Abstract
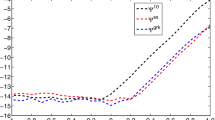
Symplectic integration of autonomous Hamiltonian systems is a well-known field of study in geometric numerical integration, but for non-autonomous systems the situation is less clear, since symplectic structure requires an even number of dimensions. We show that one possible extension of symplectic methods in the autonomous setting to the non-autonomous setting is obtained by using canonical transformations. Many existing methods fit into this framework. We also perform experiments which indicate that for exponential integrators, the canonical and symmetric properties are important for good long time behaviour. In particular, the theoretical and numerical results support the well documented fact from the literature that exponential integrators for non-autonomous linear problems have superior accuracy compared to general ODE schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, R., Marsden, J.E.: Foundations of mechanics Advanced Book Program, Reading, Mass. 2nd edn. Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Inc (1978). http://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechBOOK:1987.001
Arnol’d, V.I.: Mathematical methods of classical mechanics Graduate Texts in Mathematics. 2nd edn., vol. 60. Springer, New York (1989), doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2063-1
Asorey, M., Cariñena, J.F., Ibort, A.: Generalized canonical transformations for time-dependent systems. J. Math. Phys. 24(12), 2745–2750 (1983). doi: 10.1063/1.525672
Blanes, S., Casas, F., Oteo, J.A., Ros, J.: Magnus and Fer expansions for matrix differential equations: the convergence problem. J. Phys. A 31(1), 259–268 (1998). doi:10.1088/0305-4470/31/1/023
Blanes, S., Casas, F., Oteo, J.A., Ros, J.: The Magnus expansion and some of its applications. Phys. Rep. 470(5–6), 151–238 (2009). doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2008.11.001
Blanes, S., Diele, F., Marangi, C., Ragni, S.: Splitting and composition methods for explicit time dependence in separable dynamical systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235(3), 646–659 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.cam.2010.06.018
Celledoni, E., Marthinsen, A., Owren, B.: Commutator-free Lie group methods. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 19(3), 341–352 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0167-739X(02)00161-9
Celledoni, E., McLachlan, R.I., Owren, B., Quispel, G.R.W.: Geometric properties of Kahan’s method. J. Phys. A 46(2), 025,201, 12 (2013). doi:10.1088/1751-8113/46/2/025201
Feng, K, Qin, M.Z.: The symplectic methods for the computation of Hamiltonian equations. In: Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations (Shanghai, 1987), Lecture Notes in Math. doi:10.1007/BFb0078537, vol. 1297, pp 1–37. Springer, Berlin (1987)
Fer, F.: Résolution de l’équation matricielle d U/d t=p U par produit infini d’exponentielles matricielles. Acad. R Belg. Bull. Cl Sci. (5) 44, 818–829 (1958)
González, C.J., Thalhammer, M.: A second-order Magnus-type integrator for quasi-linear parabolic problems. Math. Comput. 76(257), 205–231 (2007). doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-06-01883-7
González, C.J., Ostermann, A., Thalhammer, M.: A second-order Magnus-type integrator for nonautonomous parabolic problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 189(1–2), 142–156 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.cam.2005.04.036
Grimm, V.K.R., Hochbruck, M.: Error analysis of exponential integrators for oscillatory second-order differential equations. J. Phys. A 39(19), 5495–5507 (2006). doi:10.1088/0305-4470/39/19/S10
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations . II, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, 2nd edn., vol. 14. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Hairer, E., Nørsett, S.P., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations. I, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, 2nd edn., vol. 8. Springer, Berlin (1993). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-78862-1
Hairer, E., Lubich, C., Wanner, G.: Geometric Numerical Integration, 2nd edn.. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 31. Springer, Berlin (2006). doi:10.1007/3-540-30666-8
Hochbruck, M., Lubich, C.: On Magnus integrators for time-dependent Schrödinger equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(3), 945–963 (2003). doi:10.1137/S0036142902403875
Iserles, A.: Solving linear ordinary differential equations by exponentials of iterated commutators. Numer. Math. 45(2), 183–199 (1984). doi:10.1007/BF01389464
Iserles, A.: On the global error of discretization methods for highly-oscillatory ordinary differential equations. BIT 42(3), 561–599 (2002). doi:10.1023/A:1022049814688
Iserles, A., Nørsett, S.P.: On the solution of linear differential equations in Lie groups. R Soc. Lond. Philos. Trans. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 357(1754), 983–1019 (1999). doi:10.1098/rsta.1999.0362
Khanamiryan, M.: Quadrature methods for highly oscillatory linear and non-linear systems of ordinary differential equations: part II. BIT 52(2), 383–405 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10543-011-0355-z
Leimkuhler, B.J., Reich, S.: Simulating Hamiltonian Dynamics. Cambridge Monographs on Applied and Computational Mathematics, vol. 14. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004). doi:10.1017/CBO9780511614118
Magnus, W.: On the exponential solution of differential equations for a linear operator. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 7, 649–673 (1954). doi:10.1002/cpa.3160070404
Marsden, J.E., Ratiu, T.S.: Introduction to Mechanics and Symmetry, 2nd edn.. Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 17. Springer, New York (1999)
Marthinsen, A., Owren, B.: Quadrature methods based on the Cayley transform. Appl. Numer. Math. 39(3–4), 403–413 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0168-9274(01)00087-3. special issue: Themes in geometric integration
Moler, C.B., Van Loan, C.F.: Nineteen dubious ways to compute the exponential of a matrix, twenty-five years later. SIAM Rev. 45(1), 3–49 (2003). doi:10.1137/S00361445024180
Ruth, R.D.: A canonical integration technique. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 30(4), 2669–2671 (1983). doi:10.1109/TNS.1983.4332919
Struckmeier, J.: Hamiltonian dynamics on the symplectic extended phase space for autonomous and non-autonomous systems. J. Phys. A 38(6), 1257–1278 (2005). doi:10.1088/0305-4470/38/6/006
Suzuki, M.: Fractal decomposition of exponential operators with applications to many-body theories and Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Lett. A 146(6), 319–323 (1990). doi:10.1016/0375-9601(90)90962-N
Yoshida, H.: Construction of higher order symplectic integrators. Phys. Lett. A 150(5–7), 262–268 (1990). doi:10.1016/0375-9601(90)90092-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Martin Stynes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marthinsen, H., Owren, B. Geometric integration of non-autonomous linear Hamiltonian problems. Adv Comput Math 42, 313–332 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-015-9425-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-015-9425-0