Abstract
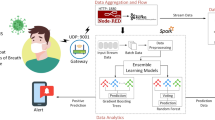
Amidst the COVID-19 humanitarian catastrophe, the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are premier technologies in the healthcare domain that have emerged to a great extent. This global health emergency highlights the need to bolster current healthcare systems for future preparedness. Conspicuously, the current paper presents a non-invasive AI-empowered model for passive health monitoring and predicting viral C-19 infection in the home environment. It consists of four notable layers: fully automated data acquisition, data analysis and Bayesian probabilistic classification, temporal COVID-19 severity prediction, and communication layer. These layers include IoT sensors embedded in the intelligent toilet system to collect required data, processes and analyses of the urine parametric data at the fog layer, and forecasting the COVID-19 severity using the XGBoost machine learning model at the cloud layer. The model has been evaluated over 53,550 data instances in a simulated environment for implementation purposes. The results implied that the proposed AI framework outperformed state-of-the-art strategies in terms of temporal approximation (94.53 s), reliability (92.69%), stability (0.89%), and predictive performance analysis (95.26%) metrics.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Source: Johns Hopkins University CSSE C-19 Data.
References
Abdulkareem KH, Mohammed MA, Salim A, Arif M, Geman O, Gupta D, Khanna A (2021) Realizing an effective COVID-19 diagnosis system based on machine learning and IoT in smart hospital environment. IEEE Internet Things J 21:15919–15928
Abdulkareem KH, Mutlag AA, Dinar AM, Frnda J, Mohammed MA, Zayr FH, Lakhan A, Kadry S, Khattak HA, Nedoma J (2022) Smart healthcare system for severity prediction and critical tasks management of COVID-19 patients in IoT-fog computing environments. Comput Intell Neurosci 2022:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5012962
Ahanger TA, Tariq U, Nusir M, Aldaej A, Ullah I, Sulman A (2021) A novel IoT-fog-cloud-based healthcare system for monitoring and predicting COVID-19 outspread. J Supercomput 78(2):1783–1806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03935-w
Ahmad F, Wysocki RW, Fernandez JJ, Cohen MS, Simcock XC (2023) Patient perspectives on telemedicine during the covid-19 pandemic. Hand 18(3):522–526
Alzuhairi MH, Al-Bayati MA (2021) Intelligent mobile cloud platform for monitoring patients of covid-19 in their home-quarantines. Turk J Comput Math Educ 12(14):4461–4477
Angerschmid A, Zhou J, Theuermann K, Chen F, Holzinger A (2022) Fairness and explanation in ai-informed decision making. Mach Learn Knowl Extr 4(2):556–579
Bhatia M, Kaur S, Sood SK (2020) IoT-inspired smart toilet system for home-based urine infection prediction. ACM Trans Comput Healthc 1(3):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1145/3379506
Bhatia M, Kaur S, Sood SK, Behal V (2020) Internet of things-inspired healthcare system for urine-based diabetes prediction. Artif Intell Med 107:101913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101913
Bhatia M, Manocha A, Ahanger TA, Alqahtani A (2022) Artificial intelligence-inspired comprehensive framework for Covid-19 outbreak control. Artif Intell Med 127:102288
Can O, Erkoç M, Ozer M, Karakanli MU, Otunctemur A (2021) The effect of COVID-19 on lower urinary tract symptoms in elderly men. Int J Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.14110
Chakraborty C, Abougreen A (2018) Intelligent internet of things and advanced machine learning techniques for COVID-19. EAI Endorsed Trans Pervasive Health Technol. https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.28-1-2021.168505
Cheema R, Gulati A et al (2012) Improving the secure socket layer by modifying the rsa algorithm. Int J Comput Sci Eng Appl 2(3):79
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 785–794
Colson P, Chaudet H, Delerce J, Pontarotti P, Levasseur A, Fantini J, La Scola B, Devaux CA, Raoult D (2023) Role of sars-cov-2 mutations in the evolution of the Covid-19 pandemic. bioRxiv pp. 2023–05
Elbasi E, Topcu AE, Mathew S (2021) Prediction of COVID-19 risk in public areas using IoT and machine learning. Electronics 10(14):1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10141677
Ge TJ, Chan CT, Lee BJ, Liao JC, Min Park S (2022) Smart toilets for monitoring COVID-19 surges: passive diagnostics and public health. NPJ Digit Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-022-00582-0
Gupta A, Singh A (2022). Early urine infection prediction framework using XGBoost ensemble model in IoT-fog environment. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1311498/v1
Imran M, Zaman U, Imran Imtiaz J, Fayaz M, Gwak J (2021) Comprehensive survey of IoT, machine learning, and blockchain for health care applications: a topical assessment for pandemic preparedness, challenges, and solutions. Electronics 10(20):2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202501
Javaid M, Khan IH (2021) Internet of things (IoT) enabled healthcare helps to take the challenges of COVID-19 pandemic. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 11(2):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.01.015
Kishor A, Chakraborty C (2022) Artificial intelligence and internet of things based healthcare 4.0 monitoring system. Wirel Pers Commun 127(2):1615–1631
Lin B, Wu S (2022) Digital transformation in personalized medicine with artificial intelligence and the internet of medical things. Omics 26(2):77–81
Ling Y, Xu SB, Lin YX, Tian D, Zhu ZQ, Dai FH, Wu F, Song ZG, Huang W, Chen J, Hu BJ, Wang S, Mao EQ, Zhu L, Zhang WH, Lu HZ (2020) Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients. Chin Med J 133(9):1039–1043. https://doi.org/10.1097/cm9.0000000000000774
Mir MH, Jamwal S, Mehbodniya A, Garg T, Iqbal U, Samori IA (2022) IoT-enabled framework for early detection and prediction of COVID-19 suspects by leveraging machine learning in cloud. J Healthc Eng 2022:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7713939
Mohammedqasim H, Ata O et al (2022) Real-time data of Covid-19 detection with IoT sensor tracking using artificial neural network. Comput Electr Eng 100:107971
Mukati N, Namdev N, Dilip R, Hemalatha N, Dhiman V, Sahu B (2021) Healthcare assistance to COVID-19 patient using internet of things (IoT) enabled technologies. Mater Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.379
Murgod P, Doshi P, Nimbargi R (2021) Urine biochemical parameters in predicting severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an experience in tertiary care centre in western India. Iran J Pathol 16(3):304–309. https://doi.org/10.30699/ijp.2021.136576.2496
Nasajpour M, Pouriyeh S, Parizi RM, Dorodchi M, Valero M, Arabnia HR (2020) Internet of things for current COVID-19 and future pandemics: an exploratory study. J Healthc Inf Res 4(4):325–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41666-020-00080-6
Nomoto H, Ishikane M, Katagiri D, Kinoshita N, Nagashima M, Sadamasu K, Yoshimura K, Ohmagari N (2020) Cautious handling of urine from moderate to severe COVID-19 patients. Am J Infect Control 48(8):969–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2020.05.034
Nuzzo JB, Gostin LO (2022) The first 2 years of COVID-19. JAMA 327(3):217. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.24394
Otoom M, Otoum N, Alzubaidi MA, Etoom Y, Banihani R (2020) An IoT-based framework for early identification and monitoring of COVID-19 cases. Biomed Signal Process Control 62:102149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102149
Paganelli AI, Velmovitsky PE, Miranda P, Branco A, Alencar P, Cowan D, Endler M, Morita PP (2022) A conceptual IoT-based early-warning architecture for remote monitoring of COVID-19 patients in wards and at home. Internet of Things 18:100399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2021.100399
Peng L, Liu J, Xu W, Luo Q, Chen D, Lei Z, Huang Z, Li X, Deng K, Lin B, Gao Z (2020) SARS-CoV-2 can be detected in urine, blood, anal swabs, and oropharyngeal swabs specimens. J Med Virol 92(9):1676–1680. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25936
Peng Y, Liu E, Peng S, Chen Q, Li D, Lian D (2022) Using artificial intelligence technology to fight Covid-19: a review. Artif Intell Rev 55:1–37
Rahman MS, Safa NT, Sultana S, Salam S, Karamehic-Muratovic A, Overgaard HJ (2022) Role of artificial intelligence-internet of things (AI-IoT) based emerging technologies in the public health response to infectious diseases in Bangladesh. Parasite Epidemiol Control 18:e00266
Rikan SB, Azar AS, Ghafari A, Mohasefi JB, Pirnejad H (2022) Covid-19 diagnosis from routine blood tests using artificial intelligence techniques. Biomed Signal Process Control 72:103263
Sharma KP, Walia K, Gupta S (2022) IoT for fight against COVID-19. In: Lecture notes in networks and systems, pp 585–596. Springer Nature, Singapore
Son BW (2023) A multipronged approach to combat Covid-19: lessons from previous pandemics for the future. Integrated science of global epidemics. Springer, Cham, pp 73–92
Sood SK, Rawat KS (2021) Fog-assisted virtual reality-based learning framework to control panic. Expert Syst. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12700
Sood SK, Rawat KS, Kumar D (2022) Analytical mapping of information and communication technology in emerging infectious diseases using CiteSpace. Telemat Inform 69:101796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2022.101796
Sood SK, Rawat KS, Kumar D (2022) A visual review of artificial intelligence and industry 4.0 in healthcare. Comput Electr Eng 101:107948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107948
Soomro TA, Zheng L, Afifi AJ, Ali A, Yin M, Gao J (2022) Artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging to combat coronavirus disease (Covid-19): a detailed review with direction for future research. Artif Intell Rev 55:1–31
Sundara Kumar M, Obaid AJ, Sankar S, Pandey D, Abdulbaqi AS (2023) Design and development of IoT wearable device for early detection of Covid-19 and monitoring through efficient data management framework in pre-pandemic life. Next generation of internet of things. Springer, Singapore, pp 177–193
Vaishya R, Javaid M, Khan IH, Haleem A (2020) Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for Covid-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab Synd 14(4):337–339
Wu J, Wang J, Nicholas S, Maitland E, Fan Q et al (2020) Application of big data technology for Covid-19 prevention and control in China: lessons and recommendations. J Med Internet Res 22(10):e21980
Yao H, Zhang N, Zhang R, Duan M, Xie T, Pan J, Peng E, Huang J, Zhang Y, Xu X, Xu H, Zhou F, Wang G (2020) Severity detection for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients using a machine learning model based on the blood and urine tests. Front Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00683
Yusuf H, Quraishi SJ (2023) IoT in healthcare in times of pandemic (Covid-19). Cyber technologies and emerging sciences. Springer, Singapore, pp 315–325
Zaidan A, Zaidan B (2020) A review on intelligent process for smart home applications based on IoT: coherent taxonomy, motivation, open challenges, and recommendations. Artif Intell Rev 53(1):141–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm their contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: DK, SKS; data collection: KSR; analysis and interpretation of results: SKS, DK; draft manuscript preparation: DK and KSR. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, D., Sood, S.K. & Rawat, K.S. Early health prediction framework using XGBoost ensemble algorithm in intelligent environment. Artif Intell Rev 56 (Suppl 1), 1591–1615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10565-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10565-6