Abstract
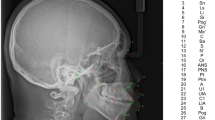
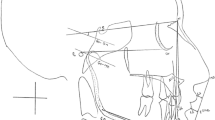
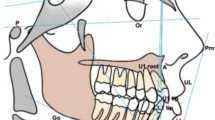
Using computer vision through artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the main technological advances in dentistry. However, the existing literature on the practical application of AI for detecting cephalometric landmarks of orthodontic interest in digital images is heterogeneous, and there is no consensus regarding accuracy and precision. Thus, this review evaluated the use of artificial intelligence for detecting cephalometric landmarks in digital imaging examinations and compared it to manual annotation of landmarks. An electronic search was performed in nine databases to find studies that analyzed the detection of cephalometric landmarks in digital imaging examinations with AI and manual landmarking. Two reviewers selected the studies, extracted the data, and assessed the risk of bias using QUADAS-2. Random-effects meta-analyses determined the agreement and precision of AI compared to manual detection at a 95% confidence interval. The electronic search located 7410 studies, of which 40 were included. Only three studies presented a low risk of bias for all domains evaluated. The meta-analysis showed AI agreement rates of 79% (95% CI: 76–82%, I2 = 99%) and 90% (95% CI: 87–92%, I2 = 99%) for the thresholds of 2 and 3 mm, respectively, with a mean divergence of 2.05 (95% CI: 1.41–2.69, I2 = 10%) compared to manual landmarking. The menton cephalometric landmark showed the lowest divergence between both methods (SMD, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.82; 1.53; I2 = 0%). Based on very low certainty of evidence, the application of AI was promising for automatically detecting cephalometric landmarks, but further studies should focus on testing its strength and validity in different samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Schwendicke F, Samek W, Krois J: Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry: Chances and Challenges. J Dent Res 99:769-774, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520915714
Naylor CD: On the prospects for a (deep) learning health care system. JAMA 320:1099-1100, 2018.
Seyed Tabib NS, Madgwick M, Sudhakar P, et al: Big data in IBD: big progress for clinical practice. Gut 69:1520-1532, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320065
Zeng T, Yu X, Chen Z: Applying artificial intelligence in the microbiome for gastrointestinal diseases: A review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 36:832-840, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.15503
Muscogiuri G, Chiesa M, Trotta M, et al: Performance of a deep learning algorithm for the evaluation of CAD-RADS classification with CCTA. Atherosclerosis 294:25-32, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.12.001
Shimizu H, Nakayama KI: Artificial intelligence in oncology. Cancer Sci 111:1452-1460, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14377
Liang G, Fan W, Luo H, et al: The emerging roles of artificial intelligence in cancer drug development and precision therapy. Biomed Pharmacother 128:110255, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110255
Olveres J, González G, Torres F, et al: What is new in computer vision and artificial intelligence in medical image analysis applications. Quant Imaging Med Surg 11:3830-3853, 2021. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1151
Kühnisch J, Meyer O, Hesenius M, et al: Caries Detection on Intraoral Images Using Artificial Intelligence. J Dent Res 101:158-165, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345211032524
Baniulyte G, Ali K: Artificial intelligence - can it be used to outsmart oral cancer? Evid Based Dent 23:12-13, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-022-0238-y
Revilla-León M, Gómez-Polo M, Barmak AB, et al: Artificial intelligence models for diagnosing gingivitis and periodontal disease: A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2022:S0022-3913(22)00075-0, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.01.026
Silva VKS, Vieira WA, Bernardino ÍM, et al: Accuracy of computer-assisted image analysis in the diagnosis of maxillofacial radiolucent lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 49:20190204, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20190204
Fukuda M, Inamoto K, Shibata N, et al: Evaluation of an artificial intelligence system for detecting vertical root fracture on panoramic radiography. Oral Radiol 36:337-343, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-019-00409-x
Francisco I, Ribeiro MP, Marques F, et al: Application of Three-Dimensional Digital Technology in Orthodontics: The State of the Art. Biomimetics (Basel) 7:23, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010023
Bichu YM, Hansa I, Bichu AY, et al: Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in orthodontics: a scoping review. Prog Orthod 22:18, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-021-00361-9
Monill-González A, Rovira-Calatayud L, d'Oliveira NG, Ustrell-Torrent JM: Artificial intelligence in orthodontics: Where are we now? A scoping review. Orthod Craniofac Res Suppl 2:6-15, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12517
Qian J, Luo W, Cheng M, Tao Y, Lin J, Lin H. Cepha NN: A Multi-Head Attention Network for Cephalometric Landmark Detection. IEEE Access. 2020;8: 112633-112641. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3002939
Lindner C, Wang CW, Huang CT, et al: Fully Automatic System for Accurate Localisation and Analysis of Cephalometric Landmarks in Lateral Cephalograms. Sci Rep 6:33581, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33581
Ma Q, Kobayashi E, Fan B, et al: Automatic 3D landmarking model using patch-based deep neural networks for CT image of oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int J Med Robot. 16:e2093, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2093
Schwendicke F, Chaurasia A, Arsiwala L, et al: Deep learning for cephalometric landmark detection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig 25:4299-4309, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03990-w
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, et al: Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 350:g7647, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Aromataris E, Munn Z (Editors). JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI, 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global. https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-01
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al: QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529-36, 2011. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
Wang CW, Huang CT, et al: Evaluation and Comparison of Anatomical Landmark Detection Methods for Cephalometric X-Ray Images: A Grand Challenge. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34:1890-900, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2412951
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 64:383-394, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
Giordano D, Leonardi R, Maiorana F, Cristaldi G, Distefano ML: Automatic Landmarking of Cephalograms by Cellular Neural Networks. In: Miksch S, Hunter J, Keravnou ET. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2005;3581. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11527770_46
Leonardi R, Giordano D, Maiorana F: An evaluation of cellular neural networks for the automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks on digital images. J Biomed Biotechnol 2009:717102, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/717102
Vucinić P, Trpovski Z, Sćepan I: Automatic landmarking of cephalograms using active appearance models. Eur J Orthod 32:233-241, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjp099
Tam WK, Lee HJ: Improving point registration in dental cephalograms by two-stage rectified point translation transform. Med Imag 2012: Image Processing. 2012;83141U. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.910935
Shahidi Sh, Oshagh M, Gozin F, Salehi P, Danaei SM: Accuracy of computerized automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks by a designed software. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 42:20110187, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20110187
Shahidi S, Bahrampour E, Soltanimehr E et al. The accuracy of a designed software for automated localization of craniofacial landmarks on CBCT images. BMC Med Imaging 14:32, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2342-14-32
Gupta A, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana HK: A knowledge-based algorithm for automatic detection of cephalometric landmarks on CBCT images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10:1737-1752, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1173-6
Tam WK, Lee HJ: Improving point correspondence in cephalograms by using a two-stage rectified point transform. Comput Biol Med 65:114-123, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.07.022
Vasamsetti S, Sardana V, Kumar P, Kharbanda OP, Sardana HK: Automatic Landmark Identification in Lateral Cephalometric Images Using Optimized Template Matching. J Med Imag Health Inform 15:458-470, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1166/jmihi.2015.1426
Codari M, Caffini M, Tartaglia GM, Sforza C, Baselli G: Computer-aided cephalometric landmark annotation for CBCT data. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:113-121, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1453-9
Zhang J, Gao Y, Wang L, et al: Automatic Craniomaxillofacial Landmark Digitization via Segmentation-Guided Partially-Joint Regression Forest Model and Multiscale Statistical Features. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63:1820-1829, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2503421
Arik SO, Ibragimov B, Xing L: Fully automated quantitative cephalometry using convolutional neural networks. J Med Imag 4:014501, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.4.1.014501
Lee H, Park M, Kim J: Cephalometric landmark detection in dental x-ray images using convolutional neural networks. Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. 2017;101341W. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2255870
de Jong MA, Gül A, de Gijt JP, et al: Automated human skull landmarking with 2D Gabor wavelets. Phys Med Biol 63:105011, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/aabfa0
Montúfar J, Romero M, Scougall-Vilchis RJ: Automatic 3-dimensional cephalometric landmarking based on active shape models in related projections. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 153:449-458, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.06.028
Montúfar J, Romero M, Scougall-Vilchis RJ: Hybrid approach for automatic cephalometric landmark annotation on cone-beam computed tomography volumes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 154:140-150, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.08.028
Neelapu BC, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, et al: Automatic localization of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks on CBCT images by extracting symmetry features of the skull. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 47:20170054, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20170054
Wang S, Li H, Li J, Zhang Y, Zou B: Automatic Analysis of Lateral Cephalograms Based on Multiresolution Decision Tree Regression Voting. J Healthc Eng 2018:1797502, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1797502
Chen R, Ma Y, Chen N, Lee D, Wang W: Cephalometric Landmark Detection by Attentive Feature Pyramid Fusion and Regression-Voting. Comput Vis Pattern Recog. 2019.
Dai X, Zhao H, Liu T, Cao D, Xie L: Locating Anatomical Landmarks on 2D Lateral Cephalograms Through Adversarial Encoder-Decoder Networks. IEEE Access. 2019;99. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940623
Kang SH, Jeon K, Kim HJ, Seo JK, Lee SH: Automatic three-dimensional cephalometric annotation system using three-dimensional convolutional neural networks: a developmental trial. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering: Imaging & Visualization 8:210-218, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2019.1674696
Lee SM, Kim HP, Jeon K, Lee SH, Seo JK. Automatic 3D cephalometric annotation system using shadowed 2D image-based machine learning. Phys Med Biol 64:055002, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ab00c9
Nishimoto S, Sotsuka Y, Kawai K, Ishise H, Kakibuchi M: Personal Computer-Based Cephalometric Landmark Detection With Deep Learning, Using Cephalograms on the Internet. J Craniofac Surg 30:91-95, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004901
Payer C, Stern D, Bischof H, Urschler M: Integrating spatial configuration into heatmap regression based CNNs for landmark localization. Med Imag Analys 54:207-219, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.03.007
Kim H, Shim E, Park J, et al: Web-based fully automated cephalometric analysis by deep learning. Comput Meth Program Biomed 194:105513, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105513
Lee JH, Yu HJ, Kim MJ, Kim JW, Choi J: Automated cephalometric landmark detection with confidence regions using Bayesian convolutional neural networks. BMC Oral Health 20:270, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-020-01256-7
Li W, Lu Y, Zheng K, et al: Structured Landmark Detection via Topology-Adapting Deep Graph Learning. Comput Vis Pattern Recog 6, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_16
Moon JH, Hwang HW, Yu Y, et al: How much deep learning is enough for automatic identification to be reliable? Angle Orthod 90:823-830, 2020. https://doi.org/10.2319/021920-116.1
Oh K, Oh IS, Le VNT, Lee DW: Deep Anatomical Context Feature Learning for Cephalometric Landmark Detection. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 25:806-817, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.3002582
Noothout JMH, De Vos BD, Wolterink JM, et al: Deep Learning-Based Regression and Classification for Automatic Landmark Localization in Medical Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39:4011-4022, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3009002
Song Y, Qiao X, Iwamoto Y, Chen YW: Automatic Cephalometric Landmark Detection on X-ray Images Using a Deep-Learning Method. Appl Sci 10:2547, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072547
Wirtz A, Lam J, Wesarg S: Automated Cephalometric Landmark Localization using a Coupled Shape Model. Curr Dir Biomed Eng 6:20203015, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1515/cdbme-2020-3015
Yun HS, Jang TJ, Lee SM, Lee SH, Seo JK: Learning-based local-to-global landmark annotation for automatic 3D cephalometry. Phys Med Biol 65:085018, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ab7a71
Zeng M, Yan Z, Liu S, Zhou Y, Qiu L: Cascaded convolutional networks for automatic cephalometric landmark detection. Med Image Anal 68:101904, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101904
Huang Y, Fan F, Syben C et al. Cephalogram Synthesis and Landmark Detection in Dental Cone-Beam CT Systems. Med Imag Analys 70:102028, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102028
Kim MJ, Liu Y, Oh SH, et al: Automatic Cephalometric Landmark Identification System Based on the Multi-Stage Convolutional Neural Networks with CBCT Combination Images. Sensors (Basel) 21:505, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020505
Kwon HJ, Koo H, Park J, Cho NI: Multistage Probabilistic Approach for the Localization of Cephalometric Landmarks. IEEE Access. 2021;9. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3052460
Lagravère MO, Low C, Flores-Mir C, et al: Intraexaminer and interexaminer reliabilities of landmark identification on digitized lateral cephalograms and formatted 3-dimensional cone-beam computerized tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 137:598-604, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.07.018
Kim JH, An S, Hwang DM: Reliability of cephalometric landmark identification on three-dimensional computed tomographic images. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:320-325, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2021.07.003
Durão AP, Morosolli A, Pittayapat P, et al: Cephalometric landmark variability among orthodontists and dentomaxillofacial radiologists: a comparative study. Imaging Sci Dent 45:213-220, 2015. https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.4.213
Míguez-Contreras M, Jiménez-Trujillo I, Romero-Maroto M, López-de-Andrés A, Lagravère MO: Cephalometric landmark identification consistency between undergraduate dental students and orthodontic residents in 3-dimensional rendered cone-beam computed tomography images: A preliminary study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 151:157-166, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.06.034
Nalçaci R, Oztürk F, Sökücü O: A comparison of two-dimensional radiography and three-dimensional computed tomography in angular cephalometric measurements. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 39:100-106, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/82724776
Sam A, Currie K, Oh H, Flores-Mir C, Lagravére-Vich M: Reliability of different three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks in cone-beam computed tomography: A systematic review. Angle Orthod 89:317-332, 2019. https://doi.org/10.2319/042018-302.1
Nanni L, Ghidoni S, Brahnam S: Handcrafted vs. non-handcrafted features for computer vision classification. Pattern Recog 71:158–72, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.05.025
Schwendicke F, Krois J: Better Reporting of Studies on Artificial Intelligence: CONSORT-AI and Beyond. J Dent Res 100:677-680, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034521998337
Acknowledgements
We are thankful for the support of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brazil (CNPq) and of Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais – Brazil (FAPEMIG).
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GQTBM: Conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript, final approval. WAV: Acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript, final approval. MTCV: Acquisition of data, drafting the manuscript, final approval. BANT: Drafting the manuscript, final approval. TLB: Drafting the manuscript, final approval. RSN: Drafting the manuscript, final approval. LRP: Drafting the manuscript, final approval. RBBJ: Conception and design, drafting the manuscript, final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Queiroz Tavares Borges Mesquita, G., Vieira, W.A., Vidigal, M.T.C. et al. Artificial Intelligence for Detecting Cephalometric Landmarks: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Digit Imaging 36, 1158–1179 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00766-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00766-w