Abstract
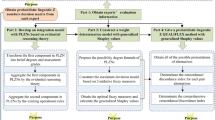
In group decision-making problems, decision makers prefer to use several linguistic terms to describe their own perception and knowledge, and give their preference intensity of each possible linguistic terms based on their own understanding and interpretation. Due to the nonlinearity of decision maker’s cognition, the gaps between adjacent linguistic terms are unbalanced. The unbalanced probabilistic linguistic term set (UPLTS) is proposed to present such situation. To this phenomenon, a resolution framework is constructed to analyze multiple attribute group decision-making problems under unbalanced probabilistic linguistic environment. Firstly, the integration model based on evidential reasoning theory is proposed to aggregate UPLTSs from different groups in view of incomplete probabilistic distributions in UPLTS. Secondly, the transformation function based on proportional 2 tuple is developed to transform UPLTS into probabilistic linguistic term set, making it easier for subsequent analysis and processing. Thirdly, Based on the multiple types of partitioned structure relationship among attributes, partitioned fuzzy measure is developed to globally capture these interactions among attributes. Then the probabilistic linguistic Choquet integral operator with partitioned fuzzy measure is proposed to obtain the comprehensive performances of alternatives. Lastly, the effectiveness and practicability of the proposed method is demonstrated using three numerical examples and comparing with other methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Choquet G (1953) Theory of capacities. Annales de l’institut Fourier 5:131–295
Dong Y, Xu Y, Yu S (2009) Computing the numerical scale of the linguistic term set for the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17(6):1366–1378
Dong Y, Wu Y, Zhang H, Zhang G (2015) Multi-granular unbalanced linguistic distribution assessments with interval symbolic proportions. Knowl Based Syst 82:139–151
Dong Y, Li C-C, Herrera F (2016) Connecting the linguistic hierarchy and the numerical scale for the 2-tuple linguistic model and its use to deal with hesitant unbalanced linguistic information. Inf Sci 367:259–278
Dutta B, Guha D, Mesiar R (2014) A model based on linguistic 2-tuples for dealing with heterogeneous relationship among attributes in multi-expert decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(5):1817–1831
Fu Z, Liao H (2019) Unbalanced double hierarchy linguistic term set: The TOPSIS method for multi-expert qualitative decision making involving green mine selection. Inf Fusion 51:271–286
Grabisch M (1996a) The representation of importance and interaction of features by fuzzy measures. Pattern Recogn Lett 17:567–575
Grabisch M (1996b) The application of fuzzy integrals in multicriteria decision making. Eur J Oper Res 89:445–456
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L (2008) A fuzzy linguistic methodology to deal with unbalanced linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16(2):354–370
Jiang YP, Liang HM, Sun M (2015) A method based on the ideal and nadir solutions for stochastic multi-attribute decision making. Comput Ind Eng 87:114–125
Khan MSA, Abdullah S, Ali A, Amin F, Hussain F (2019) Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy Choquet integral aggregation operators and their application to multi-attribute decision-making. Soft Comput 23(1):251–267
Klir GJ, Yuan B (1995) Fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic: theory and applications. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, p 563
Li P, Wei C (2019) An emergency decision-making method based on DS evidence theory for probabilistic linguistic term sets. Int J Disast Risk Reduct 37:101178
Liang GS, Chou TY, Han TC (2005) Cluster analysis based on fuzzy equivalence relation. Eur J Oper Res 166(1):160–171
Liang D, Darko AP, Xu Z, Zhang Y (2019) Partitioned fuzzy measure-based linear assignment method for Pythagorean fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making with a new likelihood. J Oper Res Soc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.159013
Lin M, Wang H, Xu Z, Yao Z, Huang J (2018) Clustering algorithms based on correlation coefficients for probabilistic linguistic term sets. Int J Intell Syst 33(12):2402–2424
Ma Z, Zhu J, Chen Y (2018) A probabilistic linguistic group decision-making method from a reliability perspective based on evidential reasoning. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2815716
Ma W, Jiang Y, Luo X (2019) A flexible rule for evidential combination in Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105512
Mao XB, Wu M, Dong JY, Wan SP, Jin Z (2019) A new method for probabilistic linguistic multi-attribute group decision making: application to the selection of financial technologies. Appl Soft Comput 77:155–175
Marichal JL (2000) An axiomatic approach of the discrete Choquet integral as a tool to aggregate interacting criteria. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(6):800–807
Mohammadi SE, Makui A (2017) Multi-attribute group decision making approach based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and evidential reasoning methodology. Soft Comput 21(17):5061–5080
Pang Q, Wang H, Xu Z (2016) Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf Sci 369:128–143
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2011) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Sugeno M (1974) Theory of fuzzy integral and its application. Doctorial dissertation, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tang M, Liao H (2019) Managing information measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their applications in designing clustering algorithms. Inf Fusion 50:30–42
Tian ZP, Nie RX, Wang JQ (2019) Probabilistic linguistic multi-criteria decision-making based on evidential reasoning and combined ranking methods considering decision-makers’ psychological preferences. J Oper Res Soc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.1632752
Wang JH, Hao J (2006) A new version of 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14(3):435–445
Wang L, Wang Y, Pedrycz W (2019) Hesitant 2-tuple linguistic Bonferroni operators and their utilization in group decision making. Appl Soft Comput 77:653–664
Wei G, Lu M, Tang X, Wei Y (2018) Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(6):1197–1233
Wu Z, Xu J, Jiang X, Zhong L (2019) Two MAGDM models based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets with possibility distributions: vIKOR and TOPSIS. Inf Sci 473:101–120
Wu YZ, Zhang Z, Kou G, Zhang HJ, Chao XR, Li CC, Dong YC, Herrera F (2020a) Distributed linguistic representations in decision making: taxonomy, key elements and applications, and challenges in data science and explainable artificial intelligence. Inf Fusion. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.08.018
Wu YZ, Dong YC, Qing JD, Pedrycz W (2020b) Flexible linguistic expressions and consensus reaching with accurate constraints in group decision making. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6):2488–2501
Yang JB, Xu DL (2002) On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A Syst Hum 32(3):289–304
Yang JB, Wang YM, Xu DL, Chin KS (2006) The evidential reasoning approach for MADA under both probabilistic and fuzzy uncertainties. Eur J Oper Res 171(1):309–343
Yu W, Zhang Z, Zhong Q, Sun L (2017) Extended TODIM for multi-criteria group decision making based on unbalanced hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Comput Ind Eng 114:316–328
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zhang X, Xing X (2017) Probabilistic linguistic VIKOR method to evaluate green supply chain initiatives. Sustainability 9(7):1231
Zhang Q, Xu K, Wang G (2016) Fuzzy equivalence relation and its multigranulation spaces. Inf Sci 346:44–57
Zhang HJ, Xiao J, Palomares I, Liang HM, Dong YC (2020) Linguistic distribution-based optimization approach for large-scale GDM with comparative linguistic information. An application on the selection of wastewater disinfection technology. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(2):376–389
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.ZR2020QG002), the Social science planning project of Shandong Province (No. 20CSDJ23), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71471172 and 71801142), the Special Funds of Taishan Scholars Project of Shandong Province (No. ts201511045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, F., Liu, P. & Liang, X. Unbalanced probabilistic linguistic decision-making method for multi-attribute group decision-making problems with heterogeneous relationships and incomplete information. Artif Intell Rev 54, 3431–3471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09927-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09927-1