
Bhattacharya A (1946) On a measure of divergence between two multinomial populations. Sankhy\(\bar{{\rm a}}\): the indian journal of statistics, pp 401–406
Ye J (2011) Cosine similarity measures for intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications. Math Comput Model 53(1–2):91–97
Malik SU (2014) Determinants of currency depreciation in Pakistan
Raza SA, Afshan S (2017) Determinants of exchange rate in Pakistan: revisited with structural break testing. Glob Bus Rev 18(4):825–848
https://www.sbp.org.pk/ and https://www.pbs.gov.pk/trade-summary
Pramanik S, Mondal K (2015) Cotangent similarity measure of rough neutrosophic sets and its application to medical diagnosis. J New Theory 4:90–102
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Umm Al-Qura University for supporting this work by Grant Code: (23UQU4350518DSR001).
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant conflict of interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Attaullah, Ullah, S., Drissi, R. et al. A new type of cosine similarity measures based on intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy rough sets for the evaluation of volatile currency: evidence from the Pakistan economy. Knowl Inf Syst 65, 4741–4758 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-023-01909-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-023-01909-3