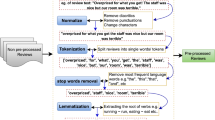
Abstract
Recently, the impact of product or service reviews on customers' purchasing decisions has become increasingly significant in online businesses. Consequently, manipulating reviews for fame or profit has become prevalent, with some businesses resorting to paying fake reviewers to post spam reviews. Given the importance of reviews in decision-making, detecting fake reviews is crucial to ensure fair competition and sustainable e-business practices. Although significant efforts have been made in the last decade to distinguish credible reviews from fake ones, it remains challenging. Our literature review has identified several gaps in the existing research: (1) most fake review detection techniques have been proposed for high-resource languages such as English and Chinese, and few studies have investigated low-resource and multilingual fake review detection, (2) there is a lack of research on deceptive review detection for reviews based on language code-switching (code-mix), (3) current multi-feature integration techniques extract review representations independently, ignoring correlations between them, and (4) there is a lack of a consolidated model that can mutually learn from review emotion, coarse-grained (overall rating), and fine-grained (aspect ratings) features to supplement the problem of sentiment and overall rating inconsistency. In light of these gaps, this study aims to provide an in-depth literature analysis describing strengths and weaknesses, open issues, and future research directions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
You L, Peng Q, Xiong Z, He D, Qiu M, Zhang X (2020) Integrating aspect analysis and local outlier factor for intelligent review spam detection. Futur Gener Comput Syst 102:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.07.044
Khan ZY, et al (2021) A deep hybrid model for recommendation by jointly leveraging ratings, reviews and metadata information. Eng Appl Artif Intell 97:104066
Manaskasemsak B, Tantisuwankul J, Rungsawang A (2021) Fake review and reviewer detection through behavioral graph partitioning integrating deep neural network. Neural Comput Appl 1:1169–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05948-1
Vidanagama DU, Silva TP, Karunananda AS (2020) Deceptive consumer review detection: a survey. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):1323–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09697-5
Duma RA, et al (2024) DHMFRD–TER: a deep hybrid model for fake review detection incorporating review texts, emotions, and ratings. Multimedia Tools Appl 83(2):4533–4549
Liu Y, Wang L, Shi T, Li J (2022) Detection of spam reviews through a hierarchical attention architecture with N-gram CNN and Bi-LSTM. Inf Syst 103:101865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2021.101865
Ren J, Yeoh W, Shan Ee M, Popovič A (2018) Online consumer reviews and sales: examining the chicken-egg relationships. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol 69(3):449–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.23967
Yu S, Ren J, Li S, Naseriparsa M, Xia F (2022) Graph learning for fake review detection. Front Artif Intell 5:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2022.922589
Ellson A (2021) A third of TripAdvisor reviews are fake’ as cheats buy five stars | The Times, Accsessed December, 20 2021,” 2018. https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/hotel-and-caf-cheats-are-caught-trying-to-buy-tripadvisor-stars-027fbcwc8. Accessed 20 Dec 2021.
Bhuvaneshwari P, Rao AN, Robinson YH (2021) Spam review detection using self attention based CNN and bi-directional LSTM. Multimed Tools Appl 80(12):18107–18124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10602-y
Luca M (2016) Reviews, reputation, and revenue : the case of Yelp.com.com (March 15, 2016). Harvard Bus. Sch. NOM Unit Work. Pap., pp 12–016.
Crawford M, Khoshgoftaar TM, Prusa JD, Richter AN, Al Najada H (2015) Survey of review spam detection using machine learning techniques. J Big Data. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-015-0029-9
Palmer A (2023) People are using A.I. chatbots to write Amazon reviews. CNBC, 2023. https://www.cnbc.com/2023/04/25/amazon-reviews-are-being-written-by-ai-chatbots.html. Accessed 16 Feb 2024
Goldrich MJ (2024) The rise of AI-generated fake reviews: what you need to know. VIVANDER ADVISORS. https://vivanderadvisors.com/the-rise-of-ai-generated-fake-reviews-what-you-need-to-know/. Accessed 16 Feb 2024
Wu J (2024) AI-generated fake reviews: a new challenge for online trust. Medium. https://bootcamp.uxdesign.cc/ai-generated-fake-reviews-a-new-challenge-for-online-trust-87e6ed825a80. Accessed 17 Feb 2024
Gambetti A, Han Q (2023) Combat AI with AI: counteract machine-generated fake restaurant reviews on social media. vol. 1, no. 1. Association for Computing Machinery, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.07731
Krishna K, Song Y, Karpinska M, Wieting J, Iyyer M (2023) Paraphrasing evades detectors of AI-generated text, but retrieval is an effective defense. no. NeurIPS, pp. 1–32. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13408
Jindal N, Liu B (2008) Opinion spam and analysis. In: WSDM’08 - Proc. 2008 Int. Conf. Web Search Data Min., pp 219–229. https://doi.org/10.1145/1341531.1341560
Mewada A, Dewang RK (2021) Research on false review detection Methods: A state-of-the-art review. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 18:100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.07.021
Ren Y (2014) Positive unlabeled learning for deceptive reviews detection. pp 488–498
Heydari A, Tavakoli MA, Salim N, Heydari Z (2015) Detection of review spam: a survey. Expert Syst Appl 42(7):3634–3642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.12.029
Patel NA, Patel R (2018) A survey on fake review detection using machine learning techniques. In: 2018 4th Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Autom. ICCCA 2018, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCAA.2018.8777594.
Ren Y, Ji D (2019) Learning to detect deceptive opinion spam: a survey. IEEE Access 7:42934–42945. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908495
Mohawesh R et al (2021) Fake reviews detection: a survey. IEEE Access 9:65771–65802. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075573
Maurya SK, Singh D, Maurya AK (2022) Deceptive opinion spam detection approaches: a literature survey. Appl Intell 53:2189–2234
He L, Wang X, Chen H, Xu G (2022) Online spam review detection : a survey of literature. Hum Centric Intell Syst 2:14–30
Kitchenham B et al (2010) Systematic literature reviews in software engineering-a tertiary study. Inf Softw Technol 52(8):792–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2010.03.006
Page MJ et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Crawford M, Khoshgoftaar TM, Prusa JD, Richter AN, Al Najada H (2015) Survey of review spam detection using machine learning techniques. J Big Data 18:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-015-0029-9
Wahyuni ED, Djunaidy A (2016) Fake review detection from a product review using modified method of iterative computation framework. MATEC Web Conf. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20165803003
Banerjee S, Kim J (2015) Using supervised learning to classify authentic and fake. In: Proc 9th Int Conf Ubiquitous Inf Manag Commun ACM, New, pp 1–7
Shojaee S, Murad MAA, Bin Azman A, Sharef NM, Nadali S (2013) Detecting deceptive reviews using lexical and syntactic features. In: 2013 13th International Conference on Intellient Systems Design and Applications, pp 53–58. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISDA.2013.6920707
Li F, Huang M, Yang Y, Zhu X (2011) Learning to identify review spam. In: IJCAI Int Jt Conf Artif Intell, pp 2488–2493. https://doi.org/10.5591/978-1-57735-516-8/IJCAI11-414
Hernández-castañeda Á, Calvo H, Gelbukh A, Flores JJG (2017) Cross-domain deception detection using support vector networks. Soft Comput 21(3):585–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2409-2
Ott M, Choi Y, Cardie C, Hancock JT (2011) Finding deceptive opinion spam by any stretch of the imagination. arXiv Prepr. arXiv1107.4557
Interno M, Sicurezza P, Dipartimento S, Poesio M (2014) Identifying fake Amazon reviews as learning from crowds. pp 279–287.
Mihalcea R, Science C, Science C (2014) Cross-cultural deception detection. pp 440–445
Mani S, Kumari S, Jain A, Kumar P (2018) Spam review detection using ensemble machine learning. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96133-0
Ott M, Cardie C, Hancock JT (2013) Negative deceptive opinion spam. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp 497–501
Sánchez-junquera J, Villaseñor-pineda L, Montes-y-gómez M, Rosso P, Stamatatos E (2020) Masking domain-specific information for cross-domain deception detection. Pattern Recognit Lett 135:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.04.020
Mohawesh R, Tran S, Ollington R, Xu S (2021) Analysis of concept drift in fake reviews detection. Expert Syst Appl 169:2021
Shan G, Zhou L (2021) From conflicts and confusion to doubts : examining review inconsistency for fake review detection. Decis Support Syst 144:113513
Yao J, Zheng Y, Jiang H (2021) An ensemble model for fake online review detection based on data resampling, feature pruning, and parameter optimization. IEEE Access 9:16914–16927. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3051174
Tufail H, Ashraf MU, Alsubhi K, Aljahdali HM (2022) The effect of fake reviews on e-commerce during and after Covid-19 pandemic: SKL-based fake reviews detection. IEEE Access 10:25555–25564. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3152806
Ott M, Cardie C, Hancock J (2012) Estimating the prevalence of deception in online review communities. In: WWW’12—Proc 21st Annu Conf World Wide Web, pp 201–210. https://doi.org/10.1145/2187836.2187864.
Rout JK, Dalmia A, Choo KKR, Bakshi S, Jena SK (2017) Revisiting semi-supervised learning for online deceptive review detection. IEEE Access 5:1319–1327. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2655032
Deng H, Zhao L, Luo N, Liu Y, Guo G, Wang X (2017) Semi-supervised learning based fake review detection. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPA/IUCC.2017.00195
Wang J, Kan H, Meng F, Mu Q, Shi G, Xiao X (2020) Fake review detection based on multiple feature fusion and rolling collaborative training. IEEE Access 8:182625–182639. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3028588
Jing-Yu C, Ya-Jun W (2022) Semi-supervised fake reviews detection based on AspamGAN. J Artif Intell Capsul Netw 4(1):17–36. https://doi.org/10.36548/jaicn.2022.1.002
Lau RYKK, Liao SY, Chi-Wai Kwok R, Xu K, Xia Y, Li Y (2011) Text mining and probabilistic language modeling for online review spam detection. ACM Trans Manag Inf Syst 2(4):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1145/2070710.2070716
Dong LY et al (2018) An unsupervised topic-sentiment joint probabilistic model for detecting deceptive reviews. Expert Syst Appl 114:210–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.07.005
Li J, Lv P, Xiao W, Yang L, Zhang P (2021) Exploring groups of opinion spam using sentiment analysis guided by nominated topics. Expert Syst Appl 171:114585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114585
Noekhah S, Binti Salim N, Zakaria NH (2020) Opinion spam detection: Using multi-iterative graph-based model. Inf Process Manag 57(1):102140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.102140
Vidanagama DU, Silva ATP, Karunananda AS (2022) Ontology based sentiment analysis for fake review detection. Expert Syst Appl 206:117869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117869
Ren Y, Ji D (2017) Neural networks for deceptive opinion spam detection: an empirical study. Inf Sci (Ny) 385–386:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.01.015
Lauriola I, Lavelli A, Aiolli F (2022) An introduction to deep learning in natural language processing: models, techniques, and tools. Neurocomputing 470:443–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.05.103
Li H et al. (2017) Bimodal distribution and co-bursting in review spam detection. In: 26th Int. World Wide Web Conf. WWW 2017, pp 1063–1072. https://doi.org/10.1145/3038912.3052582
Wang X, Liu K, Zhao J (2018) Detecting deceptive review spam via attention-based neural networks. In: Lecture Notes Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatic), vol 10619 LNAI, pp 866–876.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73618-1_76
Wang X, Liu K, Zhao J (2017) Handling cold-start problem in review spam detection by jointly embedding texts and behaviors. In: ACL 2017 - 55th Annu. Meet. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. Proc. Conf. (Long Pap., vol. 1, pp. 366–376, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P17-1034.
Bordes A, Usunier N, Garcia-dur A, Weston J, Yakhnenko O (2013) Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Adv Neural Inf Process, pp 2787–2795
Zhang W, Du Y, Yoshida T, Wang Q (2018) DRI-RCNN: an approach to deceptive review identification using recurrent convolutional neural network. Inf Process Manag 54(4):576–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2018.03.007
Hajek P, Sahut JM (2021) Mining behavioural and sentiment-dependent linguistic patterns from restaurant reviews for fake review detection. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 177:121532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121532
Ren Y, Zhang Y (2016) Deceptive opinion spam detection using neural network. In: roceedings of COLING 2016, the 26th international conference on computational linguistics: technical papers. pp 140–150, Osaka, Japan. COLING 2016 Organ. Committee., pp 140–150
Jacob MS, Rajendran PS (2021) Fuzzy artificial bee colony-based CNN-LSTM and semantic feature for fake product review classification. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 18:10. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6539
Hajek P, Barushka A, Munk M (2020) Fake consumer review detection using deep neural networks integrating word embeddings and emotion mining. Neural Comput Appl 32(23):17259–17274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04757-2
Liu W, Jing W, Li Y (2020) Incorporating feature representation into BiLSTM for deceptive review detection. Computing 102(3):701–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-019-00763-y
Li J, Ott M, Cardie C, Hovy E (2014) Hausarzt-Rechnung-22-08-11.Pdf. pp 1566–1576
Alsharif N (2011) Fake opinion detection in an e-commerce business based on a long-short memory algorithm. Soft Comput 5:2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06806-5
Li L, Qin B, Ren W, Liu T (2017) Document representation and feature combination for deceptive spam review detection. Neurocomputing 254:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.080
Li J, Ott M, Cardie C, Hovy E (2014) Towards a general rule for identifying deceptive opinion spam. In: Proceedings of 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: system demonstrations, vol 1, pp 1566–1576. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/p14-1147
Li H, Chen Z, Liu B, Wei X, Shao J (2014) Spotting fake reviews via collective positive-unlabeled learning. In: IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM), vol 2015, pp 899–904. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2014.47
Wang C, Chen C, Day M-Y, Liou J-W (2018) Detecting spamming reviews using long short-term memory recurrent neural network framework. In: Proceeding of the 2nd international conference on E-commerce, E-business, and E-government, pp 16–20
Bathla G, Singh P, Singh RK, Cambria E, Tiwari R (2022) Intelligent fake reviews detection based on aspect extraction and analysis using deep learning. Neural Comput Appl 8:20213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07531-8
Birim ŞÖ, Kazancoglu I, Kumar Mangla S, Kahraman A, Kumar S, Kazancoglu Y (2021) Detecting fake reviews through topic modelling. J Bus Res 149:884–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.05.081
Zhang W, Xie R, Wang Q, Yang Y, Li J (2022) A novel approach for fraudulent reviewer detection based on weighted topic modelling and nearest neighbors with asymmetric Kullback-Leibler divergence. Decis Support Syst 157:113765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2022.113765
Liu L, Zhao X, Wang H, Song W, Du C (2016) Research on identification method of anonymous fake reviews in E-commerce. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput Electron Control 14(4):1510. https://doi.org/10.12928/telkomnika.v14i4.3654
Zhang L, Wu Z, Cao J (2017) Detecting spammer groups from product reviews: a partially supervised learning model. IEEE Access 6:2559–2568. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2784370
Zhang L, He G, Cao J, Zhu H, Xu B (2018) Spotting review spammer groups: a cosine pattern and network based method. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 30(20):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.4686
Gao X, Li S, Zhu Y, Nan Y, Jian Z, Tang H (2019) Identification of deceptive reviews by sentimental analysis and characteristics of reviewers. J Eng Sci Technol Rev 12(1):196–202. https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.121.23
Xu Y, Yang Y, Han J, Wang E, Ming J, Xiong H (2019) Slanderous user detection with modified recurrent neural networks in recommender system. Inf Sci (NY) 505:265–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.081
Liu Y, Pang B, Wang X (2019) Opinion spam detection by incorporating multimodal embedded representation into a probabilistic review graph. Neurocomputing 366:276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.08.013
Yu S, Su J, Luo D (2019) Improving BERT-based text classification with auxiliary sentence and domain knowledge. IEEE Access 7:176600–176612. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2953990
Hazim M, Anuar NB, Ab Razak MF, Abdullah NA (2018) Detecting opinion spams through supervised boosting approach. PLoS ONE 13(6):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198884
Hammad AA, El-Halees A (2015) An approach for detecting spam in Arabic opinion reviews. Int Arab J Inf Technol 12(1):10–16
Saeed RMK, Rady S, Gharib TF (2019) An ensemble approach for spam detection in Arabic opinion texts. J. King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 34(1):1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.10.002
Ma H, Kim JM, Lee E (2019) Analyzing dynamic review manipulation and its impact on movie box office revenue. Electron Commer Res Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2019.100840
Hayat U, Saeed A, Vardag MHK, Ullah MF, Iqbal N (2022) Roman Urdu Fake reviews detection using stacked LSTM architecture. SN Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-022-01385-6
Almeida D, Almeida D (2018) Hotel online reviews: creating a multi-source aggregated index. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 30(12):3574–3591
Weng CH, Lin KC, Ying JC (2022) Detection of Chinese deceptive reviews based on pre-trained language model. Appl Sci 12(7):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073338
Xu C, Zhang J, Chang K, Long C (2013) Uncovering collusive spammers in Chinese review websites. Int Conf Inf Knowl Manag Proc. https://doi.org/10.1145/2505515.2505700
Jindal N, Liu B (2007) Review spam detection. In: 16th International World Wide Web conference, WWW2007, pp 1189–1190. https://doi.org/10.1145/1242572.1242759
Fei G, Mukherjee A, Liu B, Hsu M, Castellanos M, Ghosh R (2013) Exploiting burstiness in reviews for review spammer detection. In: Proceedings of the seventh international conference on Weblogs and social media, ICWSM 2013, vol 7, no 1, pp 175–184
Mukherjee A, Venkataraman V, Liu B, Glance N (2013) What yelp fake review filter might be doing?. In: Proceedings of the 7th International conference on Weblogs and social media, ICWSM 2013, pp 409–418
Mukherjee A, Liu B, Glance N (2012) Spotting fake reviewer groups in consumer reviews. In: WWW’12: Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on World Wide Web, pp 191–200. https://doi.org/10.1145/2187836.2187863
Budhi GS, Chiong R, Wang Z (2021) Resampling imbalanced data to detect fake reviews using machine learning classifiers and textual-based features. Multimed Tools Appl 80(9):13079–13097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10299-5
Barbado R, Araque O, Iglesias CA (2019) A framework for fake review detection in online consumer electronics retailers. Inf Process Manag 56(4):1234–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.03.002
Zhang Y, Wallace B (2015) A sensitivity analysis of (and practitioners’ guide to) convolutional neural networks for sentence classification, 2015. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1510.03820
Li H, Chen Z, Mukherjee A, Liu B, Shao J (2015) Analyzing and detecting opinion spam on a large-scale dataset via temporal and spatial patterns. Proc 9th Int Conf Web Soc Media 9:634–637
Hussain N, Mirza HT, Rasool G, Hussain I, Kaleem M (2019) Spam review detection techniques: a systematic literature review. Appl Sci 9(5):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050987
Serrano-guerrero J, Olivas JA, Romero FP, Herrera-viedma E (2015) Sentiment analysis: a review and comparative analysis of web services. Inf Sci (NY) 311:18–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2015.03.040
Akram AU, Khan HU, Iqbal S, Iqbal T, Munir EU, Cantt W (2018) Finding rotten eggs : a review spam detection model using diverse feature sets. vol 12, no 10, pp 5120–5142
Rayana S, Akoglu L (2015) Collective opinion spam detection: bridging review networks and metadata. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, vol 2015-August, pp 985–994. https://doi.org/10.1145/2783258.2783370
Mukherjee A et al. (2013) Spotting opinion spammers using behavioral footprints. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, vol. Part F1288, pp 632–640. https://doi.org/10.1145/2487575.2487580
Mohawesh R, Xu S, Springer M, Al-Hawawreh M, Maqsood S (2021) Fake or genuine? Contextualised text representation for fake review detection. pp 137–148. https://doi.org/10.5121/csit.2021.112311
Lim EP et al. (2010) Detecting product review spammers using rating behaviors. In: Proc. 19th {ACM} Conf. Inf. Knowl. Manag. {CIKM} 2010, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, Oct. 26–30, 2010 Manag. {CIKM} 2010, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, Oct. 26–30, 2010, pp 939--948. https://doi.org/10.1145/1871437.1871557
Wang H, Lu Y, Zhai C (2010) Latent aspect rating analysis on review text data: a rating regression approach. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 783–792. https://doi.org/10.1145/1835804.1835903
Li J, Fu Y, Liu D, Xu R (2020) Improving fake product detection with aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: International conference on cognitive computing, pp 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59585-2_4
Denecke K (2008) Using SentiWordNet for multilingual sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings international conference on data engineering., pp 507–512. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDEW.2008.4498370
Malik MSI, Hussain A (2017) Helpfulness of product reviews as a function of discrete positive and negative emotions. Comput Hum Behav 73(2010):290–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.03.053
Li Y, Feng X, Zhang S (2016) Detecting fake reviews utilizing semantic and emotion model. In: 2016 3rd international conference on information science and control engineering (ICISCE), pp 317–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISCE.2016.77
Saini M, Sharan A (2017) Identifying deceptive opinion spam using aspect-based emotions and human behavior modeling. Int J Hybrid Inf Technol 10(1):447–456. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2017.10.1.36
Plotkina D, Munzel A, Pallud J (2020) Illusions of truth—experimental insights into human and algorithmic detections of fake online reviews. J Bus Res 109:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.12.009
Ong T, Mannino M, Gregg D (2014) Linguistic characteristics of shill reviews. Electron Commer Res Appl 13(2):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2013.10.002
Huang YK, Yang WI, Lin TMY, Shih TY (2012) Judgment criteria for the authenticity of internet book reviews. Libr Inf Sci Res 34(2):150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2011.11.006
Arjun M, Vivek V, Bing L, Natalie G (2013) Fake review detection: classification and analysis of real and pseudo reviews. Tech Rep 80(2):159–169
Wu Y, Ngai EWTT, Wu P, Wu C (2020) Fake online reviews: literature review, synthesis, and directions for future research. Decis Support Syst 132:113280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2020.113280
Rout JK, Singh S, Jena SK, Bakshi S (2017) Deceptive review detection using labeled and unlabeled data. Multimed Tools Appl 76(3):3187–3211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3819-y
Hernández Fusilier D, Montes-y-Gómez M, Rosso P, Guzmán Cabrera R (2015) Detecting positive and negative deceptive opinions using PU-learning. Inf Process Manag 51(4):433–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2014.11.001
Cagnina LC, Rosso P (2017) Detecting deceptive opinions: intra and cross-domain classification using an efficient representation. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 25:151–174. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218488517400165
Martinez-Torres MR, Toral SL (2019) A machine learning approach for the identification of the deceptive reviews in the hospitality sector using unique attributes and sentiment orientation. Tour Manag 75(June):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.06.003
Rajamohana SP, Umamaheswari K, Abirami B (2017) Performance analysis of iBPSO and BFPA based feature selection techniques for improving classification accuracy in review spam detection. Appl Math Inf Sci 11(4):1149–1153. https://doi.org/10.18576/amis/110422
Zhang W, Bu C, Yoshida T, Zhang S (2016) CoFea: a novel approach to spam review identification based on entropy and co-training. Entropy 18(12):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18120429
Ansari G, Ahmad T, Doja MN (2018) Spam review classification using ensemble of global and local feature selectors. Cybern Inf Technol 18(4):29–42. https://doi.org/10.2478/cait-2018-0046
Pandey AC, Rajpoot DS (2019) Spam review detection using spiral cuckoo search clustering method. Evol Intell 12(2):147–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-019-00204-x
Cardoso EF, Silva RM, Almeida TA (2018) Towards automatic filtering of fake reviews. Neurocomputing 309:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.04.074
Kleinberg B, Mozes M, Arntz A, Verschuere B (2018) Using named entities for computer-automated verbal deception detection. J Forensic Sci 63(3):714–723. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13645
Zhang W, Bu C, Yoshida T, Zhang S (2016) CoSpa: a co-training approach for spam review identification with support vector machine. Information 7(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7010012
Kim J, Kang J, Shin S, Myaeng SH (2021) Can you distinguish truthful from fake reviews? User analysis and assistance tool for fake review detection. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Bridging Human–Computer Interaction and Natural Language Processing. HCINLP 2021 - Proc. 1st Work., pp 53–59
Yilmaz CM, Durahim AO (2018) SPR2EP: a semi-supervised spam review detection framework. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM international conference on advance social networks analysis mining, ASONAM 2018, pp 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1109/ASONAM.2018.8508314
A. Melleng, A. J. Loughrey, and P. Deepak, “Sentiment and emotion based text representation for fake reviews detection,” Int. Conf. Recent Adv. Nat. Lang. Process. RANLP, vol. 2019-Septe, no. 2019, pp. 750–757, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.26615/978-954-452-056-4_087.
Cao C, Li S, Yu S, Chen Z (2021) Fake reviewer group detection in online review systems. In: IEEE international conference on data mining workshops (ICDMW), vol. 2021, pp. 935–942. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW53433.2021.00122
Wang Z, Gu S, Zhao X, Xu X (2018) Graph-based review spammer group detection. Knowl Inf Syst 55(3):571–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-017-1068-7
Liu M, Shang Y, Yue Q, Zhou J (2021) Detecting fake reviews using multidimensional representations with fine-grained aspects plan. IEEE Access 9:3765–3773. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047947
Yuan C, Zhou W, Ma Q, Lv S, Han J, Hu S, Learning review representations from user and product level information for spam detection. In: Proceedings under IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM) | IEEE Conference, vol 2019, pp 1444–1449. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2019.00188.
Shaalan Y, Zhang X, Chan J, Salehi M (2021) Detecting singleton spams in reviews via learning deep anomalous temporal aspect-sentiment patterns. vol 35, no 2. Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-020-00725-5
Shehnepoor S, Salehi M, Farahbakhsh R, Crespi N (2017) NetSpam: a network-based spam detection framework for reviews in online social media. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 8(6):748–752
Kumar N, Venugopal D, Qiu L, Kumar S (2019) Detecting anomalous online reviewers: an unsupervised approach using mixture models. J Manag Inf Syst 36(4):1313–1346. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2019.1661089
Kumar J (2018) Fake review detection using behavioral and contextual features fake review detection using behavioral and contextual features
Xu C, Zhang J (2017) Collusive opinion fraud detection in online reviews: a probabilistic modeling approach. ACM Trans Web 11(4):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1145/3098859
Savage D, Zhang X, Yu X, Chou P, Wang Q (2015) Detection of opinion spam based on anomalous rating deviation. Expert Syst Appl 42(22):8650–8657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.07.019
Sun C, Du Q, Tian G (2016) Exploiting product related review features for fake review detection. vol 2016, no 1
Ni J, Li J, McAuley J (2019) Justifying recommendations using distantly-labeled reviews and fine-grained aspects. In: 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pp 188–197. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/d19-1018.
Kauffmann E, Peral J, Gil D, Ferrández A, Sellers R, Mora H (2019) A framework for big data analytics in commercial social networks: a case study on sentiment analysis and fake review detection for marketing decision-making. Ind Mark Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.08.003
Asghar MZ, Ullah A, Ahmad S, Khan A (2020) Opinion spam detection framework using hybrid classification scheme. Soft Comput 24(5):3475–3498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04107-y
Elnagar A, Khalifa YS, Einea A (2018) Hotel arabic-reviews dataset construction for sentiment analysis applications. Stud Comput Intell 740:35–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67056-0_3
Al-Mutawa RF, Al-Aama AY (2023) User opinion prediction for Arabic hotel reviews using Lexicons and artificial intelligence techniques. Appl Sci 13(10):5985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105985
Saeed RMK, Rady S, Gharib TF (2022) An ensemble approach for spam detection in Arabic opinion texts. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 34(1):1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.10.002
Berrimi M, Oussalah M, Moussaoui A, Saidi M (2023) Attention mechanism architecture for Arabic sentiment analysis. ACM Trans Asian Low-Resour Lang Inf Process. https://doi.org/10.1145/3578265
Ullah MF, Saeed A (2023) BERT model for Roman Urdu fake review identication. pp 0–15
Attri V (2023) Enhancement of fake reviews classification using deep learning hybrid models. J Surv Fish Sci 10:3254–3272
Li H et al. Modeling review spam using temporal patterns and co-bursting behaviors. 2016. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.06625
Luo N, Deng H, Zhao L, Liu Y, Wang X, Tan Z (2017) Multi-aspect feature based neural network model in detecting fake reviews. In: 2017 4th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering, pp 475–479. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISCE.2017.106
Duma R, Niu Z, Nyamawe A, Tchaye-kondi J, Yusuf A (2023) A Deep hybrid model for fake review detection by jointly leveraging review text, overall ratings and aspects ratings. Soft Comput 27:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07897-4
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62272048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ramadhani Duma was involved in the conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, resources, and writing—original draft. Zhendong Niu and Ally Nyamawe contributed to the methodology, resources, supervision, validation, editing and review, and project administration. Jude Tchaye-Kondi, Abdulganiyu Yusuf, Nuru Jingili, and Augustino Deve performed the editing and review
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this kind of study, there is nothing that requires ethical approval.
Informed consent
No formal consent is required for this kind of study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duma, R.A., Niu, Z., Nyamawe, A.S. et al. Fake review detection techniques, issues, and future research directions: a literature review. Knowl Inf Syst 66, 5071–5112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-024-02118-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-024-02118-2