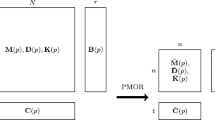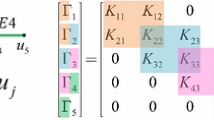Abstract
The method of elastic multibody systems enables the analysis, simulation, and optimization of mechanical systems with consideration of elastic deformations and nonlinear rigid body motions. The combination of multibody systems with elastic bodies requires to reduce the elastic degrees of freedom by model order reduction. To gain satisfying reduction results, the boundary conditions and acting loads have to be considered in the model reduction process. In a rising number of industrial applications the boundary conditions or the position of acting loads on the elastic bodies are not known a-priori. The simulation, e.g., of cranes, turning processes or gear wheels requires the definition of elastic systems with moving loads. For a good approximation of mechanical systems with moving loads a large number of ansatz functions is required to consider the local deformations generated by the changing load. This approach leads to very large reduced systems and is not feasible if the possible contact area is large or is not known prior to the simulation. In this contribution, the moving load is described by a parameter dependent input matrix. The application of parametric model order reduction techniques based on matrix interpolation to generate interpolated reduced systems without regarding the original system for each parameter value is proposed. Two mechanical examples are examined to illustrate the problems and developed solutions in the application of these methods for the simulation of moving loads in elastic multibody systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwertassek, R., Wallrapp, O.: Dynamik Flexibler Mehrkörpersysteme (in German). Braunschweig, Vieweg (1999)
Bathe, K.J.: Finite-Elemente-Methoden (in German). Springer, Berlin (1990)
Fischer, M., Eberhard, P.: Model reduction of large scale industrial models in elastic multibody dynamics. Multibody System Dynamics (2012)
Antoulas, A.: Approximation of large-scale dynamical systems. Philadelphia: SIAM (2005)
Benner, P., Mehrmann, V., Sorensen, D. (eds.): Dimension reduction of large-scale systems, vol. 45 of Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Bai, Z., Meerbergen, K., Su, Y.: Dimension reduction of large-Scale systems. In: Benner, P., Mehrmann, V., Sorensen, D. (eds.) Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol. 45 of Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, chap. Arnoldi Methods for Structure-Preserving Dimension Reduction of Second-Order Dynamical Systems, pp 173–189. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Antoulas, A., Beattie, C., Gugercin, S.: Interpolatory model reduction of large-scale dynamical systems. In: Mohammadpour, J., Grigoriadis, K. (eds.) Efficient Modeling and Control of Large-Scale Systems, pp 3–59. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Mehrmann, V., Stykel, T.: Balanced truncation model reduction for large-scale systems in descriptor Form. In: Benner, P., Mehrmann, V., Sorensen, D. (eds.) Dimension Reduction of Large-Scale Systems, of Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol. 45, pp 83–115. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Craig, R.: Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses: An overview. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Dynamics Specialists Conference, Paper-ID 2000-1573, Atlanta (2000)
Lehner, M.: Modellreduktion in elastischen mehrkörpersystemen (in German), vol. 10 Dissertation, Schriften aus dem Institut für Technische und Numerische Mechanik der Universität Stuttgart. Aachen, Shaker Verlag (2007)
Fehr, J.: Automated and error-controlled model reduction in elastic multibody systems, vol. 21 Dissertation, Schriften aus dem Institut für Technische und Numerische Mechanik der Universität Stuttgart. Aachen, Shaker Verlag (2011)
Fryba, L.: Vibration of Solids and Structures Under Moving Loads. Noordhoff International Publishing, Groningen (1999)
Nowakowski, C., Fehr, J., Fischer, M., Eberhard, P.: Model order reduction in Elastic multibody systems using the floating frame of reference formulation. In: Proceedings MATHMOD 2012 - 7th Vienna International Conference on Mathematical Modelling, Vienna, Austria (2012)
Fischer, A., Eberhard, P.: Simulation-based stability analysis of a thin-walled cylinder during turning with improvements using an adaptronic turning chisel. Arch. Mech. Eng. 58(4), 367–391 (2011)
Tamarozzi, T., Heirman, G., Desmet, W.: An on-line time dependent parametric model order reduction scheme with focus on dynamic stress recovery. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2013 (accepted for publication) (2013)
Benner, P., Gugercin, S., Willcox, K.: A Survey of Model Reduction Methods for Parametric Systems. Max Planck Institute Magdeburg Preprint MPIMD13-14 (2013)
Panzer, H., Mohring, J., Eid, R., Lohmann, B.: Parametric model order reduction by matrix interpolation. Automatisierungstechnik 58 (8), 475–484 (2010)
Amsallem, D., Farhat, C.: An online method for interpolating linear parametric reduced-order models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33, 2169–2198 (2011)
Baur, U., Beattie, C., Benner, P., Gugercin, S.: Interpolatory projection methods for parameterized model reduction. SIAM Journal for Scientific Computing 33, 2489–2518 (2009)
Baur, U., Benner, P.: Modellreduktion für parametrisierte systeme durch balanciertes abschneiden und interpolation (in German). at-Automatisierungstechnik 57 (8), 411–419 (2009)
Amsallem, D., Farhat, C.: An interpolation method for adapting reduced-order models and application to aeroelasticity. AIAA J. 46, 1803–1813 (2008)
Fischer, M., Eberhard, P.: Parametric model reduction in simulation of moving loads in elastic multibody systems. In: Proceedings Model Reduction of Parametrized Systems MoRePaS 12, Günzburg (2012)
Geuss, M., Panzer, H., Lohmann, B.: On parametric model order reduction by matrix interpolation. In: Proceedings of the European Control Conference, Zürich (2013)
Allemang, R.: The modal assurance criterion - 20 years of use and abuse. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Modal Analysis Conference, Los Angeles, pp. 14–21 (2002)
Bungartz, H.J., Griebel, M.: Sparse Grids, vol. 13, pp 147–269 (2004)
Neubauer, M.: Implementierung multivariater Interpolation für parametererhaltende Modellreduktion (in German). Bachelor Thesis BSC-007. Institute of Engineering and Computational Mechanics, University of Stuttgart (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Editors of Special Issue on MoRePas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, M., Eberhard, P. Application of parametric model reduction with matrix interpolation for simulation of moving loads in elastic multibody systems. Adv Comput Math 41, 1049–1072 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-014-9379-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-014-9379-7