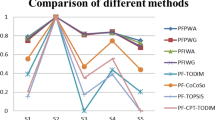
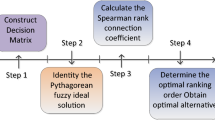
Abstract
Conflict analysis gives guidelines for conflict resolution, which has been thoroughly studied and received widespread interest. Three-way conflict analysis research has achieved remarkable results and has been extended to Pythagorean fuzzy information systems because the three-way decision coincides with three attitudes of agents on issues, where the positive and negative degrees of agents are depicted by the membership and non-membership degrees. However, agent’s opinions on issues must not be expressed only by real numbers, and the form of ranges can be used. Interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets allow the membership and non-membership degrees of a given set to have interval values, which can effectively handle this problem. This work analyzes a three-way conflict analysis based on interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy information systems. First, we introduce the concept of interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy information systems and illustrate how to divide positive, neutral, and negative alliances by the measurement function and thresholds. Then, we focus on a three-way conflict analysis based on prospect theory by considering the subjective risk attitude and preference of decision-makers. Finally, we further investigate three-way conflict analysis based on interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets and prospect theory with group decision theory, where the outcome matrices are provided by multiple experts. Several examples of software development project team conflicts are employed to illustrate the process of conducting a three-way conflict analysis based on interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy information systems and prospect theory. The comparative analysis is utilized to show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed three-way conflict analysis approach compared with other models and methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chu XL, Sun BZ, Huang QC, Zhang Y (2020) Preference degree-based multi-granularity sequential three-way group conflict decisions approach to the integration of tcm and western medicine. Computers & Industrial Engineering 143:106393
Dai D, Li HX, Jia XY, Huang B, Liang SN (2020) A co-training approach for sequential three-way decisions. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:1129–1139
Du JL, Liu SF, Liu Y, Yi JH (2022) A novel approach to three-way conflict analysis and resolution with pythagorean fuzzy information. Inf Sci 584:65–88
Huang B, Liu JB, Guo CX, Li HX, Feng GF (2021) Relative-distance-based approaches for ranking intuitionistic fuzzy values. Artif Intell Rev 54:3089–3114
Jia XY, Rao Y, Li WW, Yang SC, Yu H (2021) An automatic three-way clustering method based on sample similarity. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:1545–1556
Jiang CM, Guo DD, Xu RY (2021) Measuring the outcome of movement-based three-way decision using proportional utility functions. Appl Intell 51:8598–8612
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1979) Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47(2):263–291
Lang GM, Yao YY (2021) New measures of alliance and conflict for three-way conflict analysis. Int J Approx Reason 132:49–69
Lang GM, Miao DQ, Cai MJ (2017) Three-way decision approaches to conflict analysis using decision-theoretic rough set theory. Inf Sci 406–407:185–207
Lang GM, Miao DQ, Fujita H (2020) Three-way group conflict analysis based on pythagorean fuzzy set theory. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(3):447–461
Li XH, Chen XH (2014) Extension of the topsis method based on prospect theory and trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers for group decision making. J Syst Sci Syst Eng 23(2):231–247
Li HX, Zhang LB, Huang B, Zhou XZ (2020a) Cost-sensitive dual-bidirectional linear discriminant analysis. Inf Sci 510:283–303
Li ZW, Xie NX, Huang D, Zhang GQ (2020b) A three-way decision method in a hybrid decision information system and its application in medical diagnosis. Artif Intell Rev 53:4707–4736
Li XN, Wang X, Lang GM, Yi HJ (2021) Conflict analysis based on three-way decision for triangular fuzzy information systems. Int J Approx Reason 132:88–106
Li XN, Yang YP, Yi HJ, Yu QQ (2022) Conflict analysis based on three-way decision for trapezoidal fuzzy information systems. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13:929–945
Liang DC, Xu ZS, Liu D, Wu Y (2018) Method for three-way decisions using ideal topsis solutions at pythagorean fuzzy information. Inf Sci 435:282–295
Liu D, Yang X, Li TR (2020a) Three-way decisions: beyond rough sets and granular computing. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:989–1002
Liu PD, Wang YM, Jia F, Fujita H (2020b) A multiple attribute decision making three-way model for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int J Approx Reason 119:177–203
Liu JB, Huang B, Li HX, Bu XZ, Zhou XZ (2022) Optimization-based three-way decisions with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3151899
Mandal P, Samanta S, Pal M, Ranadive AS (2022) Three-way decision model under a large-scale group decision-making environment with detecting and managing non-cooperative behaviors in consensus reaching process. Artif Intell Rev 55:5517–5542
Metzger LP, Rieger MO (2019) Non-cooperative games with prospect theory players and dominated strategies. Games Econom Behav 115:396–409
Min F, Liu FL, Wen LY, Zhang ZH (2019) Tri-partition cost-sensitive active learning through knn. Soft Comput 23:1557–1572
Mohagheghi V, Mousavi SM, Mojtahedi M, Newton S (2020) Evaluating large, high-technology project portfolios using a novel interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy set framework: an automated crane project case study. Expert Syst Appl 162:113007
Mu ZM, Zeng SZ, Wang PY (2021) Novel approach to multi-attribute group decision-making based on interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy power maclaurin symmetric mean operator. Computers & Industrial Engineering 155:113007
Pawlak Z (1998) An inquiry into anatomy of conflicts. Inf Sci 109(1–4):65–78
Peng XD, Yang Y (2016) Fundamental properties of interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy aggregation operators. Int J Intell Syst 31(5):444–487
Peng XD, Yang Y (2017) Algorithms for interval-valued fuzzy soft sets in stochastic multi-criteria decision making based on regret theory and prospect theory with combined weight. Appl Soft Comput 54:415–430
Qian T, Wei L, Qi JJ (2019) A theoretical study on the object (property) oriented concept lattices based on three-way decisions. Soft Comput 23:9477–9489
Sun BZ, Chen XT, Zhang LY, Ma WM (2020) Three-way decision making approach to conflict analysis and resolution using probabilistic rough set over two universes. Inf Sci 507:809–822
Tang Y, Yang Y (2021) Sustainable e-bike sharing recycling supplier selection: an interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy magdm method based on preference information technology. J Clean Prod 287:125530
Tversky A, Kahneman D (1992) Advances in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty. J Risk Uncertain 5(4):297–323
Wang YM (1998) Using the method of maximizing deviations to make decision for multiindicies. Syst Eng Electron 20(7):24–26
Wang TX, Li HX, Zhang LB, Zhou XZ, Huang B (2020a) A three-way decision model based on cumulative prospect theory. Inf Sci 519:74–92
Wang TX, Li HX, Zhou XZ, Huang B, Zhu HB (2020b) A prospect theory-based three-way decision model. Knowl-Based Syst 203:106129
Wang TX, Li HX, Zhou XZ, Liu D, Huang B (2021) Three-way decision model based on third-generation prospect theory with z-numbers. Inf Sci 569:13–38
Wang BL, Liang JY, Yao YY (2022a) A trilevel analysis of uncertainty measures in partition-based granular computing. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10177-6
Wang JJ, Ma XL, Xu ZS, Zhan JM (2022b) Regret theory-based three-way decision model in hesitant fuzzy environments and its application to medical decision. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3176686
Wang TX, Li HX, Qian YH, Huang B, Zhou XZ (2022c) A regret-based three-way decision model under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 30(1):175–189
Yager RR, Abbasov AM (2013) Pythagorean membership grades, complex numbers, and decision making. Int J Intell Syst 28(5):436–452
Yang B, Li JH (2020) Complex network analysis of three-way decision researches. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:973–987
Yao YY (2010) Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf Sci 180(3):341–353
Yao YY (2018) Three-way decision and granular computing. Int J Approx Reason 103:107–123
Yao YY (2019) Three-way conflict analysis: reformulations and extensions of the pawlak model. Knowl-Based Syst 180:26–37
Yao YY (2020) Tri-level thinking: models of three-way decision. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:947–959
Yao YY (2021) The geometry of three-way decision. Appl Intell 51:6298–6325
Yao JT, Azam N (2015) Web-based medical decision support systems for three-way medical decision making with game-theoretic rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(1):3–15
Yi HJ, Zhang HM, Li XN, Yang YP (2021) Three-way conflict analysis based on hesitant fuzzy information systems. Int J Approx Reason 139:12–27
Yin LJ, Zhang QH, Zhao F, Liu D, Wang GY (2022) Superiority of three-way decisions from the perspective of probability. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10203-7
Yu CX, Shao YF, Wang K, Zhang LP (2019) A group decision making sustainable supplier selection approach using extended topsis under interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy environment. Expert Syst Appl 121:1–17
Zhan JM, Jiang HB, Yao YY (2021) Three-way multi-attribute decision-making based on outranking relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(10):2844–2858
Zhang XY, Yao YY (2022) Tri-level attribute reduction in rough set theory. Expert Syst Appl 190:116187
Zhang LB, Wang TX, Li HX, Huang B, Zhou XZ (2019) Agent evaluation based on multi-source heterogeneous information table using topsis. Adv Eng Inform 42:100971
Zhang YX, Xu ZS, Hao ZN, Liao HC (2021a) Dynamic assessment of internet public opinions based on the probabilistic linguistic bayesian network and prospect theory. Appl Soft Comput 106:107359
Zhang QH, Cheng YL, Zhao F, Wang GY, Xia SY (2021b) Optimal scale combination selection integrating three-way decision with hasse diagram. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3054063
Zhi HL, Li JH, Li YN (2022) Multi-level conflict analysis based on fuzzy formal contexts. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3167789
Zhi HL, Qi JJ, Qian T, Ren RS (2020) Conflict analysis under one-vote veto based on approximate three-way concept lattice. Inf Sci 516:316–330
Zhu HB (2016) Avoiding conflicts by group role assignment. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 46(4):535–547
Zhu HB, Sheng Y, Zhou XZ, Zhu Y (2018) Group role assignment with cooperation and conflict factors. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 48(6):851–863
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers and editor for their valuable advice to improve the quality of the article. We would like to thank the EssayStar Company (http://essaystar.com/) for their assistance in improving the English language of this article. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62206129, 62276136, 62106205, 72274098 and 61876079), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Nos. 22KJB520019 and 20KJA520006) and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0824).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhang, L., Huang, B. et al. Three-way conflict analysis based on interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets and prospect theory. Artif Intell Rev 56, 6061–6099 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10327-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10327-w