Abstract
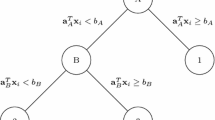
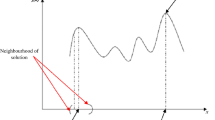
We address the pruning or filtering problem, encountered in exact value iteration in POMDPs and elsewhere, in which a collection of linear functions is reduced to the minimal subset retaining the same maximal surface. We introduce the Skyline algorithm, which traces the graph corresponding to the maximal surface. The algorithm has both a complete and an iterative version, which we present, along with the classical Lark’s algorithm, in terms of the basic dictionary-based simplex iteration from linear programming. We discuss computational complexity results, and present comparative experiments on both randomly-generated and well-known POMDP benchmarks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellman, R.E.: Dynamic Programming. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1962)
Cassandra, A.R., Littman, M.L., Zhang, N.: Incremental pruning: a simple, fast, exact method for partially observable Markov decision processes. In: Proceedings of the Conference in Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI’97), pp. 54–61 (1997)
Chvatal, V.: Linear Programming (Series of Books in the Mathematical Sciences). Freeman, San Francisco (1983)
Doshi, F., Roy, N.: The permutable POMDP: fast solutions to POMDPs for preference elicitation. In: Proceddings of the International Conference on autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS), pp. 493–500 (2008)
Feng, Z., Zilberstein, S.: Region-based incremental pruning for POMDPs. In: Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, UAI ’04, pp. 146–153 (2004)
Hansen, E.A.: Solving POMDPs by searching in policy space. In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 211–219 (1998)
Hauskrecht, M., Fraser, H.S.F.: Planning treatment of ischemic heart disease with partially observable markov decision processes. Artif. Intell. Med. 18(3), 221–244 (2000)
Hsiao, K., Kaelbling, L.P., Lozano-Pérez, T.: Grasping POMDPs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4685–4692 (2007)
Huynh, V.A., Roy, N.: icLQG: combining local and global optimization for control in information space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2851–2858 (2009)
Kalai, G.: Linear programming, the simplex algorithm and simple polytopes. Math. Program. (Ser. B) 79, 217–234 (1997)
Raphael, C., Nichols, E.: Linear dynamic programming and the training of sequence estimators. In: Chinneck, J.W., Kristjansson, B., Saltzman, M. (eds.) Operations Research and Cyber-Infrastructure, vol. 47, pp. 219–231. Springer, New York (2009)
Shani, G., Meek, C.: Improving existing fault recovery policies. In: Proceddings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 1642–1650 (2009)
Shani, G., Heckerman, D., Brafman, R.I.: An MDP-based recommender system. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6, 1265–1295 (2005)
Shani, G., Brafman, R.I., Shimony, S.E.: Forward search value iteration for POMDPs. In: Proceedings of the Interantional Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), pp. 2619–2624 (2007)
Shani, G., Brafman, R.I., Shimony, S.E.: Prioritizing point-based POMDP solvers. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B 38(6), 1592–1605 (2008)
Smallwood, R., Sondik, E.: The optimal control of partially observable processes over a finite horizon. OR 21, 1071–1088 (1973)
Smith, T., Simmons, R.: Point-based POMDP algorithms: improved analysis and implementation. In: Proceedings of the 21st Conference in Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI) (2005)
Sondik, E.J.: The optimal control of partially observable Markov processes. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University (1971)
White, C.C.: Partially observed Markov decision processes: a survey. Ann. Oper. Res. 32, 215–230 (1991)
Williams, J.D., Young, S.: Partially observable Markov decision processes for spoken dialog systems. Comput. Speech Lang. 21(2), 393–422 (2007)
Zhang, N., Liu, W.: Planning in stochastic domains: problem characteristics and approximation. Tech. Rep. HKUST-CS96-31, Dept. of Comp. Sci., Hong Kong Univ. of Sci. and Tech. (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raphael, C., Shani, G. The Skyline algorithm for POMDP value function pruning. Ann Math Artif Intell 65, 61–77 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-012-9302-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-012-9302-1