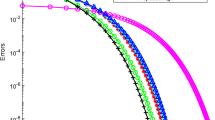
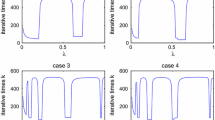
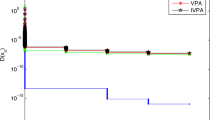
Abstract
We study the problem of finding a common element that solves the multiple-sets feasibility and equilibrium problems in real Hilbert spaces. We consider a general setting in which the involved sets are represented as level sets of given convex functions, and propose a constructible linear approximation scheme that involves the subgradient of the associated convex functions. Strong convergence of the proposed scheme is established under mild assumptions and several synthetic and practical numerical illustrations demonstrate the validity and advantages of our method compared with related schemes in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Censor, Y, Elfving, T, Kopf, N, Bortfeld, T.: The multiple-sets split feasibility problem and its applications for inverse problems. Inverse Probl. 21(6), 2071–2084 (2005). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/21/6/017
Censor, Y, Bortfeld, T, Martin, B, Trofimov, A.: A unified approach for inversion problems in intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol.. 51(10), 2353–2365 (2006). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/10/001
López, G, Martin, V, Xu, H, et al.: Iterative algorithms for the multiple-sets split feasibility problem. Biomed. Math.: Promising Directions in Imaging, Therapy Planning and Inverse Problems 243–279 (2009)
López, G, Martín-Márquez, V, Xu, HK: Perturbation techniques for nonexpansive mappings with applications. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10(4), 2369–2383 (2009). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.04.020
López, G, Martín-Márquez, V, Wang, F, Xu, HK: Solving the split feasibility problem without prior knowledge of matrix norms. Inverse Probl. 28(8), 085004 (2012). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/28/8/085004
Censor, Y, Elfving, T.: A multiprojection algorithm using Bregman projections in a product space. Numer. Algorithms 8(2), 221–239 (1994). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02142692
Censor, Y, Segal, A.: Iterative projection methods in biomedical inverse problems. Mathematical methods in biomedical imaging and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), vol. 10, pp. 65–96 (2008)
Wang, J, Hu, Y, Li, C, Yao, JC: Linear convergence of CQ algorithms and applications in gene regulatory network inference. Inverse Probl. 33(5), 055017 (2017). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6420/aa6699
Ansari, QH, Rehan, A: Split feasibility and fixed point problems. In: Nonlinear Analysis. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-1883-8∖_9, pp 281–322. Springer, India (2014)
Xu, HK: Iterative methods for the split feasibility problem in infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Inverse Probl. 26(10), 105018 (2010). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/26/10/105018https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/26/10/105018
Byrne, C.: A unified treatment of some iterative algorithms in signal processing and image reconstruction. Inverse Probl. 20(1), 103–120 (2003). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/20/1/006https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/20/1/006
Takahashi, W.: The split feasibility problem and the shrinking projection method in Banach spaces. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 16(7), 1449–1459 (2015)
Xu, H. K.: A variable Krasnosel’skii–Mann algorithm and the multiple-set split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 22(6), 2021–2034 (2006). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/22/6/007
Yang, Q.: The relaxed CQ algorithm solving the split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 20 (4), 1261–1266 (2004). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/20/4/014
Gibali, A, Mai, D T, Vinh, N T: A new relaxed CQ algorithm for solving split feasibility problems in Hilbert spaces and its applications. J. Ind. Manag. Optim.. 15(2), 963–984 (2019). Available from: https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2018080
Sahu, D R, Cho, Y J, Dong, Q L, Kashyap, M R, Li, X. H.: Inertial relaxed CQ algorithms for solving a split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. Numer. Algorithms. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-020-00999-2 (2020)
Shehu, Y, Gibali, A.: New inertial relaxed method for solving split feasibilities. Optim. Lett. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-020-01603-1 (2020)
Liou, Y C, Zhu, L J, Yao, Y, Chyu, C C: Algorithmic and analytical approaches to the split feasibility problems and fixed point roblems. Taiwan. J. Math. 17(5). Available from: https://doi.org/10.11650/tjm.17.2013.3175 (2013)
Byrne, C.: Iterative oblique projection onto convex sets and the split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 18(2), 441–453 (2002). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/18/2/310
Dong, Q L, Yao, Y, He, S.: Weak convergence theorems of the modified relaxed projection algorithms for the split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. Optim. Lett. 8(3), 1031–1046 (2013). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-013-0619-4
He, S, Zhao, Z.: Strong convergence of a relaxed CQ algorithm for the split feasibility problem. J. Inequal. Appl. 2013(1). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1029-242x-2013-197 (2013)
Yao, Y, Postolache, M, Liou, Y. C.: Strong convergence of a self-adaptive method for the split feasibility problem. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2013 (1), 201 (2013). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1812-2013-201
Dang, Y, Sun, J, Xu, H: Inertial accelerated algorithms for solving a split feasibility problem. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 13(3), 1383–1394 (2017). Available from: https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2016078
Gibali, A, Liu, L W, Tang, Y. C.: Note on the modified relaxation CQ algorithm for the split feasibility problem. Optim. Lett. 12(4), 817–830 (2017). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1148-3https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1148-3
Shehu, Y, Vuong, P T, Cholamjiak, P.: A self-adaptive projection method with an inertial technique for split feasibility problems in Banach spaces with applications to image restoration problems. J. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 21(2). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11784-019-0684-0 (2019)
Blum, E.: From optimization and variational inequalities to equilibrium problems. Mathematics Student 63, 123–145 (1994)
Facchinei, F, Pang, J. S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems, vol. II. Springer Series in Operations Research. Springer, New York (2003)
Konnov, I. V.: Equilibrium Models and Variational Inequalities, vol. 210 of Mathematics in Science and Engineering. Elsevier B. V., Amsterdam (2007)
Muu, L D, Oettli, W.: Convergence of an adaptive penalty scheme for finding constrained equilibria. Nonlinear Anal. 18(12), 1159–1166 (1992). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/0362-546X(92)90159-Chttps://doi.org/10.1016/0362-546X(92)90159-C
Chang, X, Liu, S, Deng, Z, Li, S.: An inertial subgradient extragradient algorithm with adaptive stepsizes for variational inequality problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 1–20 (2021)
Ceng, L C, Petruşel, A, Qin, X, Yao, J. C.: Two inertial subgradient extragradient algorithms for variational inequalities with fixed-point constraints. Optimization 70(5–6), 1337–1358 (2021). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2020.1858832
Bnouhachem, A, Al-Homidan, S, Ansari, Q.: An iterative method for common solutions of equilibrium problems and hierarchical fixed point problems. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2014(1), 194 (2014). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1812-2014-194
Flåm, SD, Antipin, AS: Equilibrium programming using proximal-like algorithms. Math. Program. 78(1), 29–41 (1996). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02614504
Moudafi, A.: Second-order differential proximal methods for equilibrium problems. J. Inequalities Appl. Math. 4(1), 1–7 (2003)
Shehu, Y, Iyiola, O S, Thong, D V, Van, N. T. C.: An inertial subgradient extragradient algorithm extended to pseudomonotone equilibrium problems. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 93(2), 213–242 (2021). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-020-00730-w
Sombut, K, Plubtieng, S.: Weak convergence theorem for finding fixed points and solution of split feasibility and systems of equilibrium problems. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 1–8 (2013). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/430409
Qin, X, Wang, L.: A fixed point method for solving a split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. Rev. R. Acad. Cienc. Exactas Fís. Nat. Ser. A Mat. 113(1), 315–325 (2017). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-017-0476-6
Shehu, Y, Ogbuisi, FU: An iterative method for solving split monotone variational inclusion and fixed point problems. Rev. R. Acad. Cienc. Exactas Fís. Nat. Ser. A Mat. 110(2), 503–518 (2015). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-015-0245-3
Tang, Y, Gibali, A.: Several inertial methods for solving split convex feasibilities and related problems. Rev. R. Acad. Cienc. Exactas Fís. Nat. Ser. A Mat. 114(3). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-020-00857-9 (2020)
Tang, Y, Zhu, C, Yu, H.: Iterative methods for solving the multiple-sets split feasibility problem with splitting self-adaptive step size. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2015(1). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13663-015-0430-2 (2015)
Bauschke, H H, Combettes, P. L.: Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces. Springer, New York (2011). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9467-7
Goebel, K, Simeon, R.: Uniform Convexity, Hyperbolic Geometry, and Nonexpansive Mappings. Dekker, New York (1984)
Goebel, K, Kirk, W. A.: Topics in Metric Fixed Point Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511526152
Aubin, J. P.: Optima and Equilibria: an Introduction to Nonlinear Analysis, vol. 140. Springer Science & Business Media (2013)
Takahashi, S, Takahashi, W.: Viscosity approximation methods for equilibrium problems and fixed point problems in Hilbert spaces. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 331(1), 506–515 (2007). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.08.036
Suzuki, T: Strong convergence theorems for infinite families of nonexpansive mappings in general Banach spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2005(1), 685918 (2005). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1155/fpta.2005.103
Xu, H. K.: Iterative algorithms for nonlinear operators. J. London Math. Soc. 66(1), 240–256 (2002). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1112/s0024610702003332
Maingé, P. E.: New approach to solving a system of variational inequalities and hierarchical problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 138(3), 459–477 (2008). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-008-9433-zhttps://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-008-9433-z
Dai, Y. H.: Fast algorithms for projection on an ellipsoid. SIAM J. Optim. 16(4), 986–1006 (2006). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1137/040613305
Yu, H, Zhan, W, Wang, F.: The ball-relaxed CQ algorithms for the split feasibility problem. Optimization 67(10), 1687–1699 (2018). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2018.1485677
He, S, Zhao, Z, Luo, B.: A relaxed self-adaptive CQ algorithm for the multiple-sets split feasibility problem. Optimization 64(9), 1907–1918 (2015). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2014.895898https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2014.895898
Suantai, S, Pholasa, N, Cholamjiak, P.: Relaxed CQ algorithms involving the inertial technique for multiple-sets split feasibility problems. Rev. R. Acad. Cienc. Exactas Fís. Nat. Ser. A Mat. RACSAM 113(2), 1081–1099 (2019). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-018-0535-7
Cegielski, A.: Iterative Methods for Fixed Point Problems in Hilbert Spaces, vol. 2057 of Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Kesornprom, S, Pholasa, N, Cholamjiak, P.: On the convergence analysis of the gradient-CQ algorithms for the split feasibility problem. Numer. Algorithms 84(3), 997–1017 (2020). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-019-00790-y
Reich, S, Truong, M T, Mai, T. N. H.: The split feasibility problem with multiple output sets in Hilbert spaces. Optim Lett. 14 (8), 2335–2353 (2020). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-020-01555-6https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-020-01555-6
Suantai, S, Eiamniran, N, Pholasa, N, Cholamjiak, P.: Three-step projective methods for solving the split feasibility problems. Mathematics 7(8), 712 (2019). Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080712https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080712
Wang, F.: Polyak’s gradient method for split feasibility problem constrained by level sets. Numer. Algorithms 77(3), 925–938 (2018). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-017-0347-4
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Center of Excellence in Theoretical and Computational Science (TaCS-CoE), KMUTT. Guash Haile Taddele was supported by the ”Petchra Pra Jom Klao Ph.D. Research Scholarship from King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi” (Grant No.37/2561). Moreover, this project is funded by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) under Research Grants for Talented Mid-Career Researchers (Contract no. N41A640089). We are also very grateful to the Editor and Reviewers for taking the time and effort necessary to review the manuscript. We sincerely appreciate all valuable comments and suggestions, which helped us to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Center of Excellence in Theoretical and Computational Science (TaCS-CoE), Faculty of Science, KMUTT. The first author was supported by the ”Petchra Pra Jom Klao Ph.D. Research Scholarship from King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi” with Grant No. 37/2561. Moreover, this project is funded by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) under Research Grants for Talented Mid-Career Researchers (Contract no. N41A640089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Stefan Volkwein
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taddele, G.H., Li, Y., Gibali, A. et al. Linear approximation method for solving split inverse problems and its applications. Adv Comput Math 48, 39 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-022-09959-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-022-09959-x