Abstract
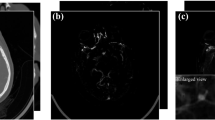
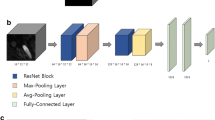
The accuracy of computed tomography angiography (CTA) image interpretation depends on the radiologist. This study aims to develop a new method for automatically detecting intracranial aneurysms from CTA images using deep learning, based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) implemented on the DeepMedic platform. Ninety CTA scans of patients with intracranial aneurysms are collected and divided into two datasets: training (80 subjects) and test (10 subjects) datasets. Subsequently, a deep learning architecture with a three-dimensional (3D) CNN model is implemented on the DeepMedic platform for the automatic segmentation and detection of intracranial aneurysms from the CTA images. The samples in the training dataset are used to train the CNN model, and those in the test dataset are used to assess the performance of the established system. Sensitivity, positive predictive value (PPV), and false positives are evaluated. The overall sensitivity and PPV of this system for detecting intracranial aneurysms from CTA images are 92.3% and 100%, respectively, and the segmentation sensitivity is 92.3%. The performance of the system in the detection of intracranial aneurysms is closely related to their size. The detection sensitivity for small intracranial aneurysms (≤ 3 mm) is 66.7%, whereas the sensitivity of detection for large (> 10 mm) and medium-sized (3–10 mm) intracranial aneurysms is 100%. The deep learning architecture with a 3D CNN model on the DeepMedic platform can reliably segment and detect intracranial aneurysms from CTA images with high sensitivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of Data and Materials
Data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Etminan N, Dorfler A, Steinmetz H: Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms- Pathogenesis and Individualized Management. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117:235-242, 2020
Laarman MD, et al.: Intracranial Aneurysm-Associated Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Alter Regulatory DNA in the Human Circle of Willis. Stroke 49:447-453, 2018
Suarez JI, Tarr RW, Selman WR: Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 354:387-396, 2006
Rinkel GJ: Natural history, epidemiology and screening of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Rev Neurol (Paris) 164:781-786, 2008
Pedersen HK, et al.: CTA in patients with acute subarachnoid haemorrhage. A comparative study with selective, digital angiography and blinded, independent review. Acta Radiol 42:43–49, 2001
Duan H, Huang Y, Liu L, Dai H, Zhou LJBEO: Automatic detection on intracranial aneurysm from digital subtraction angiography with cascade convolutional neural networks18, 2019
Chen X, et al.: Meta-analysis of computed tomography angiography versus magnetic resonance angiography for intracranial aneurysm97, 2018
Miki, et al.: Computer-Assisted Detection of Cerebral Aneurysms in MR Angiography in a Routine Image-Reading Environment: Effects on Diagnosis by Radiologists, 2016
Stepan-Buksakowska IL, et al.: Computer-aided diagnosis improves detection of small intracranial aneurysms on MRA in a clinical setting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1897-1902, 2014
Yang X, Blezek DJ, Cheng LTE, Ryan WJ, Kallmes DF, Erickson BJJJoDI: Computer-aided detection of intracranial aneurysms in MR angiography24:86–95, 2011
Faron A, et al.: Performance of a Deep-Learning Neural Network to Detect Intracranial Aneurysms from 3D TOF-MRA Compared to Human Readers, 2019
Nakao T, et al.: Deep neural network‐based computer‐assisted detection of cerebral aneurysms in MR angiography, 2018
Lecun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton GJN: Deep learning521:436, 2015
Suzuki, Physics KJR, Technology: Overview of deep learning in medical imaging, 2017
Shen D, Wu G, Suk HIJARoBE: Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis19:221-248, 2017
Litjens G, et al.: A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis42:60-88, 2017
Dai X, et al.: Deep learning for automated cerebral aneurysm detection on computed tomography images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 15:715-723, 2020
Park A, et al.: Deep Learning-Assisted Diagnosis of Cerebral Aneurysms Using the HeadXNet Model. JAMA Netw Open 2:e195600, 2019
Shi Z, et al.: A clinically applicable deep-learning model for detecting intracranial aneurysm in computed tomography angiography images. Nat Commun 11:6090, 2020
Kamnitsas K, et al.: Efficient Multi-Scale 3D CNN with Fully Connected CRF for Accurate Brain Lesion Segmentation36:61, 2016
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun JJIToPA, Intelligence M: Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks39:1137-1149, 2017
Szegedy C, et al.: Going Deeper with Convolutions, 2014
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A: You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. Proc. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition: City
Redmon J, Farhadi AJae-p: YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement, 2018
Albarqouni S, Baur C, Achilles F, Belagiannis V, Demirci S, Navab NJIToMI: AggNet: Deep Learning From Crowds for Mitosis Detection in Breast Cancer Histology Images35:1313-1321, 2016
Hirasawa T, Aoyama K, Tanimoto T, Ishihara S, Tada TJGCOJotIGCA, Association tJGC: Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images87:1–8, 2018
Setio AAA, et al.: Pulmonary Nodule Detection in CT Images: False Positive Reduction Using Multi-View Convolutional Networks35:1160-1169, 2016
Öman O, Mäkelä T, Salli E, Savolainen S, Kangasniemi MJERE: 3D convolutional neural networks applied to CT angiography in the detection of acute ischemic stroke3, 2019
Sichtermann T, Faron A, Sijben R, Teichert N, Freiherr J, Wiesmann MJAJoN: Deep learning-based detection of intracranial aneurysms in 3D TOF-MRA, 2018
Funding
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81601558), Breeding Foundation of Zhuhai People’s Hospital of China (2019PY-16), and the Medical Research Foundation of Zhuhai City of China (20191207A010017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL and JM: literature search, study design, data collection, data processing and experimentation, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing; NS and LC: data processing and experimentation; XY, YT, JW, and JL: data collection and manual labeling of CTA images of People’s Hospital (Zhuhai Hospital Affiliated with Jinan University); HT and KW: data collection of DSA and surgery; LY, JL, YW, and BZ: data analysis and interpretation; YW and MC: data collection and manual labeling of CTA images of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University; and ZW and LL: study design, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhuhai People’s Hospital and the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent to Participate
Verbal informed consent was obtained prior to the interview.
Consent for Publication
Participants have consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Mao, J., Sun, N. et al. Deep Learning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms from Computed Tomography Angiography Images. J Digit Imaging 36, 114–123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00698-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00698-5