Abstract
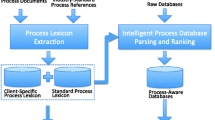
Many organizations use business policies to govern their business processes, often resulting in huge amounts of policy documents. As new regulations arise such as Sarbanes-Oxley, these business policies must be modified to ensure their correctness and consistency. Given the large amounts of business policies, manually analyzing policy documents to discover process information is very time-consuming and imposes excessive workload. In order to provide a solution to this information overload problem, we propose a novel approach named Policy-based Process Mining (PBPM) to automatically extracting process information from policy documents. Several text mining algorithms are applied to business policy texts in order to discover process-related policies and extract such process components as tasks, data items, and resources. Experiments are conducted to validate the extracted components and the results are found to be very promising. To the best of our knowledge, PBPM is the first approach that applies text mining towards discovering business process components from unstructured policy documents. The initial research results presented in this paper will require more research efforts to make PBPM a practical solution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldowaisan TA, Gaafar LK (1999) Business process reengineering: an approach for process mapping. Omega 27(5):515–524
Basu A, Blanning RW (2000) A formal approach to workflow analysis. Inf Syst Res 11(1):17–36
Basu A, Kumar A (2002) Research commentary: workflow management issues in e-Business. Inf Syst Res 13(1):1–14
Bunescu R, Mooney R (2005) A shortest path dependency kernel for relation extraction. In: Proceedings of conference on human language technology and empirical methods in natural language processing (HLT/EMNLP), Morristown, NJ, pp 724–731
Cobb CG (2004) Enterprise process mapping: integrating systems for compliance and business excellence. ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee, p 128
Collins M, Duffy N (2002) Convolution kernels for natural language. In: Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems 14, MIT
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, New York
Culotta A, Sorensen J (2004) Dependency tree kernels for relation extraction. In: Proceedings of 42nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (ACL-04), Barcelona, Spain, pp 423–429
Datta A (1998) Automating the discovery of AS-IS business process models: probabilistic and algorithmic approaches. Inf Syst Res 9(3):275–301
Grigori D, Casati F, Castellanos M, Dayal U, Sayal M, Shan M-C (2004) Business process intelligence. Comput Ind 53:321–343
Hofacker I, Vetschera R (2001) Algorithmical approaches to business process design. Comput Oper Res 28(13):1253–1275
Hunt VD (1996) Process mapping: how to reengineer your business processes. Wiley, New York, p 288
Kettinger WJ, Teng JTC, Guha S (1997) Business process change: a study of methodologies, techniques, and tools. MIS Q 21(1):55–80
Lafferty J, McCallum A, Pereira F (2001) Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In: Proceedings of the 18th international conference on machine learning, San Francisco, CA, pp 282–289
Lodhi H, Saunders C, Shawe-Taylor J, Cristianini N, Watkins C (2002) Text classification using string kernels. J Mach Learn Res 2(3):419–444
Madison D (2005) Process mapping, process improvement and process management. Paton Press, Chico, p 320
Marsh E, Perzanowski D (1998) Muc-7 evaluation of I.E technology: overview of results. In: Proceedings of the seventh message understanding conference (MUC-7)
McCallum A, Freitag D, Pereira F (2000) Maximum entropy Markov models for information extraction and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on machine learning, San Francisco, CA, pp 591–598
OMG (2005) UML superstructure specification, v2.0. http://www.omg.org/cgi-bin/doc?formal/05-07-04
Peltier TR (2004) Information security policies and procedures: a practitioner’s reference, 2nd edn. Auerbach Publication, Boca Raton
Rabiner L (1989) A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc IEEE 77(2):257–285
Reijers HA, Limam S, van der Aalst WMP (2003) Product-based workflow design. J Manag Inf Syst 20(1):229–262
Scheer A-W (2000) ARIS—business process modeling, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Sha F, Pereira F (2003) Shallow parsing with conditional random fields. In: Proceedings of the 2003 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics on human language technology, pp 134–141
van der Aalst WMP (2000) Reengineering knock-out processes. Decis Support Syst 30(4):451–468
van der Aalst WMP, Weijters A (2004) Process mining: a research agenda. Comput Ind 53(3):231–244
van der Aalst WMP, Reijers HA, Weijters A, van Dongen BF, de Medeiros AKA, Song M, Verbeek HMW (2007) Business process mining: an industrial application. Inf Syst 32(1):713–732
Voorhees E (2001) SAIC information extraction. http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/related_projects/muc/
Wang HJ, Zhao JL (2005) Policy-driven business process modeling in e-business. In: Proceedings of the fourth workshop on E-business (WeB 2005), Las Vegas, Nevada
Wang HJ, Zhao JL, Zhang L-J (2006) Policy-driven process mapping (PDPM): towards process design automation. In: Proceedings of the 2006 international conference on information systems (ICIS 2006), Milwaukee, Wisconsin
Zelenko D, Aone C, Richardella A (2003) Kernel methods for relation extraction. J Mach Learn Res 3(6):1083–1106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, H.J., Zhang, Z. et al. A policy-based process mining framework: mining business policy texts for discovering process models. Inf Syst E-Bus Manage 8, 169–188 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-009-0112-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-009-0112-x