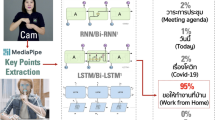
Abstract
Sign language plays a pivotal role in facilitating communication for the deaf community, bridging the gap with the broader society. Nevertheless, mastering sign language poses significant challenges due to the intricate nuances of body movements, hand gestures, and facial expressions. Sign language recognition technology is a pivotal solution aimed at enabling clear communication between deaf individuals and the wider community, thereby reducing the risk of miscommunication. This study introduces an innovative approach to address these challenges. We focus on the recognition of Indonesian Sign Language using a skeleton-based method, harnessing the capabilities of MediaPipe to extract critical hand and pose key points from sign language videos. The core of our approach involves the implementation of a long short-term memory (LSTM) model, which has showcased exceptional promise in accurately interpreting BISINDO. The proposed LSTM architecture excels with a remarkable validation accuracy of 92.857%, surpassing the accuracy and computational efficiency of previously proposed LSTM models. This significant advancement in technology propels us closer to bridging the communication gap between the deaf community and the broader population.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The source code and the material and findings data of this study are openly available in full access by GitHub: https://github.com/Rezzy94.
References
Johnson, R.E.: Sign language, culture & community in a traditional Yucatec Maya village. Sign. Lang. Stud. 1073, 461–474 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1353/sls.1991.0031
Supriyati, E., Iqbal, M.: Recognition system of indonesia sign language based on sensor and artificial neural network. Makara J. Technol. 17, 25–31 (2013)
Suharjito, T., Gunawan, N.: SIBI sign language recognition using convolutional neural network combined with transfer learning and non-trainable parameters. Proc. Comput. Sci. 179, 72–80 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.12.011
Yugopuspito, P., Made Murwantara, I., Sean, J.: Mobile sign language recognition for Bahasa Indonesia using convolutional neural network. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series. 84–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3282353.3282356
Palfreyman, N.: Sign language varieties of Indonesia a linguistic and sociolinguistic investigation, (2015)
Hartanto, R., Susanto, A., Santosa, P.I.: Preliminary design of static indonesian sign language recognition system. In: Proceedings - 2013 International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering: “Intelligent and Green Technologies for Sustainable Development”, ICITEE 2013. 187–192 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITEED.2013.6676236
Zakaria, Z., Firmanyah, R.A., Prabowo, Y.A.: Rancang bangun Flex Sensor Gloves untuk penerjemah Bahasa Isyarat menggunakan K-Nearest Neighbors. Seminar Nasional Sains dan Teknologi Terapan VII. 361–366 (2019)
Mamuriyah, N., Deasy, D.: Perancangan pembuatan aplikasi pengenalan dan penerjemah bahasa isyarat sibi menggunakan leap motion dengan hidden markov models. Telcomatics (2020). https://doi.org/10.37253/telcomatics.v5i1.838
Xiao, Q., Qin, M., Yin, Y.: Skeleton-based Chinese sign language recognition and generation for bidirectional communication between deaf and hearing people. Neural Netw. 125, 41–55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.030
Caterini, A.L., Chang, D.E.: Recurrent neural networks. In: Deep Neural Networks in a Mathematical Framework. pp. 59–79. Springer International Publishing (2018)
Toharudin, T., Pontoh, R.S., Caraka, R.E., Zahroh, S., Lee, Y., Chen, R.C.: Employing long short-term memory and facebook prophet model in air temperature forecasting. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03610918.2020.1854302
Fischer, A.: Training restricted Boltzmann machines. KI - Künstliche Intell. 29, 441–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13218-015-0371-2
Sequeira, S., Banu, P.K.N.: Comparisons of stock price predictions using stacked RNN-LSTM. (2021)
Yin, W., Schütze, H.: Attentive convolution: equipping CNNs with RNN-style attention mechanisms. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 6, 687–702 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1162/tacl_a_00249
Rahimyar, A.H., Nguyen, H.Q., Wang, X.: Stock Forecasting Using M-Band Wavelet-Based SVR and RNN-LSTMs Models. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education, ICISCAE 2019. pp. 234–240 (2019)
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L.A., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Guadarrama, S., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 677–691 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2599174
Graves, A., Jaitly, N.: Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. In: 31st International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2014. 5, 3771–3779 (2014)
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 4, 3104–3112 (2014)
Zhang, X.Y., Yin, F., Zhang, Y.M., Liu, C.L., Bengio, Y.: Drawing and recognizing chinese characters with recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 849–862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2695539
Liu, T., Zhou, W., Li, H.: Sign language recognition with long short-term memory. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). pp. 1–4. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Signal Processing Society, Arizona (2016)
Adaloglou, N.M., Chatzis, T., Papastratis, I., Stergioulas, A., Papadopoulos, G.T., Zacharopoulou, V., Xydopoulos, G., Antzakas, K., Papazachariou, D., Daras, P.: None: a comprehensive study on deep learning-based methods for sign language recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 9210, 1–14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3070438
Midyanti, D.M., Gustiar, D., Sitorus, S.H.: Penerjemahan bahasa isyarat menggunakan metode generalized learning vector quantization (Glvq). Coding J. Komput. dan Aplikasi 8, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.26418/coding.v8i3.42156
Darmatasia, D.: Pengenalan sistem isyarat bahasa indonesia (sibi) menggunakan gradient-convolutional neural network. Jurnal INSTEK (Inform Sains dan Teknologi) 6, 56 (2021). https://doi.org/10.24252/instek.v6i1.18637
Lugaresi, C., Tang, J., Nash, H., McClanahan, C., Uboweja, E., Hays, M., Zhang, F., Chang, C.-L., Yong, M.G., Lee, J., Chang, W.-T., Hua, W., Georg, M., Grundmann, M.: MediaPipe: A Framework for Building Perception Pipelines. ArXiv. (2019)
Cao, Z., Hidalgo, G., Simon, T., Wei, S.E., Sheikh, Y.: OpenPose: realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43, 172–186 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2929257
Güler, R.A., Neverova, N., Kokkinos, I.: DensePose: Dense Human Pose Estimation in the Wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 7297–7306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00762
Bazarevsky, V., Grishchenko, I., Raveendran, K., Zhu, T., Zhang, F., Grundmann, M.: BlazePose: On-device Real-time Body Pose tracking. ArXiv. (2020)
Dokmanic, I., Parhizkar, R., Ranieri, J., Vetterli, M.: Euclidean distance matrices: essential theory, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32, 12–30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2015.2398954
Kapuściński, T., Warchol, D.: Hand posture recognition using skeletal data and distance descriptor. Appl. Sci. (Switzerland) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062132
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. (1997). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Bengio, Y., Simard, P., Frasconi, P.: Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/72.279181
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9, 1735–1780 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Graves, A.: Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin (2012)
Le, X.H., Ho, H.V., Lee, G., Jung, S.: Application of long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network for flood forecasting. Water (Switzerland) 11, 2–19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071387
Gers, F.A., Schmidhuber, J., Cummins, F.: Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 12, 2451–2471 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1162/089976600300015015
Cho, K., van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: EMNLP 2014 - 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Proceedings of the Conference. pp. 1724–1734. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha (2014)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. 1–9 (2014)
Gholamalinezhad, H., Khosravi, H.: Pooling Methods in Deep Neural Networks, a Review. ArXiv. (2020)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 50, 84–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Kingma, D.P., Lei Ba, J.: ADAM: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In: ICLR. pp. 1–15 (2015)
Zhang, Z., Sabuncu, M.R.: Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2018-Decem, 8778–8788 (2018)
Liu, T., Zhou, W., Li, H.: Sign language recognition with long short-term memory. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). pp. 2871–2875. IEEE (2016)
Pu, J., Zhou, W., Zhang, J., Li, H.: Sign Language Recognition Based on Trajectory Modeling with HMMs. In: International Conference on Multimedia Modeling. pp. 686–698. Springer-Verlag, Miami (2016)
Acknowledgements
Rezzy Eko Caraka is partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2023R1A2C1006845). Yunho Kim acknowledges support from the National Research Foundation of Korea NRF-2022R1A5A1033624 and Grant NRF-2023R1A2C1006845.
Funding
The work presented in this paper has been funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea NRF-2022R1A5A1033624 and Grant NRF-2023R1A2C1006845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
REC conceived the research and constructed the experimental design. REC, YK, and BP managed the project. REC, FZM, and RK analyzed the data. REC participated in the verification and interpretation of data. REC, KS, FZM, and RK wrote the manuscript. REC, KS, RK, YK, PUG, BY, FZM, and BP read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Caraka, R.E., Supardi, K., Kurniawan, R. et al. Empowering deaf communication: a novel LSTM model for recognizing Indonesian sign language. Univ Access Inf Soc 24, 771–783 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01095-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01095-1