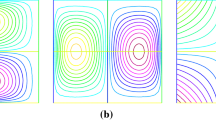
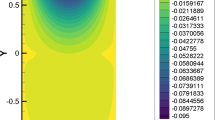
Abstract
Based on finite element discretization and a fully overlapping domain decomposition, we propose and study some parallel iterative subgrid stabilized algorithms for the simulation of the steady Navier-Stokes equations with high Reynolds numbers, where the quadratic equal-order elements are used for the velocity and pressure approximations, and the subgrid-scale model based on an elliptic projection is employed to penalize instability introduced by the dominant convective term in the Navier-Stokes system. In the present algorithms, each subproblem is defined in the whole domain with the vast majority of the degrees of freedom associated with the particular subdomain that it is responsible for and hence can be solved in parallel with other subproblems. All of the subproblems are nonlinear and are independently solved by some iterative methods. Stability and convergence of the proposed parallel iterative algorithms are analyzed under some (strong) uniqueness conditions. Furthermore, new results of stopping criteria for nonlinear iterations are derived. Numerical examples which verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Temam, R.: Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Approximation of the Navier-Stokes Equations. Springer, Berlin (1979)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Method for Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Glowinski, R.: Finite element methods for incompressible viscous flow. In: Ciarlet, P. G., Lions, J. L. (eds.) Handbook of Numerical Analysis, Vol. IX, Numerical Methods for Fluids Part, p 3. Elsevier Scinence Publisher, Amsterdam (2003)
Elman, H.C., Silvester, D.J., Wathen, A.J.: Finite Element and Fast Iterative Solvers: With Applications in Incompressible Fluid Dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2005)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations. Math. Comput. 69, 881–909 (2000)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for nonlinear problem. Adv. Comput. Math. 14, 293–327 (2001)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H., Li, J.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Stokes problem. Numer. Math. 109, 415–434 (2008)
Shang, Y.Q., Wang, K.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for the transient Stokes equations. Numer. Algor. 54, 195–218 (2010)
Yang, Y.D., Han, J.Y.: The multilevel mixed finite element discretizations based on local defect-correction for the Stokes eigenvalue problem. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 289, 249–266 (2015)
Bi, H., Han, J.Y., Yang, Y.D.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the transmission eigenvalue problem. J. Sci. Comput. 78, 351–375 (2019)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Navier-Stokes problem. J. Comput. Math. 24, 227–238 (2006)
He, Y.N., Mei, L.Q., Shang, Y.Q.: Nowton iterative parallel finite element algorithm for the steady Navier-Stokes equations. J. Sci. Comput 44, 92–106 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N., Kim, D.: A new parallel finite element algorithm for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47, 1262–1279 (2011)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: A parallel Oseen-linearized algorithm for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 209, 172–183 (2012)
Zhang, Y.H., Hou, Y.R., Li, Y.: Shan others, Local and parallel finite element algorithm for stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33, 1513–1539 (2017)
Tang, Q.L., Huang, Y.Q.: Local and parallel finite flement algorithm based on Oseen-type iteration for the stationary incompressible MHD flow. J. Sci. Comput. 70, 1–26 (2017)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: Parallel iterative finite element algorithms based on full domain decomposition for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60, 719–737 (2010)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: Parallel iterative stabilized finite element algorithms based on the lowest equal-order elements for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 357, 35–56 (2019)
Yu, J.P., Shi, F., Zheng, H.B.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on the partition of unity for the Stokes problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(5), C547–C567 (2014)
Zheng, H.B., Yu, J.P., Shi, F.: Local and parallel finite element algorithm based on the partition of unity for incompressible flows. J. Sci. Comput. 65, 512–532 (2015)
Du, G.Z., Zuo, L.Y.: A parallel partition of unity scheme based on two-grid discretizations for the Navier-Stokes problem. J. Sci. Comput. 75, 1445–1462 (2018)
Bank, R.E., Holst, M.: A new paradigm for parallel adaptive meshing algorithms. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22, 1411–1443 (2000)
Bank, R.E., Jimack, P.K.: A new parallel domain decomposition method for the adaptive finite element solution of elliptic partial differential equations, Concurr. Comput. Pract. Expert 13, 327–350 (2001)
Mitchell, W.F.: Parallel adaptive multilevel methods with full domain partitions. Appl. Numer. Anal. Comput. Math. 1(1-2), 36–48 (2004)
Layton, W.: A connection between subgrid scale eddy viscosity and mixed methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 133, 147–157 (2002)
Guermond, J., Marra, A., Quartapelle, L.: Subgrid stabilized projection method for 2D unsteady flows at high Reynolds numbers. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 195, 5857–5876 (2006)
Kaya, S., Lyton, W., Riviere, B.: Subgrid stabilized defect correction methods for the Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1639–1654 (2006)
Zhang, Y., He, Y.N.: Assessment of subgrid-scale models for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234, 593–604 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q.: A two-level subgrid stabilized Oseen iterative method for the steady Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 233, 210–226 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q.: A new two-level defect-correction method for the steady Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 391, 113009 (2020)
Yang, X.C., Shang, Y.Q., Zheng, B.: A simplified two-level subgrid stabilized method with backtracking technique for incompressible flows at high Reynolds numbers. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37, 2067–2088 (2020)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the Navier-Stokes equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 403, 667–679 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q., Huang, S.M.: A parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method based on two-grid discretization for simulation of 2D/3D steady incompressible flows. J. Sci. Comput. 60, 564–583 (2014)
Brooks, A.N., Hughes, T.J.R.: Streamline upwind/Petrov-Galerkin formulations for convective dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 32, 199–259 (1982)
Hughes, T.J.R., Franca, L.P., Balestra, M.: A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: V. Circumventing the Babuska-Brezzi condition: a stable Petrov-Galerkin formulation of the Stokes problem accomodating equal-order interpolations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 59, 85–99 (1986)
Hughes, T.J.R., Franca, L.P., Hulbert, G.M.: A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: VIII. The Galerkin/least-squares method for advective-diffusive equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 73, 173–189 (1989)
Blasco, J., Codina, R.: Stabilization finite elements method for the transient Navier-Stokes equations based on a pressure gradient projection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 182, 277–300 (2000)
Becker, R., Braack, M.: A finite elements pressure gradient stabilization for the Stokes equations based on local projections. Calcolo 38, 173–199 (2000)
Zheng, H.B., Shan, L., Hou, Y.R.: A quadratic equal-order stabilized method for Stokes problem based on two local Gauss integrations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 26, 180–1190 (2010)
Qiu, H.L., An, R., Mei, L.Q., Xue, C.F.: Two-step algorithms for the stationary incompressible Navier-Stokes equations with friction boundary conditions. Appl. Numer. Math. 120, 97–114 (2017)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: Parallel iterative stabilized finite element methods based on the quadratic equal-order elements for incompressible flows. Calcolo 57, 34 (2020)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel stabilized finite element variational multiscale method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 159, 128–158 (2021)
Li, K.T., Huang, A.X., Huang, Q.H.: Finite Element Methods and Their Applications. Academic Press, Beijing (2006)
Adams, R.: Sobolev Spaces. Academaic Press Inc, New York (1975)
He, Y.N., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on the finite element discretization for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Kechkar, N., Silvester, D.: Analysis of locally stabilized mixed finite element methods for the Stokes problem. Math. Comput. 58, 1–10 (1992)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20 (3-4), 251–265 (2012)
Erturk, E., Corke, T.C., Gokcol, C.: Numerical solutions of 2-D steady incompressible driven cavity flow at high Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 48, 747–774 (2005)
Liu, Q.F., Hou, Y.R.: A postprocess mixed finite element method for the Navier-Stokes equations. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 23, 461–475 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions and comments, which led to an improvement of the paper.
Funding
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11361016), Cooperative Program of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, China (No. Qian Ke He LH [2015]7042), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Municipality, China (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX1044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Paul Houston
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, B., Qin, J. & Shang, Y. Stability and convergence of some parallel iterative subgrid stabilized algorithms for the steady Navier-Stokes equations. Adv Comput Math 48, 35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-022-09950-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-022-09950-6
Keywords
- Navier-Stokes equations
- Iterative finite element discretization
- Stabilized method
- Subgrid-scale model
- Parallelization
- Domain decomposition